This article by Dr. F. David Rodriguez is published in the journal, Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2021
Credit: Dr. F. David Rodriguez
Abusive alcohol drinking considerably impacts human health. Alcoholism, better defined as Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD), includes a group of pathological entities related to alcohol-induced damage. Individuals with AUD exhibit compulsive alcohol drinking and negative emotional states when alcohol drinking ceases. In the most severe AUD forms, the individuals lose control over consumption despite a decided will to stop. Some controversial issues have arisen as to whether the definition of AUD can help to delimit and characterize clinical entities related to abusive alcohol ingestion.
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that approximately 3,3 million people (5,9% of global deaths) die yearly because of harmful alcohol consumption (According to WHO, as of 4 February 2021, there have been 2,25 million deaths caused by COVID-19, globally). Besides, alcohol is directly responsible for 5 % of disabling diseases and injuries worldwide.
Authorized agencies have officially approved very few pharmacological treatments to treat AUD (for example, disulfiram, opioid antagonists, acamprosate, baclofen, or topiramate). Many patients are reluctant to treatment for different reasons based on their features (age, gender, ethnicity, genetic and epigenetic background) and their alcohol drinking behavior.
Currently, no silver bullet shall rescue humankind from the burden of alcohol on health. Notwithstanding, a better understanding of ethanol’s repercussion on molecular cell targets is imperious to plan out pharmacological strategies that ameliorate or block alcohol detriment.
Despite limited favorable results, efforts continue to find drugs acting on causes and effects observed in AUD, including relapse, withdrawal, stress, or anxiety. Nowadays, clinical studies in phases I and II explore the effectiveness of drugs in AUD treatment. Examples of compounds investigated are glutamate and GABA modulators, neuropeptide antagonists, or regulators of neuroimmune responses. Some drugs administered for the treatment of mental disorders have proved efficient in the treatment of AUD. For example, aripiprazole, an antipsychotic drug, and agomelatine, a melatonergic antidepressant, showed beneficial effects by preventing alcohol relapse and craving.
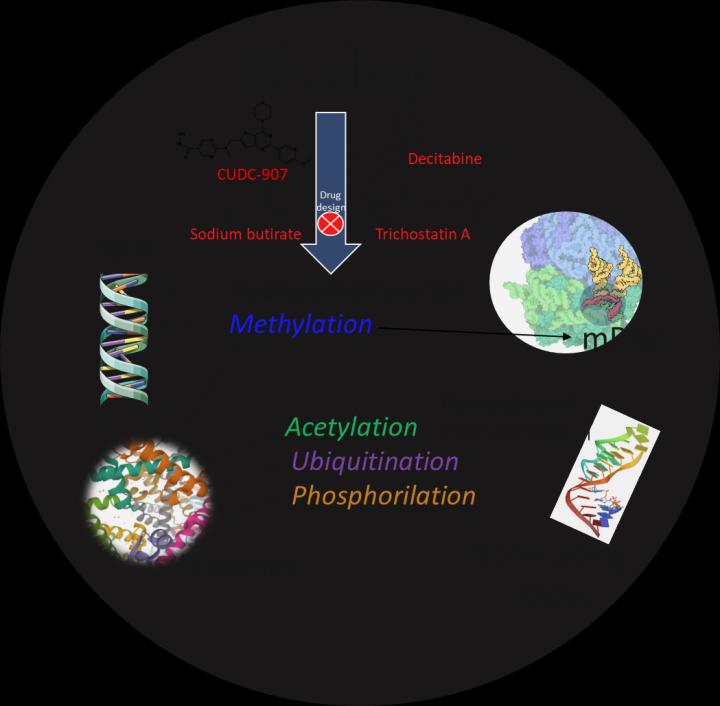
The influence of alcohol on epigenetic mechanisms is a relatively new explored field that offers new avenues for research in the field. The term epigenetics includes chemical changes in DNA, proteins (histones, mainly), mRNAs, and non-coding RNAs with regulatory capacity that control gene expression.
This study provides an in-depth review of recent research that reveals the impact of alcohol on the biochemical mechanisms responsible for epigenetic control within cells. Besides, it analyzes candidate drugs that may counteract the impact of alcohol on epigenetic mechanisms and serve to advance new and tailored pharmacological treatments. Research carried out in animal models and humans (with the obvious ethical limitations imposed on human research) provides valuable information on the epigenetic regulatory processes intercepted by alcohol. The design and laboratory synthesis of new drugs aimed at specific molecular targets offers significant advances in this field.
###
AUDs are chronic and complex diseases that also claim attention, efforts, and study from the realms of psychology, psychiatry, and social sciences.
For more information, visit: https:/
Media Contact
Faizan ul Haq
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




