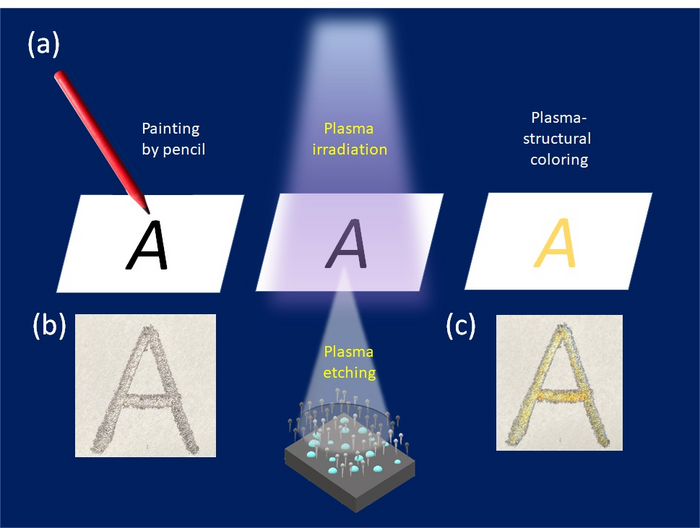
New developments for achieving structural coloring through plasma irradiation of graphite can reduce the reliance upon harmful color dyes. Colors achieved by plasma irradiation are completely erasable and can be manipulated using time exposed to the plasma irradiation, intensity of the irradiation and the thickness of the graphite layer applied. The application of plasma-structural coloring aims to lessen the environmental toll typical adverse dyes have and combat them with the technology surrounding structural colors. Structural colors look different than how we perceive colors dyed by pigment, because structural colors are based on viewing how the light scatters when reflected, giving an iridescent quality to the observed colors. In nature, this type of coloring can be seen in peacock feathers and some insects like beetles.
Credit: ADAPTED WITH PERMISSION FROM ACS APPL. MATER. INTERFACES 2023, 15, 3, 4781–4788. COPYRIGHT 2023 AMERICAN CHEMICAL SOCIETY.
New developments for achieving structural coloring through plasma irradiation of graphite can reduce the reliance upon harmful color dyes. Colors achieved by plasma irradiation are completely erasable and can be manipulated using time exposed to the plasma irradiation, intensity of the irradiation and the thickness of the graphite layer applied. The application of plasma-structural coloring aims to lessen the environmental toll typical adverse dyes have and combat them with the technology surrounding structural colors. Structural colors look different than how we perceive colors dyed by pigment, because structural colors are based on viewing how the light scatters when reflected, giving an iridescent quality to the observed colors. In nature, this type of coloring can be seen in peacock feathers and some insects like beetles.
Many inks used for coloring, whether it is on paper or textiles, are bad for the health of the environment. The process of making dyes along with the volatile compounds comprising the dyes are major pollutants, and a sustainable solution is in order. This solution may be seen by way of structural coloring through plasma irradiation.
“We called this technique ‘plasma structural coloring’. The method is an entirely new technique that changes the color of the penciling part on a paper by plasma irradiation. The technique is an environmentally friendly coloring method and can be applied to various activities, such as study and art,” said Hiroshi Moriwaki, professor in the Department of Applied Biology at Shinshu University.
The new finding was published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on Jan. 11th.
“Structural colors” are colors that are viewed by the human eye due to the interference of light reflected off the surface of a nanostructured material, such as the graphite from a pencil. The study looked into how plasma irradiation can manipulate the appearance of color by testing materials, plasma intensity and time needed to alter the color.
In the new study, the structural colors and coloring using plasma irradiation were put to the test. They showed some promise: graphite on paper was successfully changed into blue, yellow, and red corresponding to the length of exposure to the plasma irradiation. The colors were also found to be angle-independent, so no matter which way the colors were viewed, the color observed was fixed.
“We would like to make readers understand that we have developed a simple method for the formation of structural colors at low cost and in a short time. We believe this method can contribute to the achievement of a sustainable society.” Moriwaki said.
Another benefit to structural colors is their stability: they don’t degrade or fade through chemical reactions like other dyes might. Increasing the durability of colors will yield higher-quality work without the concern of fading in the future. This is of particular use in the art world, where many works have to be shielded from light to preserve the intensity of the colors and quality of the piece.
“The ultimate goal is to spread the method of coloring pencil writing by the plasma irradiation. For that purpose, it is important to develop a simple and easy-to-use small plasma device suitable for this method. In addition, we think it would be interesting if an artist could create paintings colored only with structural colors.” Moriwaki said.
The next step in perfecting the plasma-structural coloring process is to reduce the variability in the colors through the process. Additionally, the most effective tools are currently a specific type of pencil with high-graphite content, so finding a way to make the process available on a broader spectrum of tools may also be useful for future studies. Making the device simple and cost-effective will broaden the use of this product too, further reducing the need for harmful dyes amongst artists and other people who frequently use colored ink in their craft.
Hiroshi Moriwaki and Tomoya Kamine, both from the Department of Applied Biology, Faculty of Textile Science and Technology at Shinshu University, were the authors of this research.
###
About Shinshu University:
Shinshu University is a national university founded in 1949 located nestling under the Japanese Alps in Nagano known for its stunning natural landscapes. Our motto, “Powered by Nature – strengthening our network with society and applying nature to create innovative solutions for a better tomorrow” reflects the mission of fostering promising creative professionals and deepening the collaborative relationship with local communities, which leads up to our contribution to regional development by innovation in various fields. We’re working on providing solutions for building sustainable society through interdisciplinary research fields: material science (carbon, fiber and composites), biomedical science (for intractable diseases and preventive medicine) and mountain science, and aiming to boost research and innovation capability through collaborative projects with distinguished researchers from the world. For more information visit our website or follow us on Twitter @ShinshuUni for our latest news.
Journal
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces
DOI
10.1021/acsami.2c19642
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
“Plasma-Structural Coloring” of Penciling on a Paper
Article Publication Date
11-Jan-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.




