Credit: Courtesy of MIPT & Skoltech
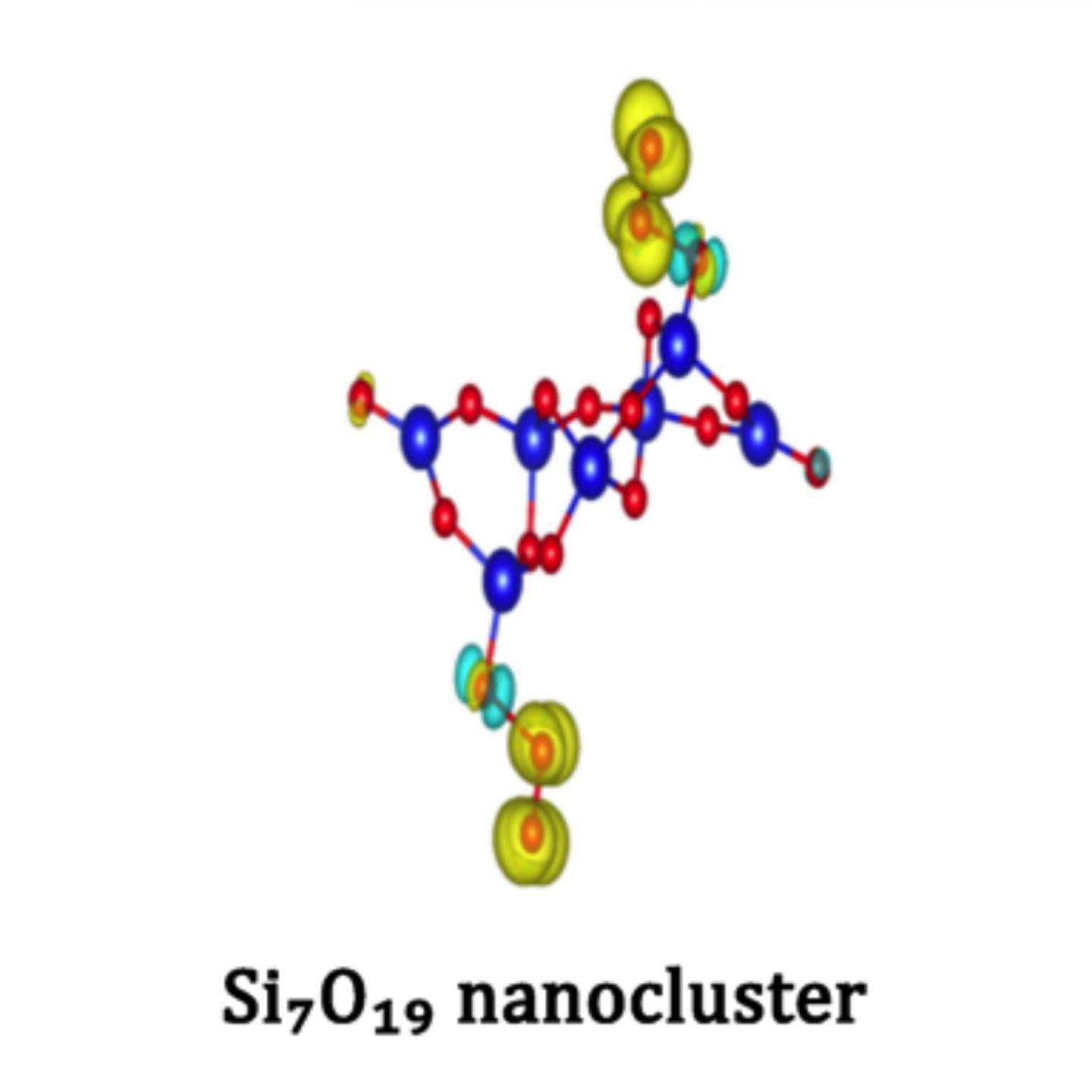
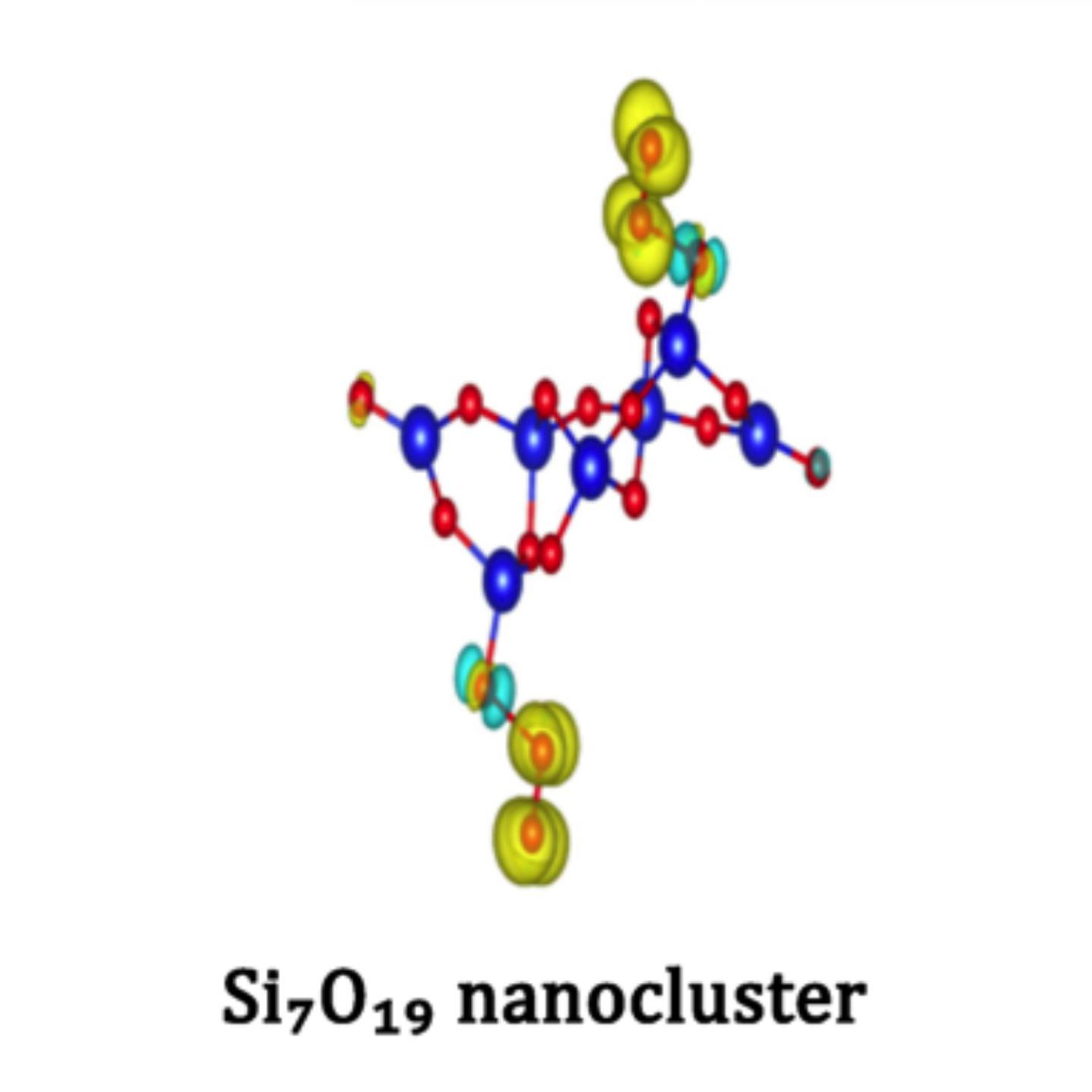
Scientists from LPI RAS, Skoltech, and MIPT led by Skoltech Professor Artem Oganov and leading scientist of LPI RAS Yurii Uspenskii have found unusual properties of silicon nanoparticles. They have shown that at normal conditions silica nanoparticles are enriched in oxygen. Such nanoparticles are magnetic and contain reactive oxygen species (in particular, peroxo- and ozonide ions and oxo-radicals). This may explain the known high toxicity and carcinogenicity of silica dust.
Silicon nanoparticles are promising for many applications including nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, solar cells, biomedical imaging sensors, etc. This has placed them into the focus of intense research for over two decades. Silicon nanoparticles oxidize in the presence of oxygen, but details of this process are still unclear. It is well-known that silicon dioxide dust has a negative effect on human health and causes silicosis and lung cancer, but the nature of this effect is unknown.
Scientists from the Oganov and Uspenskii groups used the USPEX algorithm (Universal Structure Predictor: Evolutionary Xtallography) and showed that at normal atmospheric conditions silica nanoparticles exist not with the expected classical composition SiO? postulated by classical chemistry, but in an oxygen-enriched form (e.g., Si?O??). Extra oxygen atoms demonstrate magnetic properties and form reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS, such as peroxide ions, are highly reactive with biomolecules and have long been suggested to be a major cause of cancer.
"We were very much surprised that at normal conditions in oxygen atmosphere we found stability of new reactive and magnetic silica nanoparticles, instead of the classical SiO? nanoparticles," says Sergey Lepeshkin, the leading author of the study, which provides a likely explanation of the known high carcinogenicity of silica dust.
The research results were published in the Nanoscale journal.
###
Media Contact
Nicolas
[email protected]
@phystech
https://mipt.ru/english/