When you get infected with a virus, some of the first weapons your body deploys to fight it were passed down to us from our microbial ancestors billions of years ago. According to new research from The University of Texas at Austin, two key elements of our innate immune system came from a group of microbes called Asgard archaea.
When you get infected with a virus, some of the first weapons your body deploys to fight it were passed down to us from our microbial ancestors billions of years ago. According to new research from The University of Texas at Austin, two key elements of our innate immune system came from a group of microbes called Asgard archaea.
Specifically, viperins and argonautes, two proteins that are known to play important roles in the immune systems of all complex life — from insects to plants to humans — came from the Asgard archaea. Versions of these defense proteins are also present in bacteria, but the versions in complex life forms are most closely related to those in Asgard archaea, according to the new scientific study published in the journal Nature Communications.
This research bolsters the idea that all complex life, called eukaryotes, arose from a symbiotic relationship between bacteria and Asgard archaea.
“It adds more support to the fact that the Asgards are our microbial ancestors,” said Brett Baker, associate professor of integrative biology and marine science and senior author. “It says that not only did eukaryotes get all these rich structural proteins that we’ve seen before in Asgards, now it’s saying that even some of the defense systems in eukaryotes came from Asgards.”
The researchers identified for the first time a large arsenal of defense systems in archaea that were previously known only in bacteria.
When viperins detect foreign DNA, which might indicate a dangerous virus, they edit the DNA so that the cell can no longer make copies of the DNA, which stops the virus from spreading. When argonautes detect foreign DNA, they chop it up, also halting the virus. Additionally, in more complex organisms, argonautes can block the virus from making proteins in a process called RNA silencing.
“Viral infections are one of the evolutionary pressures that we have had since life began, and it is critical to always have some sort of defense,” said Pedro Leão, now an assistant professor at Radboud University in the Netherlands and a recent postdoctoral researcher in Baker’s lab. “When bacteria and archaea discovered tools that worked, they were passed down and are still part of our first line of defense.”
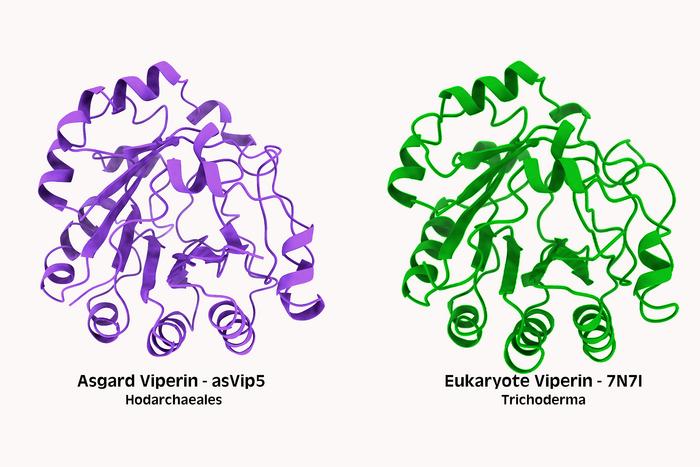
The researchers compared proteins involved in immunity across the tree of life and found many closely related ones. Then they used an AI tool called ColabFold to predict whether ones that had similar amino acid sequences also had similar three-dimensional shapes (aka structures). (It’s the shape of a protein that determines how it functions.) This showed that variations of the viperin protein probably maintained the same structure and function across the tree of life. They then created a kind of family tree, or phylogeny, of these sister amino acid sequences and structures that showed evolutionary relationships.
Finally, the researchers took viperins from Asgard archaea genomes, cloned them into bacteria (so the bacteria would express the proteins), challenged the bacteria with viruses, and showed that Asgard viperins do in fact provide some protection to the modified bacteria. They survived better than bacteria without the immune proteins.
“This research highlights the integral role cellular defenses must have played from the beginning of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic life,” said Emily Aguilar-Pine, a former undergraduate researcher who contributed to the project. “It also inspires questions about how our modern understanding of eukaryotic immunity can benefit from unraveling some of its most ancient origins.”
“It’s undeniable at this point that Asgard archaea contributed a lot to the complexity that we see in eukaryotes today,” Leão said. “So why wouldn’t they also be involved in the origin of the immune system? We have strong evidence now that this is true.”
Other authors, all from UT, are Mary Little, Kathryn Appler, Daphne Sahaya, Kathryn Currie, Ilya Finkelstein and Valerie De Anda.
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-024-50195-2
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Asgard archaea defense systems and their roles in the origin of eukaryotic immunity
Article Publication Date
31-Jul-2024