Credit: Joshua-Tor lab/CSHL 2019
Cold Spring Harbor, NY — Noroviruses are a leading cause of food-borne illness outbreaks, accounting for 58% of all outbreaks and cause 685 million cases worldwide each year. There is no effective therapeutic against them. Having knowledge of the intricate structure of the outer layer of noroviruses, the capsid, which allows the virus to attach to its human host, could help in vaccine development.
In vaccines, specific antibodies recognize the capsids and bind to them so they can no longer interact with human cells. “We need to understand what the norovirus capsid shapes actually look like, and the shape differences between different strains,” said James Jung, a postdoctoral fellow in Dr. Leemor Joshua-Tor’s lab at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL).
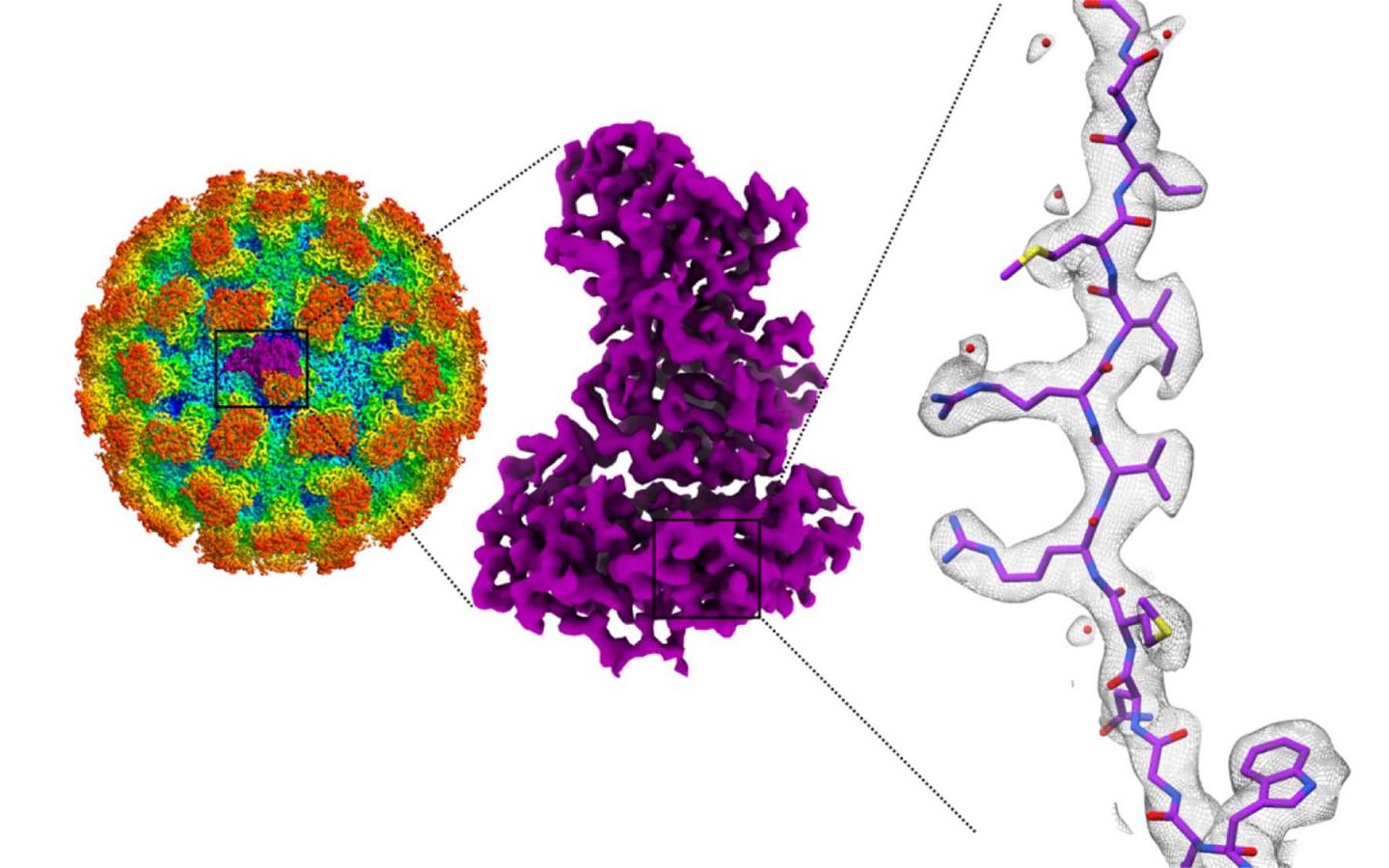
Jung and Joshua-Tor led a team to solve the high-resolution structures of four different strains of noroviruses using a cryo-electron microscope. This allowed them to see the intricate architecture of virus shells in high-definition. Their findings are published in the journal PNAS.
Jung gleaned new insights that could help in guiding the development of therapeutics to fight norovirus infection. “Previously, it was thought that the norovirus shells exist in single-sized assemblies consisting of 180 building blocks and 90 surface spikes. What we found was an unexpected mixture of different shell sizes and shapes. We found a smaller form, which consists of just 60 building blocks with 30 surface spikes placed further apart. We also found larger shells made out of 240 building blocks with 120 surface spikes that are lifted significantly above the base of the shell and form a two-layered architecture that could interact differently with the human cells,” he said.
The spikes on the shell interact with the host. Jung found that the distance and orientation of the spikes varied across the different strains of noroviruses. “That means each strain will interact differently with human cells,” Jung explained. “The way the antibodies bind is also going to be different. Vaccines should be formulated to take into account the variations across strains and structural forms.”
###
About Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Founded in 1890, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory has shaped contemporary biomedical research and education with programs in cancer, neuroscience, plant biology and quantitative biology. Home to eight Nobel Prize winners, the private, not-for-profit Laboratory employs 1,100 people including 600 scientists, students and technicians. The Meetings & Courses Program annually hosts more than 12,000 scientists. The Laboratory’s education arm also includes an academic publishing house, a graduate school and the DNA Learning Center with programs for middle and high school students and teachers. For more information, visit http://www.
Media Contact
Sara Roncero-Menendez
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




