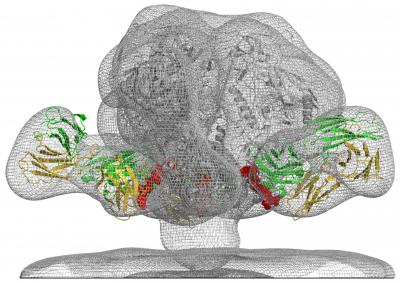
A team led by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has reported a research trifecta. They discovered a new vulnerable site on HIV for a vaccine to target, a broadly neutralizing antibody that binds to that target site, and how the antibody stops the virus from infecting a cell. The study was led by scientists at the Vaccine Research Center (VRC) of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of NIH.
The new target is a part of HIV called the fusion peptide, a string of eight amino acids that helps the virus fuse with a cell to infect it. The fusion peptide has a much simpler structure than other sites on the virus that HIV vaccine scientists have studied.
The scientists first examined the blood of an HIV-infected person to explore its ability to stop the virus from infecting cells. The blood was good at neutralizing HIV but did not target any of the vulnerable spots on the virus where broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies (bnAbs) were known to bind.
The researchers isolated a powerful bnAb in the blood that they named VRC34.01, and found that it binds to the fusion peptide and a sugar molecule. The scientists then crystallized the antibody while it was bound to the virus. This allowed them to characterize in atomic-level detail how VRC34.01 attaches to HIV and revealed that the antibody stops the virus from infecting a cell by binding to a key cell-surface molecule.
The scientists also report that it is not unusual for the immune system to try to stop HIV from infecting a cell by attacking the fusion peptide. When they screened the blood of 24 HIV-infected volunteers, they found that blood samples from 10 people targeted a similar binding site as VRC34.01.
The researchers are now working to create a vaccine designed to elicit antibodies similar to the VRC34.01 antibody.
###
ARTICLE:
R Kong, et al. Fusion peptide of HIV-1 as a site of vulnerability to neutralizing antibody. Science DOI: 10.1126/science.aae0474 (2016).
WHO:
NIAID Director Anthony S. Fauci, M.D., VRC Director John R. Mascola, M.D., and Peter D. Kwong, Ph.D., chief of the VRC Structural Biology Section, are available for comment.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Laura S. Leifman, (301) 402-1663, [email protected].
NIAID conducts and supports research–at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide–to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
Media Contact
Laura S. Leifman
[email protected]
301-402-1663
@NIAIDNews
http://www.niaid.nih.gov
The post NIH-led team discovers new HIV vaccine target appeared first on Scienmag.