High-tech imaging of carp scales by Berkeley Lab scientists reveals remarkable properties that could lead to advanced synthetic materials
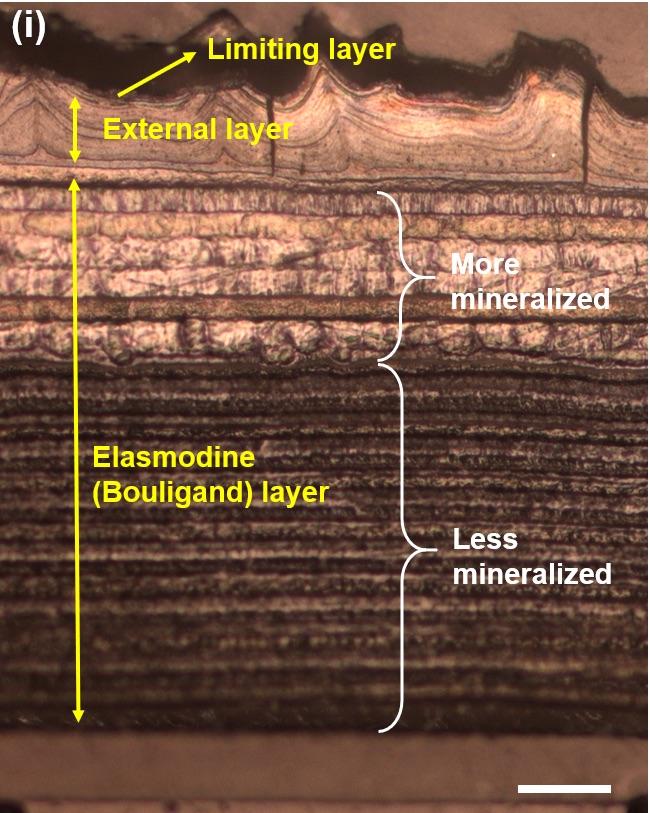
Credit: Quan et al., Structure and Mechanical Adaptability of a Modern Elasmoid Fish Scale from the Common Carp, Matter
Humans have drawn technological inspiration from fish scales going back to ancient times: Romans, Egyptians, and other civilizations would dress their warriors in scale armor, providing both protection and mobility. Now, using advanced X-ray imaging techniques, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) scientists have characterized carp scales down to the nanoscale, enabling them to understand how the material is resistant to penetration while retaining flexibility.
The researchers used powerful X-ray beams at Berkeley Lab’s Advanced Light Source (ALS) to watch how the fibers in carp scales react as stress is applied. As they wrote in their paper, published recently in the journal Matter, what they found “may well provide further inspiration for the design of advanced synthetic structural materials with unprecedented toughness and penetration resistance.”
“The structure of biological materials is absolutely fascinating,” said lead author Robert Ritchie, of Berkeley Lab’s Materials Sciences Division, who headed this work with Marc Meyers, a professor of nanoengineering and mechanical engineering at UC San Diego. “We like to mimic these properties in engineering materials, but the first step is to see how nature does it.”
Fish scales have a hard outer shell with a softer inner layer that is tough and ductile. When something like a predator’s teeth try to sink into the scales, the outer shell resists the penetration but the inner has to absorb all the excess load to keep the scale in one piece. How does it do this? It turns out that the fibers in the scale, which is made up of collagen plus minerals, are in a twisted orientation, called a Bouligand structure. When stress is applied to the material, the fibers rotate in sequence in order to absorb the excess load.
“It’s called adaptive reorientation. It’s like a smart material,” said Ritchie, who is also a professor of materials science and engineering at UC Berkeley. “Using a technique called small angle X-ray scattering, we can follow that in real time using the synchrotron. We irradiate it with X-rays, and we can actually see the fibers rotating and moving.”
The collagen that makes up human skin, on the other hand, is “all messed up like a bowl of spaghetti, but it can unravel and align to absorb energy, which makes skin incredibly resistant to tearing,” Ritchie said. The Bouligand structure in the carp scale is much more organized but still makes for a very effective toughening mechanism.
The other noteworthy characteristic of a carp scale is the gradient between the hard and soft layers. “If we were making that as armor, we would have an interface between the hard and soft material. The interface is invariably a location where cracks and failures start,” said Ritchie, an expert in how materials fail. “The way nature does it: Instead of having these interfaces where there’s discontinuity between one material and another, nature makes a perfect gradient from the hard to the soft (tougher) material.”
Working in collaboration with the researchers at UC San Diego, the team has previously studied the arapaima, an Amazonian freshwater fish whose scales are so tough they are impenetrable to piranha, as well as other species. For this study they chose the carp, a modern version of the ancient coelacanth fish, also known for having scales that act as armor.
Now that the deformation and failure mechanisms of carp scales have been characterized, trying to reproduce these properties in an engineering material is the next challenge. Ritchie noted that advances in 3D printing could provide a way to produce gradients the way nature does, and thus make a material that is both hard and ductile.
“Once we get a better handle on how to manipulate 3D printing, we can start to make more materials in the image of nature,” he said.
###
The ALS is a Department of Energy Office of Science user facility. The study was supported by a grant from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 13 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab’s facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
Media Contact
Julie Chao
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




