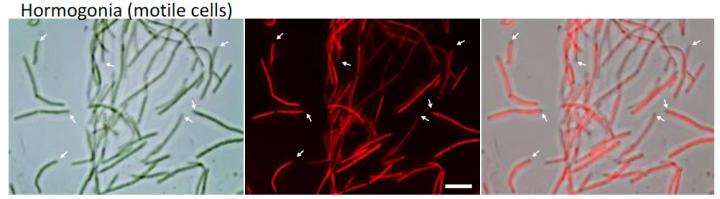
Credit: Copyright Yasuyuki Hashidoko, Hokkaido University.
The cycad Cycas revoluta is a palm-like plant that grows on rocky coastal cliffs in the sub-tropics and tropics. It has a symbiotic relationship with the Nostoc species of bacteria that can convert nitrogen from the atmosphere into ammonia, which the host plant can then use for its growth. Scientists knew that cycad roots produce a compound that can induce Nostoc species within the soil to transform into their motile form, hormogonia, and attracting them to the roots. However, nobody has determined what exactly the compound is.
In the current study published in the journal Scientific Reports, agricultural chemist Yasuyuki Hashidoko and colleagues at Hokkaido University investigated an extract made from the “coralloid roots” of C. revoluta plants. These are specialized roots that branch out from the plant’s main root system.
They found that the extract was able to trigger the transformation of Nostoc bacteria into hormogonia. Further analyses revealed the main active elements present in the extract were a mixture of diacylglycerols; typical compounds contained in plants that are composed of two fatty acid chains linked together.
The team tested each of the diacylglycerols for their abilities to act as hormogonia-inducing factors (HIF), and found that 1-palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl-sn-glycerol showed pronounced HIF-like activity on the bacteria. The investigations also enabled the researchers to theorize which specific changes to fatty acid chain segments led to the compounds having more, less, or no HIF-like activity.
“These findings appear to indicate that some common diacylglycerols act as hormogonium-inducing signal for Nostoc cyanobacteria, enabling them to move and transfer to host plants,” the researchers conclude. “Since the bacteria can provide host plants nitrogen to help them grow, better understanding of the system could someday lead to more efficient, less fertilizer-dependent agricultural production.”
###
Media Contact
Naoki Namba
@hokkaidouni
011-706-2185
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




