Credit: KBRI
Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI, President Suh Pann-ghill) announced that the research team led by Dr. Jae-Yeol Joo discovered new cryptic splice variants and SNVs in PLCg1 gene of AD-specific models for the first time using Splice-AI.
This research outcome was published in PNAS, a world-renowned academic journal.
* (Title) Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease-Specific phospholipase c gamma-1 SNV by Deep Learning-Based Approach for High-Throughput Screening
Alternative splicing variant regulates gene expression and influences diverse phenotypes. Especially, genetic variants arising due to RNA splicing are frequently found in individuals having neurodevelopmental disorders.
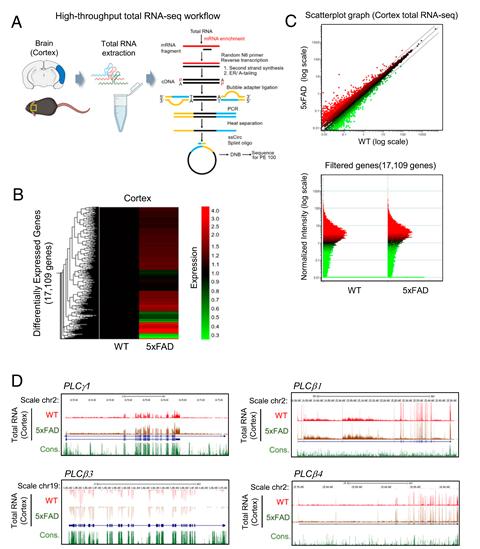
The research team revealed splicing hidden within the transcriptome to AD models via deep learning-based Splice-AI.
The novel 14 alternative splicing sites in the PLCg1 gene body, the key element of the signal transduction mechanism, were identified through deep learning.
Especially, Splice-AI analysis predicted a total of 14 splicing sites in the human PLCg1 gene, accurate delta scores, and positions were analyzed and a novel splicing site in exon 26 of human PLCg1 was identified. (exon 26 of the PLCg1 gene is 100% identical with exon 27 of the same gene in mice in terms of amino acid sequence).
* (Splicing) A form of RNA processing that regulates gene expression through the medium of genetic information
* (PLCg1, phospholipase c gamma-1) An essential protein involved in cell signal transduction and human cell growth and death
* (Exon) A part of a gene that contains protein synthesis information
Abnormal RNA processing was identified with an SNV in exon 27 of the PLCg1 gene within the brain of AD mouse models.
The research team revealed for the first time that SNV lead to changes in amino acids of proteins at exon 27. This region is very important for homeostasis because, mutated sequence is evolutionary conserved sequence through various species such as human, ape, mouse, chicken, zebrafish and so on. Moreover, AD specific nucleotide alteration sites were distributed in the histone modification region in PLCg1 gene body during the brain development.
Dr. Joo mentioned, “Emerging variants of the coronavirus have been reported in England in December 2020, and that is more transmissible than previously circulating viruses.
This variants coronavirus has mutation and altered their spike protein amino acid.
Our research will give valuable information and technique for various human diseases and through the convergence and utilization of brain research with AI technology, which is the core of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, to understand various diseases including AD, we will be able to obtain critical information for diagnosis and treatment strategy.”
###
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI) basic research program.
Media Contact
Jae-Yeol Joo
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




