Credit: University of Basel, Department of Physics
Graphene consists of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a honeycomb structure. The material is of interest not only in basic research but also for various applications given to its unique properties, which include excellent electrical conductivity as well as astonishing strength and rigidity. Research teams around the world are working to further expand these characteristics by substituting carbon atoms in the crystal lattice with atoms of different elements. Moreover, the electric and magnetic properties can also be modified by the formation of pores in the lattice.
Ladder-like structure
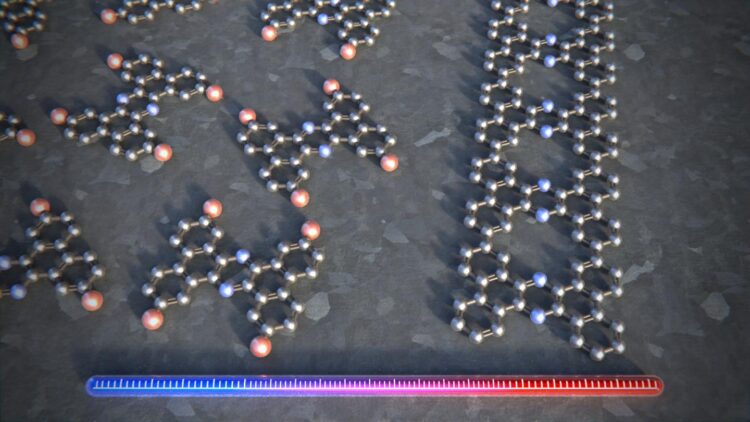
Now, a team of researchers led by the physicist Professor Ernst Meyer of the University of Basel and the chemist Dr. Shi-Xia Liu from the University of Bern have succeeded in producing the first graphene ribbons whose crystal lattice contains both periodic pores and a regular pattern of nitrogen atoms. The structure of this new material resembles a ladder, with each rung containing two atoms of nitrogen.
In order to synthesize these porous, nitrogen-containing graphene ribbons, the researchers heated the individual building blocks step by step on a silver surface in a vacuum. The ribbons are formed at temperatures up to 220°C. Atomic force microscopy allowed the researchers not only to monitor the individual steps in the synthesis, but also to confirm the perfect ladder structure – and stability – of the molecule.
Extraordinary properties
Using scanning tunneling microscopy, the scientists from the Department of Physics and the Swiss Nanoscience Institute (SNI) at the University of Basel also demonstrated that these new graphene ribbons were no longer electrical conductors, like pure graphene, but actually behaved as semiconductors. Colleagues from the Universities of Bern and Warwick confirmed these findings by performing theoretical calculations of the electronic properties. “The semiconducting properties are essential for the potential applications in electronics, as their conductivity can be adjusted specifically,” says Dr. Rémy Pawlak, first author of the study.
From the literature, it is known that a high concentration of nitrogen atoms in the crystal lattice causes graphene ribbons to magnetize when subjected to a magnetic field. “We expect these porous, nitrogen-doped graphene ribbons to display extraordinary magnetic properties,” says Ernst Meyer. “In the future, the ribbons could therefore be of interest for applications in quantum computing.”
###
Media Contact
Ernst Meyer
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.





