In late 2021, Salvatore Torquato, on sabbatical from Princeton’s Department of Chemistry, reached across the aisle as it were and invited a young astrophysicist at the Institute for Advanced Study to apply the tools of statistical mechanics to his own work on the distribution of galaxies.
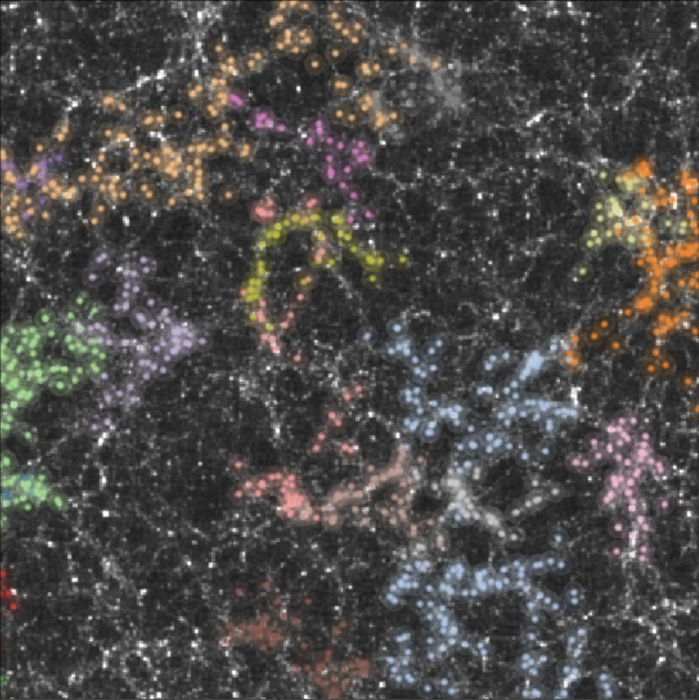
Credit: Graphic courtesy of Princeton University Department of Physics, and the Simons Foundation.
In late 2021, Salvatore Torquato, on sabbatical from Princeton’s Department of Chemistry, reached across the aisle as it were and invited a young astrophysicist at the Institute for Advanced Study to apply the tools of statistical mechanics to his own work on the distribution of galaxies.
The astrophysicist, Oliver Philcox, now a postdoc at the Simons Foundation, was intrigued. A year-long collaboration ensued.
The questions at the heart of their unusual partnership were straightforward: can the statistical descriptors Torquato has worked with throughout his career find application in unlikely places like cosmology, and can they accurately characterize the complexity in the distribution of galaxies? The answer to both questions: yes, indeed.
Their collaboration came to fruition this week with a paper in Physical Review X, “The Disordered Heterogeneous Universe: Galaxy Distribution and Clustering Across Length Scales.” In it, the researchers demonstrate they can uncover useful information about the spatial distribution of galaxies from a few descriptors more commonly used to classify the microstructure of materials.
Astrophysicists have long explored questions about the large-scale structure of the Universe through standard tools of physical cosmology. What Torquato and Philcox did was offer proof that a new array of descriptors can be used to characterize structural data across length scales, from the atomic scale to the largest scale in the Universe … including the Universe.
Torquato uses the word “zoology” to capture the array of theoretical and computational techniques he uses in his work. What he means is: applying statistical descriptors that describe complex materials microstructures to determine their physical and chemical properties at the macroscale.
Applying these techniques on the largest scale to locate similarities, Torquato and Philcox treated galaxies as a cloud of individual points akin to particles in a material.
“So, okay, I have two regions of space: it can be the galaxies and then everything outside the galaxies. Among other things, you can study the holes between the galaxies similarly to the way you would study the structure of materials,” said Torquato, a theoretical chemist and the Lewis Bernard Professor of Natural Sciences, Professor of Chemistry and the Princeton Materials Institute..
“If I say, I want to put a ball between the galaxies that doesn’t touch any of the galaxies, how big a ball do I need? You could apply that statistical question to any complicated structure, whether it’s the distribution of galaxies or the distribution of atoms. That’s the beauty of it.
“Interestingly,” he added, “the unique structure of the Universe provides new challenges to ascertain even better descriptors for describing terrestrial materials.”
Philcox, formerly a graduate student in Princeton’s Department of Astrophysical Sciences, embraced this “zoology” to enlarge his own toolbox. A key example was his use of the pair-connectedness function, which Philcox defines as a particular way to characterize materials by looking at the distribution of pairs of points.
“Delving into the zoology with Sal certainly led to some interesting discoveries of statistics used in materials science that could be used in cosmology, but hadn’t yet, the pair-connectedness function being the most notable one,” said Philcox. “Conventional cosmological statistics answer the question: if I pick two points at random, what is their separation, probabilistically?
“The pair-connectedness function does a similar thing but includes topological information. Essentially, it groups the particles in a material into connected structures, then looks at the distribution of separations between two points within that structure, rather than globally.”
Using this and other functions, researchers were able to generate tables of numbers that served as a measure of order or disorder across length scales. When applied to questions of spatial relationships between galaxies, the tools underscored a kind of correlated disorder – a complex structural property that is “definitely” not random.
“We’re asking exactly the same questions about large-scale structure that cosmologists have always asked using more standard descriptors: how do we describe this structure; how do we characterize it; how do we quantify it; what can we get from it in terms of the physics,” Torquato said. “We’re just using some new theoretical tools to do so.”
Added Philcox: “I think it’s an important message that there are some conceptually very simple tools that can allow us to extract new information about the Universe, particularly with regard to its clustering, that are quite orthogonal to what’s already used. We’re excited to see how these can be used in practice.”
Journal
Physical Review X
DOI
10.110310.1103/PhysRevX.13.011038
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Disordered heterogeneous universe: Galaxy distribution and clustering across length scales
Article Publication Date
14-Mar-2023
COI Statement
N/A




