Using photons to create more powerful and power-efficient processing units for artificial intelligence
Credit: Mario Miscuglio
WASHINGTON, July 21, 2020 — Machine learning performed by neural networks is a popular approach to developing artificial intelligence, as researchers aim to replicate brain functionalities for a variety of applications.
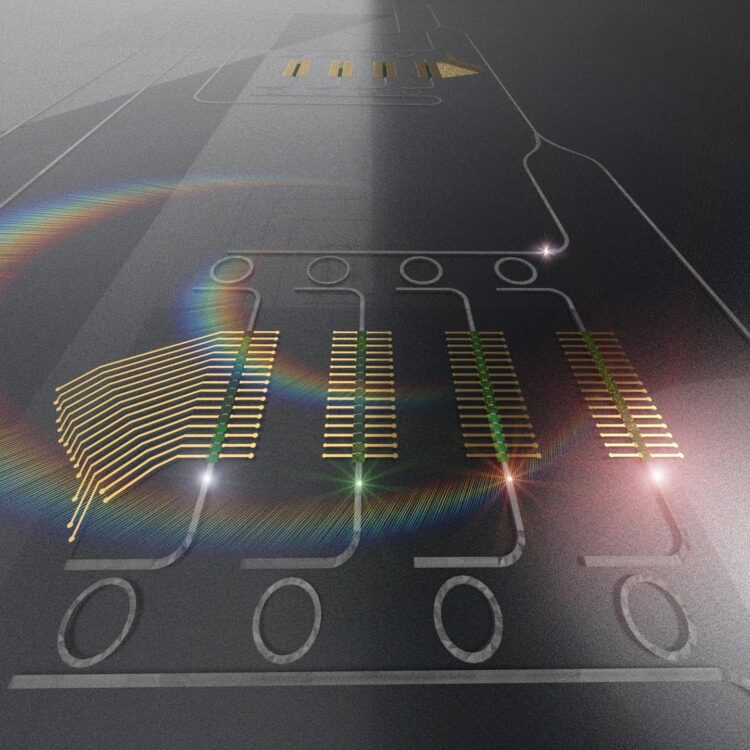
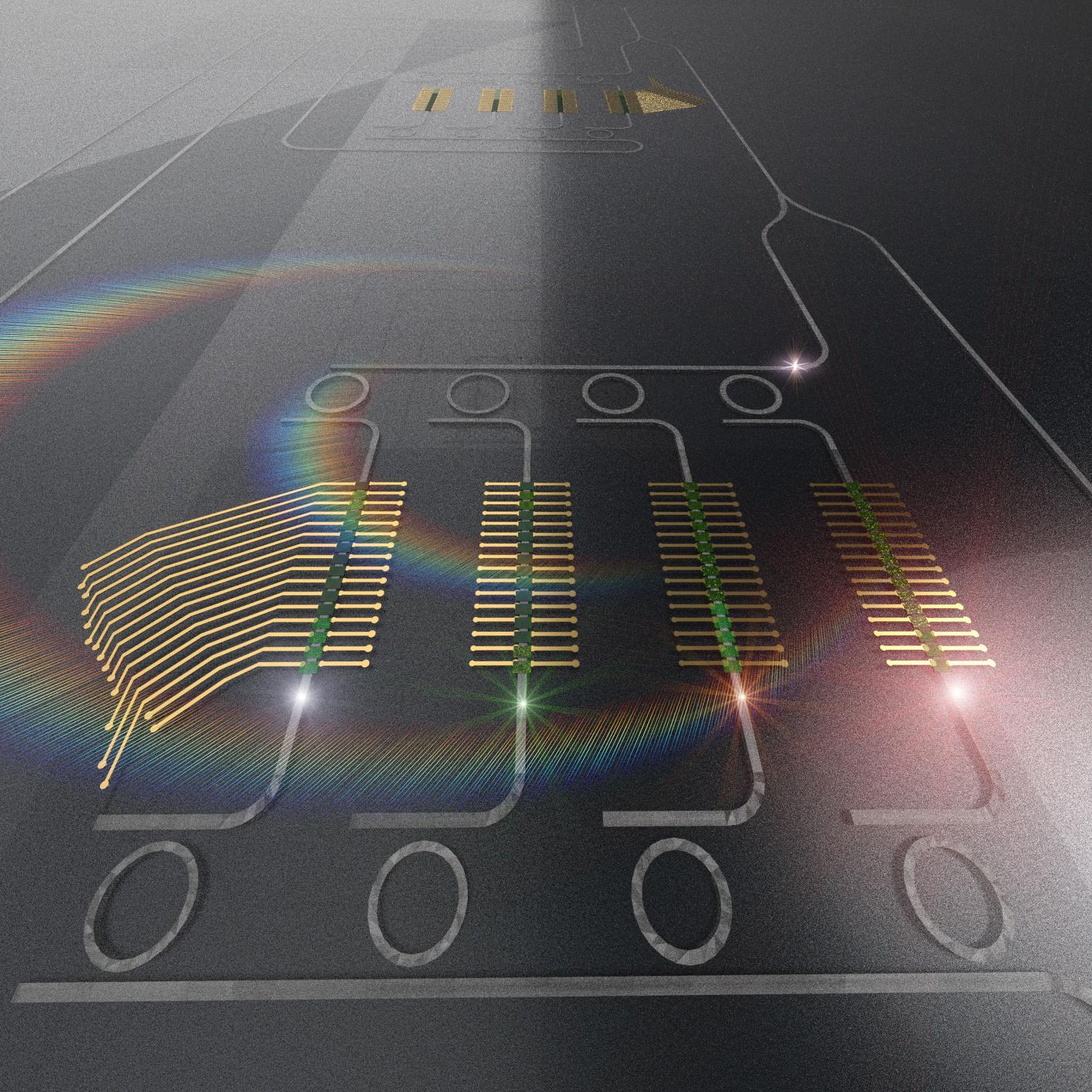
A paper in the journal Applied Physics Reviews, by AIP Publishing, proposes a new approach to perform computations required by a neural network, using light instead of electricity. In this approach, a photonic tensor core performs multiplications of matrices in parallel, improving speed and efficiency of current deep learning paradigms.
In machine learning, neural networks are trained to learn to perform unsupervised decision and classification on unseen data. Once a neural network is trained on data, it can produce an inference to recognize and classify objects and patterns and find a signature within the data.
The photonic TPU stores and processes data in parallel, featuring an electro-optical interconnect, which allows the optical memory to be efficiently read and written and the photonic TPU to interface with other architectures.
“We found that integrated photonic platforms that integrate efficient optical memory can obtain the same operations as a tensor processing unit, but they consume a fraction of the power and have higher throughput and, when opportunely trained, can be used for performing inference at the speed of light,” said Mario Miscuglio, one of the authors.
Most neural networks unravel multiple layers of interconnected neurons aiming to mimic the human brain. An efficient way to represent these networks is a composite function that multiplies matrices and vectors together. This representation allows the performance of parallel operations through architectures specialized in vectorized operations such as matrix multiplication.
