Credit: (Christophe Chantre/Harvard University)
Harvard researchers have developed a lightweight, portable nanofiber fabrication device that could one day be used to dress wounds on a battlefield or dress shoppers in customizable fabrics. The research was published recently in Macromolecular Materials and Engineering.
There are many ways to make nanofibers. These versatile materials — whose target applications include everything from tissue engineering to bullet proof vests — have been made using centrifugal force, capillary force, electric field, stretching, blowing, melting, and evaporation.
Each of these fabrication methods has pros and cons. For example, Rotary Jet-Spinning (RJS) and Immersion Rotary Jet-Spinning (iRJS) are novel manufacturing techniques developed in the Disease Biophysics Group at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering. Both RJS and iRJS dissolve polymers and proteins in a liquid solution and use centrifugal force or precipitation to elongate and solidify polymer jets into nanoscale fibers. These methods are great for producing large amounts of a range of materials- – including DNA, nylon, and even Kevlar — but until now they haven't been particularly portable.
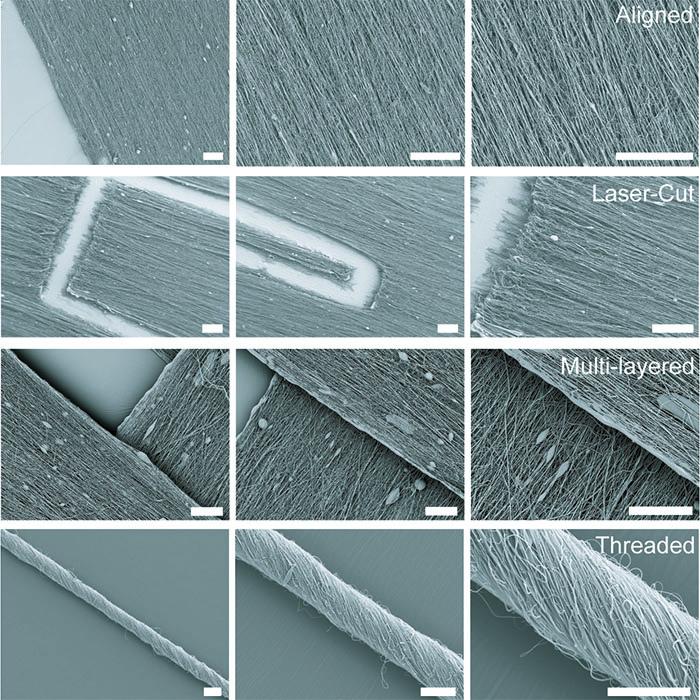
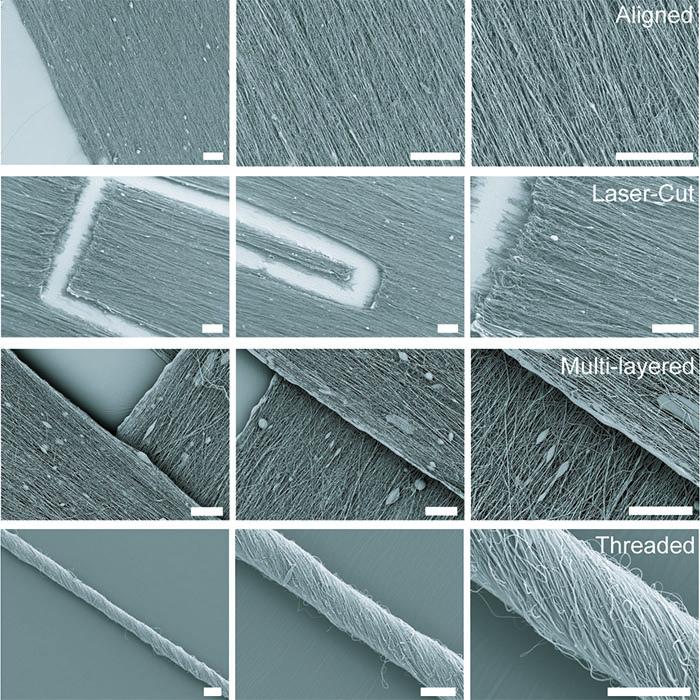
The Disease Biophysics Group recently announced the development of a hand-held device that can quickly produce nanofibers with precise control over fiber orientation. Regulating fiber alignment and deposition is crucial when building nanofiber scaffolds that mimic highly aligned tissue in the body or designing point-of-use garments that fit a specific shape.
"Our main goal for this research was to make a portable machine that you could use to achieve controllable deposition of nanofibers," said Nina Sinatra, a graduate student in the Disease Biophysics Group and co-first author of the paper. "In order to develop this kind of point-and-shoot device, we needed a technique that could produce highly aligned fibers with a reasonably high throughput."
The new fabrication method, called pull spinning, uses a high-speed rotating bristle that dips into a polymer or protein reservoir and pulls a droplet from solution into a jet. The fiber travels in a spiral trajectory and solidifies before detaching from the bristle and moving toward a collector. Unlike other processes, which involve multiple manufacturing variables, pull spinning requires only one processing parameter — solution viscosity — to regulate nanofiber diameter. Minimal process parameters translate to ease of use and flexibility at the bench and, one day, in the field.
Pull spinning works with a range of different polymers and proteins. The researchers demonstrated proof-of-concept applications using polycaprolactone and gelatin fibers to direct muscle tissue growth and function on bioscaffolds, and nylon and polyurethane fibers for point-of-wear apparel.
"This simple, proof-of-concept study demonstrates the utility of this system for point-of-use manufacturing," said Kit Parker, the Tarr Family Professor of Bioengineering and Applied Physics and director of the Disease Biophysics Group. "Future applications for directed production of customizable nanotextiles could extend to spray-on sportswear that gradually heats or cools an athlete's body, sterile bandages deposited directly onto a wound, and fabrics with locally varying mechanical properties."
###
Media Contact
Leah Burrows
[email protected]
617-496-1351
@hseas
http://www.seas.harvard.edu/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag