CRISPR-based ‘allelic drive’ allows genetic editing with selective precision and broad implications
Credit: Bier Lab, UC San Diego
New CRISPR-based gene drives and broader active genetics technologies are revolutionizing the way scientists engineer the transfer of specific traits from one generation to another.
Scientists at the University of California San Diego have now developed a new version of a gene drive that opens the door to the spread of specific, favorable subtle genetic variants, also known as “alleles,” throughout a population.
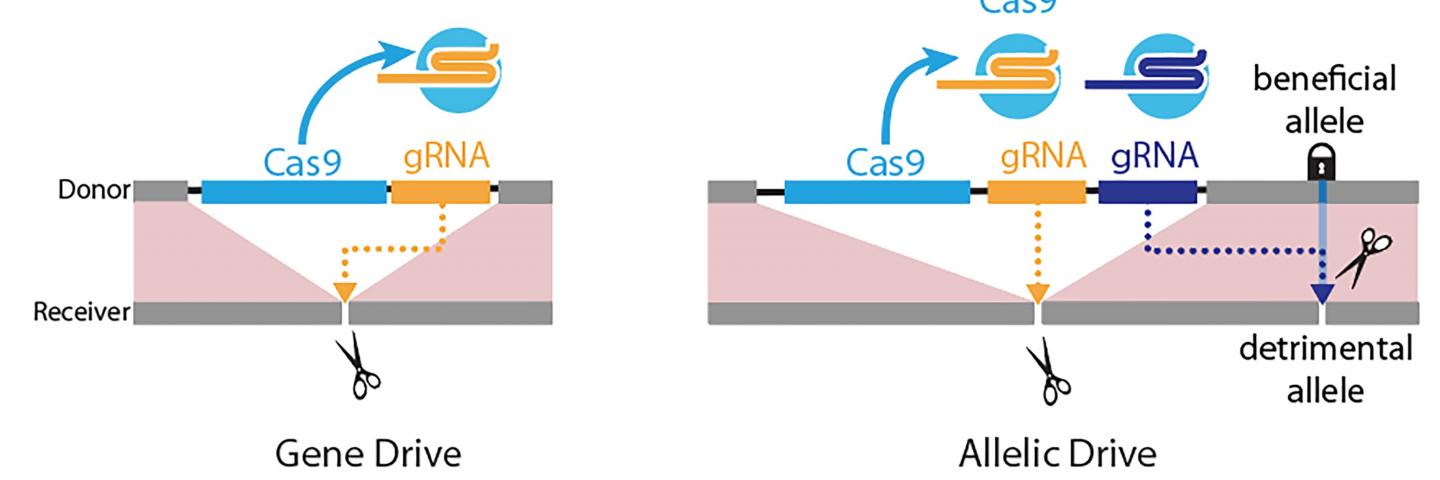
The new “allelic drive,” described April 9 in Nature Communications, is equipped with a guide RNA (gRNA) that directs the CRISPR system to cut undesired variants of a gene and replace it with a preferred version of the gene. The new drive extends scientists’ ability to modify populations of organisms with precision editing. Using word processing as an analogy, CRISPR-based gene drives allow scientists to edit sentences of genetic information, while the new allelic drive offers letter-by-letter editing.
In one example of its potential applications, specific genes in agricultural pests that have become resistant to insecticides could be replaced by original natural genetic variants conferring sensitivity to insecticides using allelic drives that selectively swap the identities of a single protein residue (amino acid).
In addition to agricultural applications, disease-carrying insects could be a target for allelic drives.
“If we incorporate such a normalizing gRNA on a gene-drive element, for example, one designed to immunize mosquitoes against malaria, the resulting allelic gene drive will spread through a population. When this dual action drive encounters an insecticide-resistant allele, it will cut and repair it using the wild-type susceptible allele,” said Ethan Bier, the new paper’s senior author. “The result being that nearly all emerging progeny will be sensitive to insecticides as well as refractory to malaria transmission.”
“Forcing these species to return to their natural sensitive state using allelic drives would help break a downward cycle of ever-increasing and environmentally damaging pesticide over-use,” said Annabel Guichard, the paper’s first author.
The researchers describe two versions of the allelic drive, including “copy-cutting,” in which researchers use the CRISPR system to selectively cut the undesired version of a gene, and a more broadly applicable version referred to as “copy-grafting” that promotes transmission of a favored allele next to the site that is selectively protected from gRNA cleavage.
“An unexpected finding from this study is that mistakes created by such allelic drives do not get transmitted to the next generation,” said Guichard. “These mutations instead produce an unusual form of lethality referred to as ‘lethal mosaicism.’ This process helps make allelic drives more efficient by immediately eliminating unwanted mutations created by CRISPR-based drives.”
Although demonstrated in fruit flies, the new technology also has potential for broad application in insects, mammals and plants. According to the researchers, several variations of the allelic drive technology could be developed with combinations of favorable traits in crops that, for example, thrive in poor soil and arid environments to help feed the ever-growing world population.
Beyond environmental applications, allelic drives should enable next-generation engineering of animal models to study human disease as well as answer important questions in basic science. As a member of the Tata Institute for Genetics and Society (TIGS), Bier says allelic drives could be used to aid in environmental conservation efforts to protect vulnerable endemic species or stop the spread of invasive species.
Gene drives and active genetics systems are now being developed for use in mammals. The scientists say allelic drives could accelerate new laboratory strains of animal models of human disease that aid in the development of new cures.
###
Other authors of the paper include: Tisha Haque, Marketta Bobik, Xiang-Ru Xu, Carissa Klanseck, Raja Kushwah, Bhagyashree Kaduskar and Valentino Gantz of UC San Diego’s Division of Biological Sciences and Mateus Berni of the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Media Contact
Mario Aguilera
[email protected]




