Credit: Professor Takuro Niidome
Many diseases are treated with protein-based drugs. However, due to the size of the molecules, the only effective delivery method is through injection, which can suffer from low patient compliance. Furthermore, many of these types of drugs require multiple treatments that can take hours to complete, as is the case with rheumatoid arthritis. New drug delivery methods should be discovered and implemented to relieve patients of this taxing and expensive experience.
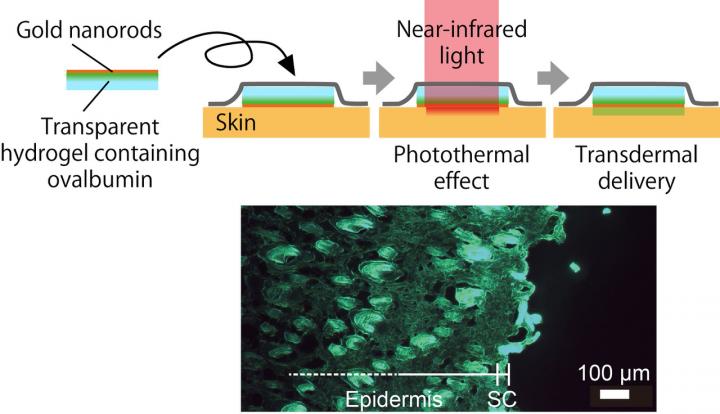
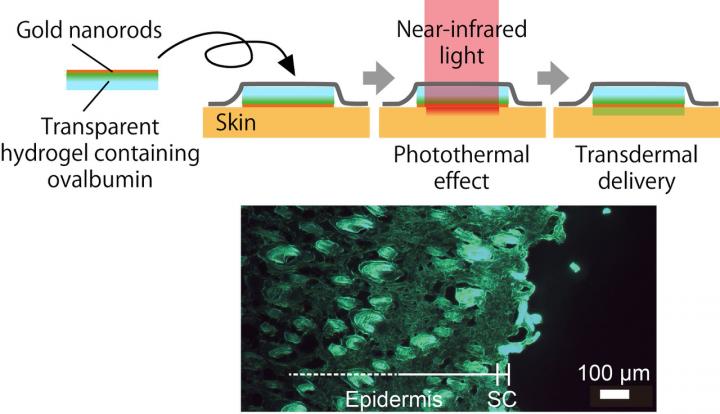
In an attempt to produce a better drug delivery system, researchers from Kumamoto University in Japan focused on a transdermal protein delivery system. There are multiple techniques currently being studied for this type of drug delivery mechanism, from microneedles to iontophoresis (transdermal drug delivery via electric current), but the Kumamoto University researchers designed to improve a technique called transdermal thermal ablation. This technique increases the permeability of the skin by heating and removing the first skin layer, the stratum corneum (SC). The difficulty is performing this without damaging deeper skin layers.
The researchers used a combination of transparent gel patches, gold nanorods, and near-infrared (NIR) light to create a unique thermal ablation system for transdermal drug delivery. They added fluorescently labeled ovalbumin (FITC-OVA) to the patches to determine the extent of protein translocation after NIR irradiation on murine skin. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments were performed using gel patches with gold nanorods, gel patches without gold nanorods (control 1), and gel patches with gold nanorods but without any form of irradiation (control 2). The two controls did not produce any thermal ablation effect on the skin, but the NIR irradiated gold nanorod patches heated the skin to around 43 degrees Celsius. This resulted in significant protein translocation for the in vitro experiment and moderate translocation for the in vivo experiment. The difference between these two results was likely due to a loosening of the skin cells after freezing for the in vitro experiment.
"Our experiments have shown that the photothermal effect on gold nanorods by irradiation of near-infrared light causes the skin to heat up and become more permeable," said Professor Takuro Niidome, leader of the research project. "It should be noted that our technique has yet to deliver any specific protein drugs, but we are confident that the research will contribute to the development of effective transdermal delivery systems."
This research can be found online in Elsevier's European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics.
###
[Reference]
Haine, A. T.; Koga, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Higashi, T.; Motoyama, K.; Arima, H. & Niidome, T., Enhancement of transdermal protein delivery by photothermal effect of gold nanorods coated on polysaccharide-based hydrogel, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, Elsevier BV, 2017, 119, 91-95. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.06.005
Media Contact
J. Sanderson
[email protected]
http://ewww.kumamoto-u.ac.jp/en/news/
Original Source
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0939641117306847 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpb.2017.06.005