Newly detected ‘energy-clustering’ structures inside rare-earth nanoparticles generate intense violet light, which is ideal for studying photon-induced transformations
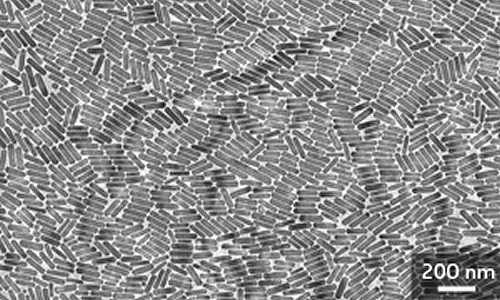
A novel type of pill-shaped nanocrystal emits the correct light frequencies for triggering and detecting many biological reactions. Credit: J. Wang et al.
Labeling biomolecules with light-emitting nanoparticles is a powerful technique for observing cell movement and signaling under realistic, in vivo conditions. The small size of these probes, however, often limits their optical capabilities. In particular, many nanoparticles have trouble producing high-energy light with wavelengths in the violet to ultraviolet range, which can trigger critical biological reactions.
Now, an international team led by Xiaogang Liu from the A*STAR Institute of Materials Research and Engineering and the National University of Singapore has discovered a novel class of rare-earth nanocrystals that preserve excited energy inside their atomic framework, resulting in unusually intense violet emissions1.
Nanocrystals selectively infused, or ‘doped’, with rare-earth ions have attracted the attention of researchers, because of their low toxicity and ability to convert low-energy laser light into violet-colored luminescence emissions — a process known as photon upconversion. Efforts to improve the intensity of these emissions have focused on ytterbium (Yb) rare-earth dopants, as they are easily excitable with standard lasers. Unfortunately, elevated amounts of Yb dopants can rapidly diminish, or ‘quench’, the generated light.
This quenching probably arises from the long-range migration of laser-excited energy states from Yb and toward defects in the nanocrystal. Most rare-earth nanocrystals have relatively uniform dopant distributions, but Liu and co-workers considered that a different crystal arrangement — clustering dopants into multi-atom arrays separated by large distances — could produce localized excited states that do not undergo migratory quenching.
The team screened numerous nanocrystals with different symmetries before discovering a material that met their criteria: a potassium fluoride crystal doped with Yb and europium rare earths (KYb2F7:Eu). Experiments revealed that the isolated Yb ‘energy clusters’ inside this pill-shaped nanocrystal (see image) enabled substantially higher dopant concentrations than usual — Yb accounted for up to 98 per cent of the crystal’s mass — and helped initiate multiphoton upconversion that yielded violet light with an intensity eight times higher than previously seen.
The researchers then explored the biological applications of their nanocrystals by using them to detect alkaline phosphatases, enzymes that frequently indicate bone and liver diseases. When the team brought the nanocrystals close to an alkaline phosphate-catalyzed reaction, they saw the violet emissions diminish in direct proportion to a chemical indicator produced by the enzyme. This approach enables swift and sensitive detection of this critical biomolecule at microscale concentration levels.
“We believe that the fundamental aspects of these findings — that crystal structures can greatly influence luminescence properties — could allow upconversion nanocrystals to eventually outperform conventional fluorescent biomarkers,” says Liu.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by The Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR).