WASHINGTON, June 20, 2023 – Penguins aren’t just cute: they’re also speedy. Gentoo penguins are the fastest swimming birds in the world, and that ability comes from their unique and sophisticated wings.
Credit: Hao et al.
WASHINGTON, June 20, 2023 – Penguins aren’t just cute: they’re also speedy. Gentoo penguins are the fastest swimming birds in the world, and that ability comes from their unique and sophisticated wings.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and King Mongkut‘s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang developed a model to explore the forces and flow structures created by penguin wings underwater. They determined that wing feathering is the main factor for generating thrust.
Penguin wings, aka flippers, bear some resemblance to airplane wings covered with scaly feathers. To maximize efficiency underwater instead of in the air, penguin wings are shorter and flatter than those of flying birds.
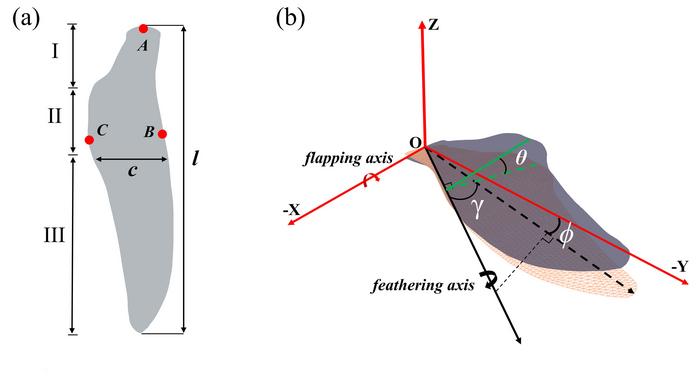
The animals can adjust swimming posture by active wing feathering (changing the angle of their wings to reduce resistance), pitching, and flapping. Their dense, short feathers can also lock air between the skin and water to reduce friction and turbulence.
“Penguins’ superior swimming ability to start/brake, accelerate/decelerate, and turn swiftly is due to their freely waving wings. They allow penguins to propel and maneuver in the water and maintain balance on land,” said author Prasert Prapamonthon. “Our research team is always curious about sophisticated creatures in nature that would be beneficial to mankind.”
The hydrodynamic model takes in information about the flapping and feathering of the wings, including amplitude, frequency, and direction, and the fluid parameters, such as velocity and viscosity. Using the immersed boundary method, it solves for the motion of the wing and the thrust, lift, and lateral forces.
To establish the movement of wings across species, researchers use the ratio of wing flapping speed to forward speed. This value avoids any differences between air and water. Additionally, the authors define an angle of thrust, determined by the angle of the wings. Both of these parameters have a significant impact on the penguin’s thrust.
“We proposed the concept of angle of thrust, which explains why finned wings generate thrust: Thrust is primarily determined by the angle of attack and the relative angle of the wings to the forward direction,” said Prapamonthon. “The angle of thrust is an important concept in studying the mechanism of thrust generated by flapping motion and will be useful for designing mechanical wing motion.”
These findings can guide the design of aquatic vehicles by quickly estimating propulsion performance without high experimental or computational costs.
In the future, the team plans to examine a more realistic 3D penguin model. They will incorporate different wing properties and motion, such as starting, braking, turning, and jumping in and out of water.
###
The article “Hydrodynamic performance of a penguin wing: Effect of feathering and flapping” is authored by Zhanzhou Hao, Bo Yin, Prasert Prapamonthon, and Guowei Yang. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on June 20, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0147776). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0147776.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
###
Journal
Physics of Fluids
DOI
10.1063/5.0147776
Article Title
Hydrodynamic performance of a penguin wing: Effect of feathering and flapping
Article Publication Date
20-Jun-2023




