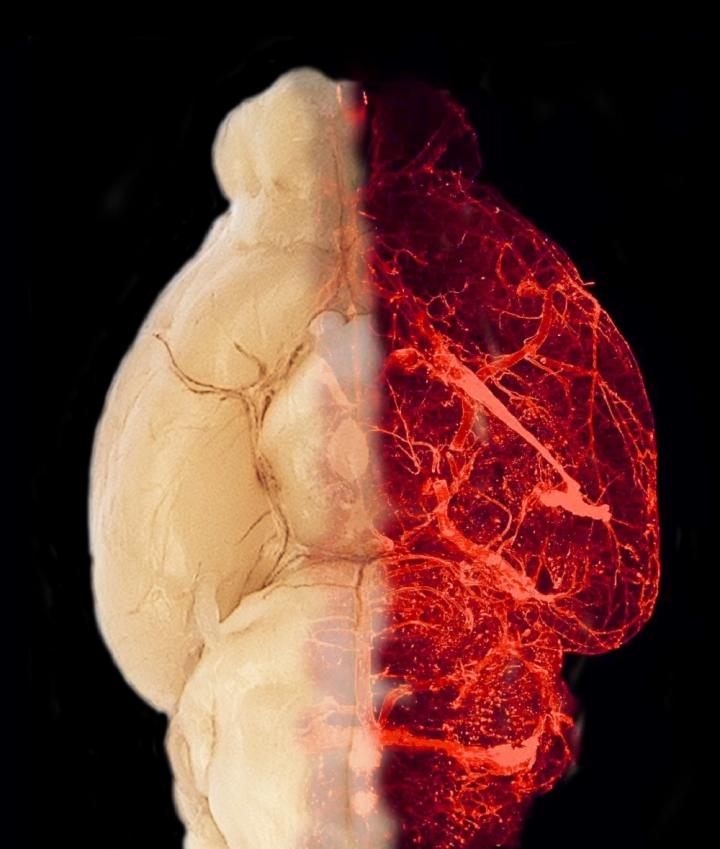
Hypertension is a widespread comorbidity of patients with obesity that greatly increases the risk of mortality and disability. In recent years, researchers have found that a high-calorie diet increases the density of blood vessels (hypervascularization) in the hypothalamus – an important “eating control” area in our brain. Researchers hypothesized that elevated hormone levels of leptin are associated with a higher risk of developing hypertension. However, the exact mechanisms that contribute to the condensed growth of blood vessels in the hypothalamus were unknown.
New research conducted by Cristina García-Cáceres’ research group at Helmholtz Zentrum München has now revealed that obese mice do not increase the amount of blood vessels in the hypothalamus when they lack the hormone leptin. Leptin is produced by adipose tissue, is involved in the control of hunger and satiety, and plays an important role in the regulation of fat metabolism in humans and mammals.
“We provide a paradigm shift in our understanding of how the hypothalamus controls blood pressure in obesity,” explains first author Tim Gruber. “While previous research has focused primarily on neurons, our research highlights the new role of astrocytes, historically assumed less relevant than neurons, in controlling blood pressure”.
Looking into the future, according to study leader Cristina García-Cáceres, one important question remains: How exactly do astrocytes communicate with neurons? “We have started to answer this question using in vivo real-time imaging of astrocyte-neuron circuit function in the hypothalamus,” the researcher says.
###
Helmholtz Zentrum München
Helmholtz Zentrum München is a research center with the mission to discover personalized medical solutions for the prevention and therapy of environmentally-induced diseases and promote a healthier society in a rapidly changing world. It investigates important common diseases which develop from the interaction of lifestyle, environmental factors and personal genetic background, focusing particularly on diabetes mellitus, allergies and chronic lung diseases. Helmholtz Zentrum München is headquartered in Neuherberg in the north of Munich and has about 2,500 staff members. It is a member of the Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany with more than 43,000 employees at 18 research centers.
Media Contact
Verena Schulz
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.