NIH scientists use epigenetics to help predict disease development
Credit: NIEHS
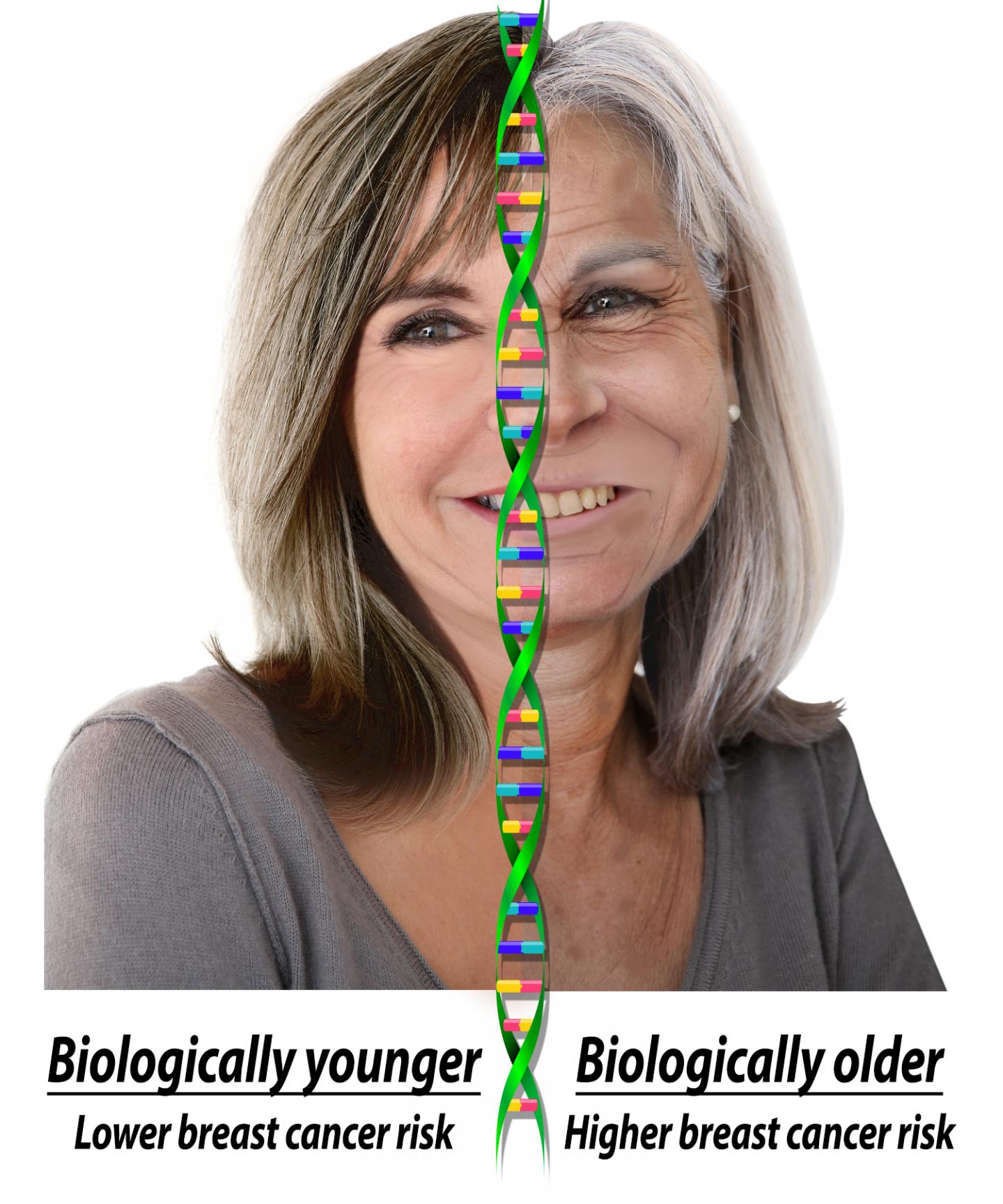
Biologic age, a DNA-based estimate of a person’s age, is associated with future development of breast cancer, according to scientists at the National Institutes of Health. Biologic age was determined by measuring DNA methylation, a chemical modification to DNA that is part of the normal aging process. The study showed for every five years a woman’s biologic age was older than her chronologic or actual age, known as age acceleration, she had a 15 percent increase in her chance of developing breast cancer. The study was published online Feb. 22 in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
Scientists from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS), part of NIH, speculate that biologic age may be tied to environmental exposures. If so, it may be a useful indicator of disease risk. They used three different measures, called epigenetic clocks, to estimate biologic age. These clocks measure methylation found at specific locations in DNA. Researchers use these clocks to estimate biologic age, which can then be compared to chronologic age.
The researchers used DNA from blood samples provided by women enrolled in the NIEHS-led Sister Study, a group of more than 50,000 women in the U.S. and Puerto Rico. The study was specifically designed to identify environmental and genetic risk factors for breast cancer. The research team measured methylation in a subset of 2,764 women, all of whom were cancer-free at the time of blood collection.
“We found that if your biologic age is older than your chronologic age, your breast cancer risk is increased. The converse was also true. If your biologic age is younger than your chronologic age, you may have decreased risk of developing breast cancer,” said corresponding author Jack Taylor, M.D., Ph.D., head of the NIEHS Molecular and Genetic Epidemiology Group. “However, we don’t yet know how exposures and lifestyle factors may affect biologic age or whether this process can be reversed.”
Lead author Jacob Kresovich, Ph.D., a postdoctoral fellow in the Taylor group, had read studies that used epigenetic clocks to predict age-related mortality. Since age is the leading risk factor for breast cancer, he hypothesized that age acceleration may be associated with higher breast cancer risk.
“If you look at a group of people who are all the same age, some may be perfectly healthy while others are not,” Kresovich said. “That variability in health may be better captured by biologic age than chronologic age.”
Kresovich suggests that using DNA methylation to measure biologic age may help scientists better understand who is at risk for developing cancer and other age-related diseases. This research is an example of epigenetics, a field that studies how biochemical processes turn individual genes on or off, without affecting the DNA sequence.
The Taylor group plans to continue using epigenetic data, along with information on genetics, environment, and lifestyle to better understand how these factors interact and contribute to disease risks.
###
About the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS): NIEHS supports research to understand the effects of the environment on human health and is part of the National Institutes of Health. For more information on NIEHS or environmental health topics, visit http://www.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Grant Numbers:
ZIAES049033
ZIAES049032
ZIAES044005
Reference: Kresovich JK, Xu Z, O’Brien KM, Weinberg CR, Sandler DP, Taylor JA. 2019. Methylation-based biological age and breast cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst; doi:10.1093/jnci/djz020 [Online 22 February 2019].
Media Contact
Robin Arnette
[email protected]
919-541-5143
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




