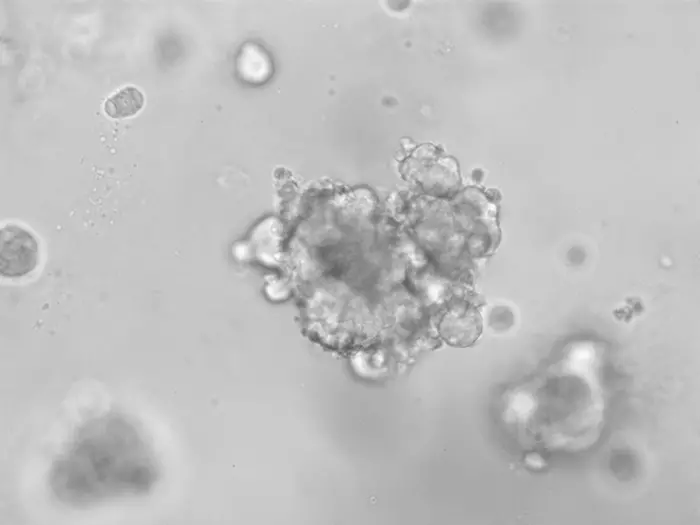
Credit: Credit: Talya Dayton, copyright: Hubrecht Institute.
The Organoid Group (Hubrecht Institute) and the Rare Cancers Genomics Team (IARC/WHO) found a way to grow samples of different types of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) in the lab. While generating their new model, the researchers discovered that some pulmonary NETs need the protein EGF to be able to grow. These types of tumors may therefore be treatable using inhibitors of the EGF receptor. The results were published in Cancer Cell on 11 December 2023.
Neuroendocrine tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are relatively rare tumors that can be slow-growing. However, some NETs can be aggressive and hard to treat. It is not yet possible to predict which tumors will become aggressive. There are very few models to study NETs in the lab, which limits research into this type of tumor.
New disease model
Researchers from the Organoid Group (Hubrecht Institute) and the Rare Cancers Genomics Team (IARC/WHO) therefore set out to develop new models to study NETs. They derived cells from patients with NETs and were able to culture them into 3D structures called organoids. These organoids mimic the behavior of actual NETs and can therefore be used to study this type of tumor in the lab. The new model is the first organoid model of the disease.
Growth factor
While generating the organoids, the researchers found that some pulmonary NETs need a protein called the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF) to grow. “If we inhibit the receptor for EGF, some organoids die. Apparently, these organoids are dependent on EGF for their survival,” says Talya Dayton, co-first author on the paper published in Cancer Cell. “We need further research to confirm our findings, but this may indicate that patients with EGF-dependent NETs could be treated with inhibitors of the EGF receptor.” Inhibitors of the EGF receptor are already a course of treatment for other types of tumors.
Aggressive tumors
Tumors are usually thought to be independent of growth factors. That some NETs turn out to be dependent on the growth factor EGF is therefore surprising. “We think that their EGF-dependence might explain, in part, why some of these tumors grow slowly. We also think this might mean that one of the ways in which NETs can become aggressive is by becoming growth-factor independent. If they no longer need the growth factor, their growth may accelerate” Dayton explains.
Potential new therapy
The newly developed model for NETs provides a new way to study the disease in the lab. Dayton: “This allows us and other scientists to understand the biology of these tumors so we can hopefully find effective therapies.” Although further research is needed, the model already points to a new route of treatment for patients with pulmonary NETs.
Publication
Druggable Growth Dependencies and Tumor Evolution Analysis in Patient-Derived Organoids of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms from Multiple Body Sites. Talya L. Dayton*, Nicolas Alcala*, Laura Moonen, Lisanne den Hartigh, Veerle Geurts, Lise Mangiante, Lisa Lap, Antonella F.M. Dost, Joep Beumer, Sonja Levi, Rachel S. van Leeuwaarde, Wenzel M/ Hackeng, Kris Samsom, Catherine Voegele, Alexandra Sexton-Oates, Harry Begthel, Jeroen Korving, Lisa Hillen, Lodewijk A.A. Brosens, Sylvie Lantuejoul, Sridevi Jaksani, Niels F.M. Kok, Koen J. Hartemink, Houke M. Klomp, Inne H.M. Borel Rinkes, Anne-Marie Dingemans, Gerlof D. Valk, Menno R. Vriens, Wieneke Buikhuisen, José van den Berg, Margot Tesselaar, Jules Derks, Ernst Jan Speel, Matthieu Foll, Lynnette Fernández-Cuesta and Hans Clevers. Cancer Cell, 2023.
*Co-first authors
Hans Clevers is advisor/guest researcher at the Hubrecht Institute for Developmental Biology and Stem Cell Research (KNAW) and at the Princess Máxima Center for Pediatric Oncology. He holds a professorship in Molecular Genetics from the Utrecht University and is an Oncode Investigator. Hans Clevers has been the Head of Pharma Research and Early Development (pRED) at Roche since 2022. He previously held directorship/President positions at the Hubrecht Institute, the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences and the Princess Máxima Center for pediatric oncology.
About the Hubrecht Institute
The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute focused on developmental and stem cell biology. Because of the dynamic character of the research, the institute as a variable number of research group, around 20, that do fundamental, multidisciplinary research on healthy and diseased cells, tissues and organisms. The Hubrecht Institute is a research institute of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW), situated on Utrecht Science Park. Since 2008, the institute is affiliated with the UMC Utrecht, advancing the translation of research to the clinic. The Hubrecht Institute has a partnership with the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). For more information, visit www.hubrecht.eu.
Journal
Cancer Cell
DOI
10.1016/j.ccell.2023.11.007
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Druggable Growth Dependencies and Tumor Evolution Analysis in Patient-Derived Organoids of Neuroendocrine Neoplasms from Multiple Body Sites
Article Publication Date
11-Dec-2023
COI Statement
HC is inventor on several patents related to organoid technology.