However, the more intelligent the task and the higher accuracy of the prediction desired, the more complex the network becomes. Such networks demand larger amounts of data for computation and more power to process that data.
Current digital processors suitable for deep learning, such as graphics processing units or tensor processing units, are limited in performing more complex operations with greater accuracy by the power required to do so and by the slow transmission of electronic data between the processor and the memory.
The researchers showed that the performance of their TPU could be 2-3 orders higher than an electrical TPU. Photons may also be an ideal match for computing node-distributed networks and engines performing intelligent tasks with high throughput at the edge of a networks, such as 5G. At network edges, data signals may already exist in the form of photons from surveillance cameras, optical sensors and other sources.
“Photonic specialized processors can save a tremendous amount of energy, improve response time and reduce data center traffic,” said Miscuglio.
For the end user, that means data is processed much faster, because a large portion of the data is preprocessed, meaning only a portion of the data needs to be sent to the cloud or data center.
###
The article, “Photonic tensor cores for machine learning,” is authored by Mario Miscuglio and Volker Sorger. The article will appear in Applied Physics Reviews on July 21, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0001942). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Reviews features articles on significant and current topics in experimental or theoretical research in applied physics, or in applications of physics to other branches of science and engineering. The journal publishes both original research on pioneering studies of broad interest to the applied physics community, and reviews on established or emerging areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.