Credit: Purdue University/Hyowon Lee
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A Purdue University team has developed a novel testing platform to evaluate how breast cancer cells respond to the recurrent stretching that occurs in the lungs during breathing. The technology is designed to better understand the effects that the local tissue has on metastatic breast cancer to study how metastases grow in a new tissue.
“One of the key features of breast cancer is that most patients survive if the disease stays local, but there is a greater than 70% drop in survival if the cells have metastasized,” said Luis Solorio, a Purdue assistant professor of engineering, who co-led the research team. “However, once the cells leave the primary tumor, they are often no longer responsive to the drugs that initially worked for the patient. We wanted to develop a system that could help us better understand how the physiology of a new tissue space effected tumor cells upon invasion into the new organ.”
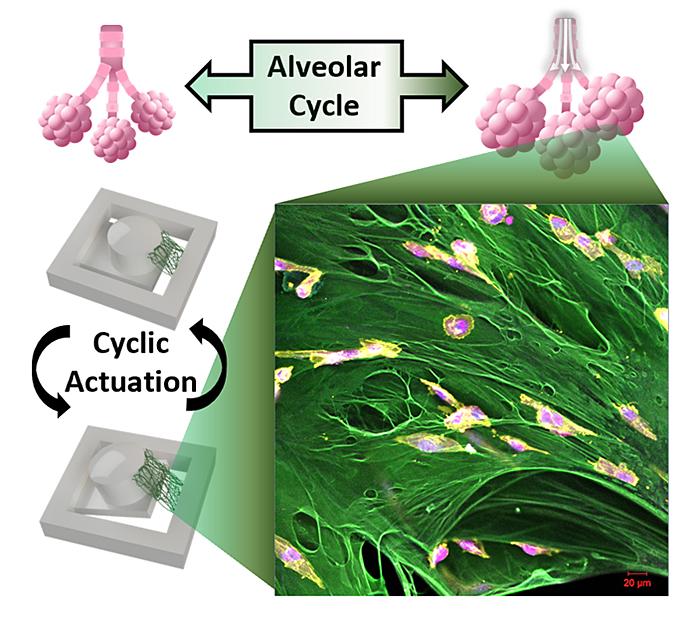
The Purdue researchers created a magnetically moving cell culturing system where the cancer cells can be grown in 3D on a suspended extracellular matrix protein that is abundant in early metastatic lung tissue in order to evaluate the impact of mechanical forces.
They were able to incorporate the strain amplitude and rate of breathing in this tissue mimic. The researchers found that the cells quit dividing under these conditions. The research is published in Advanced Functional Materials.
“Never before has the concept of motion been interrogated as a component of the tumor microenvironment,” said Michael Wendt, a Purdue associate professor of medicinal chemistry and molecular pharmacology. “We now understand that healthy organs utilize motion to resist metastatic colonization. The development of this microactuator system will not only continue to yield increased biological understanding, of metastasis, but it will also serve as a platform for us to better evaluate pharmacological inhibitors of the most lethal aspect of cancer progression.”
Hyowon “Hugh” Lee, an associate professor of engineering and a researcher at the Birck Nanotechnology Center, co-led the research team.
“This is the first attempt to engineer a cell culture system that can apply mechanical forces on a suspended tissue,” Lee said. “Most bioreactors with mechanical stimulation capabilities rely on growing 2D cell culture on flat non-biological substrates, but we are using a custom magnetic actuator and suspending a layer of fibronectin to grow 3D cancer cells like a miniature tissue.
“Our system better mimics the physiological environment without using artificial substrates. Using this platform, we show that certain cancer cells slow down their proliferation due to the cyclic stretching of breathing.”
This work was the collaboration of five different laboratories to characterize the mechanical and biological properties of the new device.
Sarah Calve, a Purdue adjunct professor of biomedical engineering, and Adrian Buganza Tepole, a Purdue assistant professor of mechanical engineering, interfaced with the mechanical characteristics of the stretching protein. They measured the response of the material to stretching and developing a mapping of the strains felt by the cancer cells at various locations on the device.
Angel Enriquez, a doctoral student in Lee’s lab, said, “One key takeaway has been the benefits of collaboration with people outside of your field of expertise and how they can provide more complete research.”
Sarah Libring, a doctoral student and a co-first author from Solorio’s Lab, said, “It’s been amazing to be part of the development of a new device like this because by bringing together the expertise of multiple professors and multiple labs, we are now able to study cancer cells on dynamically moving fibronectin fibrils that hasn’t been previously possible.”
###
The team works with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization to patent and license their technologies. For more information, contact OTC at [email protected] and mention track code 68700.
About Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization
The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization operates one of the most comprehensive technology transfer programs among leading research universities in the U.S. Services provided by this office support the economic development initiatives of Purdue University and benefit the university’s academic activities through commercializing, licensing and protecting Purdue intellectual property. The office is located in the Convergence Center for Innovation and Collaboration in Discovery Park District, adjacent to the Purdue campus. In fiscal year 2020, the office reported 148 deals finalized with 225 technologies signed, 408 disclosures received and 180 issued U.S. patents. The office is managed by the Purdue Research Foundation, which received the 2019 Innovation and Economic Prosperity Universities Award for Place from the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities. In 2020, IPWatchdog Institute ranked Purdue third nationally in startup creation and in the top 20 for patents. The Purdue Research Foundation is a private, nonprofit foundation created to advance the mission of Purdue University. Contact [email protected] for more information.
About Purdue University
Purdue University is a top public research institution developing practical solutions to today’s toughest challenges. Ranked the No. 5 Most Innovative University in the United States by U.S. News & World Report, Purdue delivers world-changing research and out-of-this-world discovery. Committed to hands-on and online, real-world learning, Purdue offers a transformative education to all. Committed to affordability and accessibility, Purdue has frozen tuition and most fees at 2012-13 levels, enabling more students than ever to graduate debt-free. See how Purdue never stops in the persistent pursuit of the next giant leap at purdue.edu.
Sources:
Hyowon “Hugh” Lee, [email protected]
Luis Solorio, [email protected]
Michael Wendt, [email protected]
Sarah Calve, [email protected]
Adrian Buganza Tepole, [email protected]
Angel Enriquez, [email protected]
Sarah Libring, [email protected]
Media Contact
Chris Adam
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




