A study to be published in Blood describes for the first time the structure of Ixolaris, a protein found in tick saliva, and its action on the inhibition of thrombus formation
Credit: Ana Paula Valente
A collaboration between researchers from Brazil and the United States may open new avenues for the treatment of thrombosis, the leading cause of death among cancer patients. In a study to be published in Blood, the scientists describe the Ixolaris structure, an important anticoagulant protein found in tick saliva, and its interaction with Factor Xa, a key enzyme in the process of blood clotting.
Ana Paula Valente, Viviane de Paula, Robson Monteiro and Fabio C. L. Almeida, of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, in collaboration with Nikolaos Sgourakis, of the University of California, Santa Cruz, and Ivo Francischetti, of the National Institute of Health, in the United States, conducted the study.
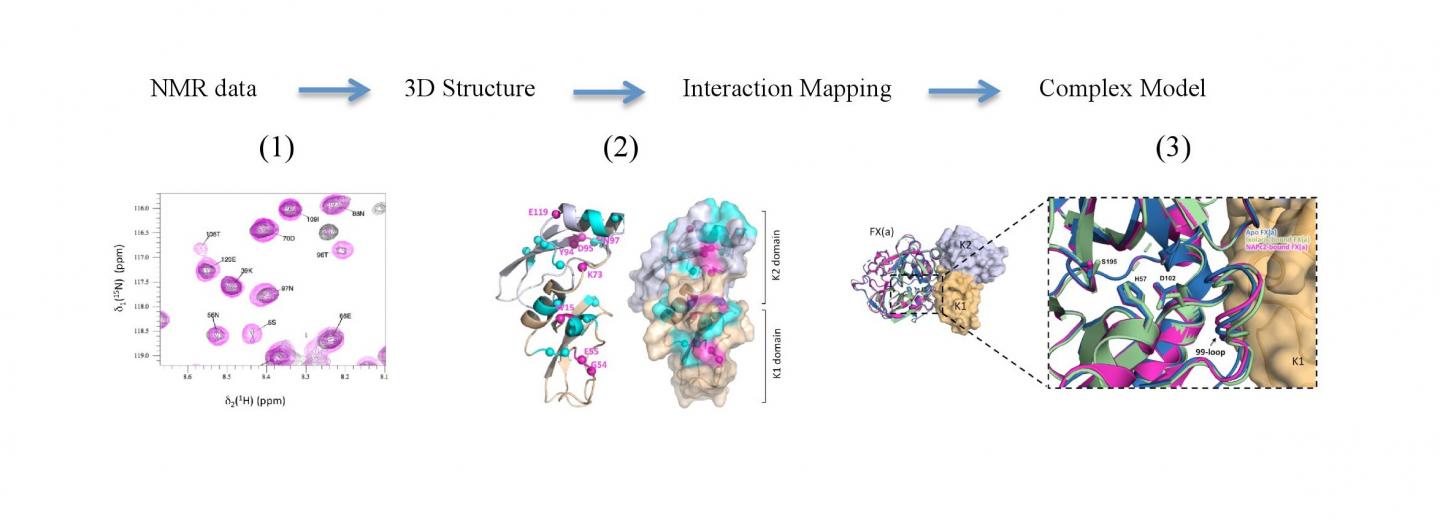
The anticoagulant effects of Ixolaris were already known, but this is the first description of the molecular mechanism of its action on the functioning of Factor Xa, an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the blood clotting. Using nuclear magnetic resonance, the researchers were able to construct a 3D model of the structure formed by the association of these two proteins.
The unprecedented result brings important insights into understanding the molecular mechanisms behind hemostasis, a complex process that regulates blood clotting and whose malfunction can lead to thrombosis. The expectation is that, from such a study, it will be possible to develop drugs capable of interrupting the formation of clots without interfering in the process of hemostasis as a whole.
The chain of phenomena leading to blood clotting involves several proteases, enzymes like Factor Xa that act by activating or inactivating other proteins. “The challenge is to develop a specific inhibitor that does not interfere with other similar enzymes of the body. Ixolaris has the advantage of binding to a non-canonical site, that is, a site more specific to that enzyme”, explains Ana Paula Valente, professor at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro.
Understanding these structures and their mechanisms is crucial for the advancement of studies in the area. “The structural information about these complexes is scarce because they are huge and challenging systems. The great merit of this study is that we have been able to obtain relevant molecular information from such a difficult system”, says Valente.
The results may also contribute to the development of new treatments for thrombosis. “This 3D structure study opens up numerous possibilities for structure-based drug design targeting human coagulation factors that could be used as a therapeutic option to attenuate coagulation and inflammation associated with thrombosis”, adds Viviane de Paula, first author of the work, professor at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro and visiting scientist at UCSC.
###
The article entitled “NMR structure determination of ixolaris and Factor X interaction 1 reveals a noncanonical mechanism of Kunitz inhibition” has been accepted for publication in Blood and will be available online next week.
The study was funded by the Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for Research Support in the State of Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), the Coordination of Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES / MEC) and the National Institute of Science and Technology for Structural Biology and Bioimaging (INBEB).
Media Contact
Ana Paula Valente
[email protected]




