Researchers at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro discover a crucial link between phase transition (aggregation) and cancer pathology
Credit: Guilherme de Oliveira
Cancer has been recently shown to be affected by protein clusters, particularly by the aggregation of mutant variants of the tumor suppressor protein p53, which are present in more than half of malignant tumors. However, how the aggregates are formed is not yet fully understood. The understanding of this process is expected to provide new therapeutic tools able to prevent proteins to clump and cancer progression.
In Brazil, researchers at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro have identified a key mechanism behind the mutant p53 aggregation process, linked to cancer pathology, opening new paths for the development of novels drugs against the disease.
The latest findings have been published in advance in the scientific journal Chemical Science, by The Royal Society of Chemistry.
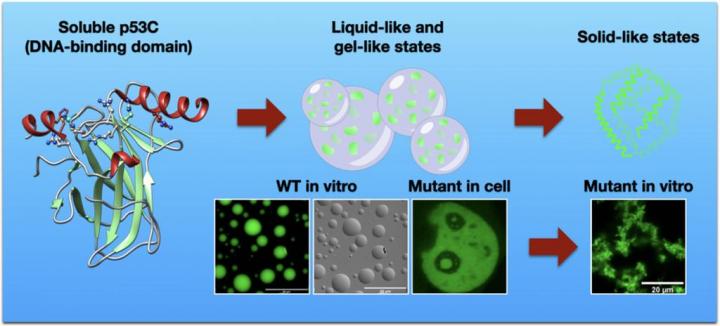
Led by the Prof. Jerson Lima Silva, the research team discovered that the formation of aggregates of p53 is preceded by liquid-to-liquid phase separation, a chemical segregation of a homogenous fluid, that then progresses to phase transition, or phase changes, resulting in ether a gel-like state or a solid-like state of the protein. Once a phase transition to a solid state is established, the aggregates of mutant p53 comparable to amyloids observed in neurodegenerative diseases are formed, thereby playing a crucial role in cancer development. This process was shown to occur in the nucleus, particular in nuclear compartments, by the use of different biophysical and fluorescence microscopy tools.
In the present study, it is shown that polyanions, such as heparin and RNA, were able to modulate the phase separation and phase transition in vitro. Heparin leads the p53 condensates into a gel-like state, whereas RNA resulted in the conversion into a solid-like state of the protein.
The new findings extend the concept of phase separation and of the amyloid-like aggregation found in neurodegenerative diseases to malignant tumors involving mutant p53.
The study also points out that the phase transitions to solid-like amorphous and amyloid-like states of mutant p53 are formidable targets for the development of novel diagnostic and therapeutic strategies against cancer.
“By providing insight into the formation of p53 condensates and identifying the exact conditions that lead to the formation of aggregated structures, we can now work towards developing strategies to prevent their formation. In the end, this may lead to new therapies for treating different malignant tumors, such as breast, ovarian and prostate cancer”, explains the project’s lead investigator Lima Silva, whose laboratory at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro has been studying p53 mutations and aggregation for over 18 years.
###
The article titled “Phase separation of p53 precedes aggregation and is affected by oncogenic mutations and ligands” is published online in Chemical Science.
Elaine C. Petronilho and Murilo M. Pedrote are the first authors. Additional authors on the study include Mayra A. Marques, Yulli M. Passos, Michelle F. Mota, Benjamin Jakobus, Gileno dos Santos de Sousa, Filipe Pereira da Costa, Adriani L. Felix, Giulia D. S. Ferretti, Fernando P. Almeida, Yraima Cordeiro, Tuane Vieira, Guilherme A. P. de Oliveira.
This research was funded by the Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for Research Support in the State of Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), the National Council for Scientifc and Technological Development (CNPq), and the National Institute of Science and Technology for Structural Biology and Bioimaging (INBEB).
Media Contact
Prof. Jerson Lima Silva
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




