‘The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing worldwide, and HCC is amongst the leading causes of cancer death globally’
Oncotarget published “Characterization of the inflammatory microenvironment and hepatic macrophage subsets in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma models” which reported that HCC typically develops on a background of chronic inflammation and fibrosis with tumor associated macrophages playing an important role in chronic inflammation-induced HCC and progression.
However, the liver harbors unique macrophages, resident liver Kupffer cells and monocyte-derived macrophages, and their contribution to HCC and to the population of TAMs is incompletely known.
Here, the authors characterized the tumor microenvironment and the proportion and transcriptional profile of hepatic macrophages in two commonly used HCC mouse models.
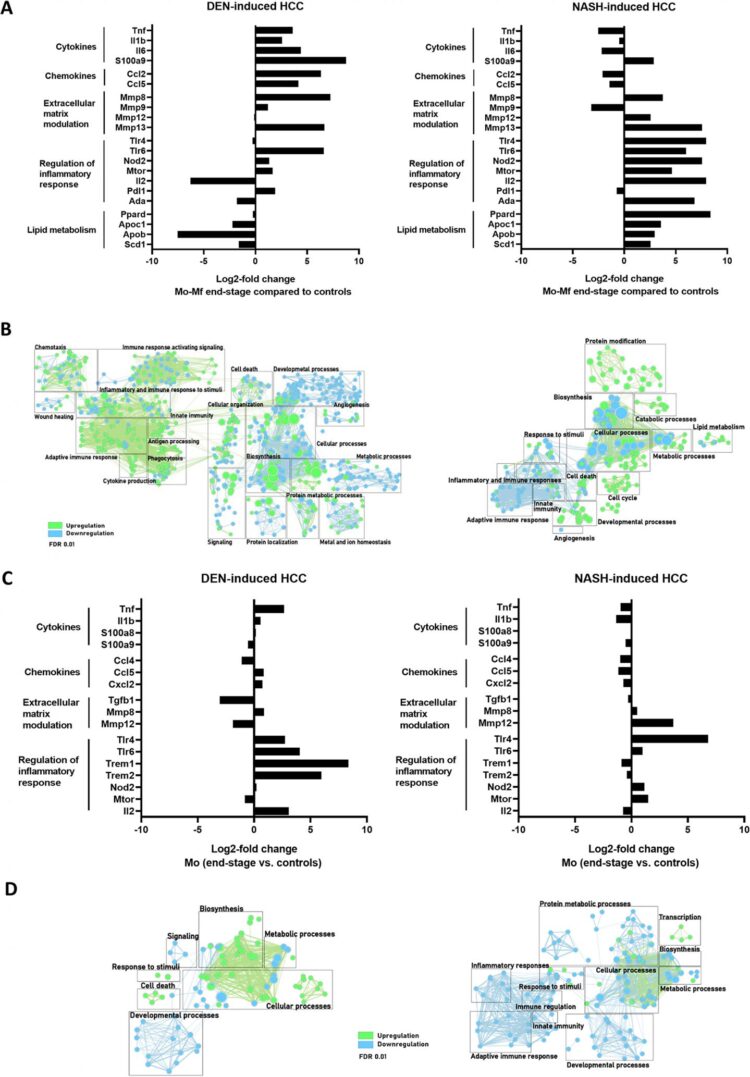
A gradually increased expression of inflammatory, immune regulatory, fibrotic and cell proliferation pathways and markers was observed during diethylnitrosamine – and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis -induced HCC development.
These insights are useful to further unravel sequential pathogenic events during hepatocarcinogenesis and direct future development of new treatment strategies for HCC.
Dr. Lindsey Devisscher from The Ghent University said, “The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing worldwide, and HCC is amongst the leading causes of cancer death globally.“
“The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing worldwide, and HCC is amongst the leading causes of cancer death globally.”
HCC is considered a classic inflammation-related cancer, whereby inflammation drives carcinogenesis by inducing continuous cycles of tissue damage, necrosis with regeneration and subsequent fibrosis, cell dysplasia and ultimately HCC lesions.
The observations that there were at least 4 nodules with an average tumor growth rate of 150% from 16 to 20 weeks of age, no visible metastasis and preserved liver function suggested that HCC induced in this model is equivalent to more advanced stages B to C of the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging system for patients.
The liver tumor microenvironment consists of cancer cells surrounded by extracellular matrix elements and different stromal cells such as fibroblasts, endothelial cells and inflammatory cells which secrete a variety of growth factors, cytokines or matrix remodeling enzymes.
Indeed, they previously reported that in models of DEN- and NASH-induced HCC, Mo massively infiltrate the liver KCs, whereas KC are partially depleted during chronic liver injury, including end-stage HCC.
This study assessed the time-dependent characteristics of the inflammatory micro-environment in the two aforementioned HCC mouse models, with an emphasis on the differential transcriptional profile of liver M/Users/anxiolydiot/Desktop/press-formatting-html.html subsets and the sequential changes in phenotype during the progression of HCC.
The Devisscher Research Team concluded in their Oncotarget Research Output, “HCC is an inflammation driven tumor, in which hepatic macrophage populations play a central role. KCs, Mo and Mo-M/Users/anxiolydiot/Desktop/press-formatting-html.html have divergent phenotypes that change with disease progression and these cell populations contribute to the population of TAMs in HCC. The knowledge that KCs also express typical TAM markers further contributes to the understanding of hepatocarcinogenesis in two different frequently used experimental mouse HCC models.“
###
DOI – https:/
Full text – https:/
Correspondence to – Lindsey Devisscher – [email protected]
Keywords –
hepatocellular carcinoma,
macrophage subsets,
tumor microenvironment,
tumor associated macrophages,
inflammation
About Oncotarget
Oncotarget is a bi-weekly, peer-reviewed, open access biomedical journal covering research on all aspects of oncology.
To learn more about Oncotarget, please visit https:/
SoundCloud – https:/
Facebook – https:/
Twitter – https:/
LinkedIn – https:/
Pinterest – https:/
Reddit – https:/
Oncotarget is published by Impact Journals, LLC please visit https:/
Media Contact
[email protected]
18009220957×105
Media Contact
RYAN JAMES JESSUP
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.