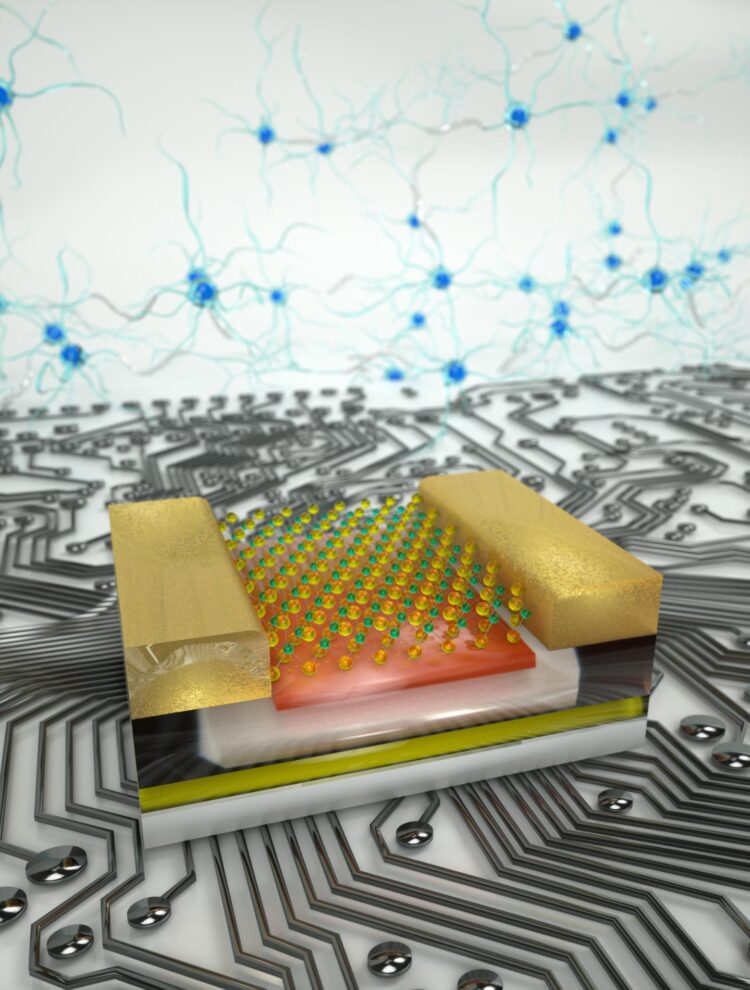
EPFL engineers have developed a computer chip that combines two functions – logic operations and data storage – into a single architecture, paving the way to more efficient devices.
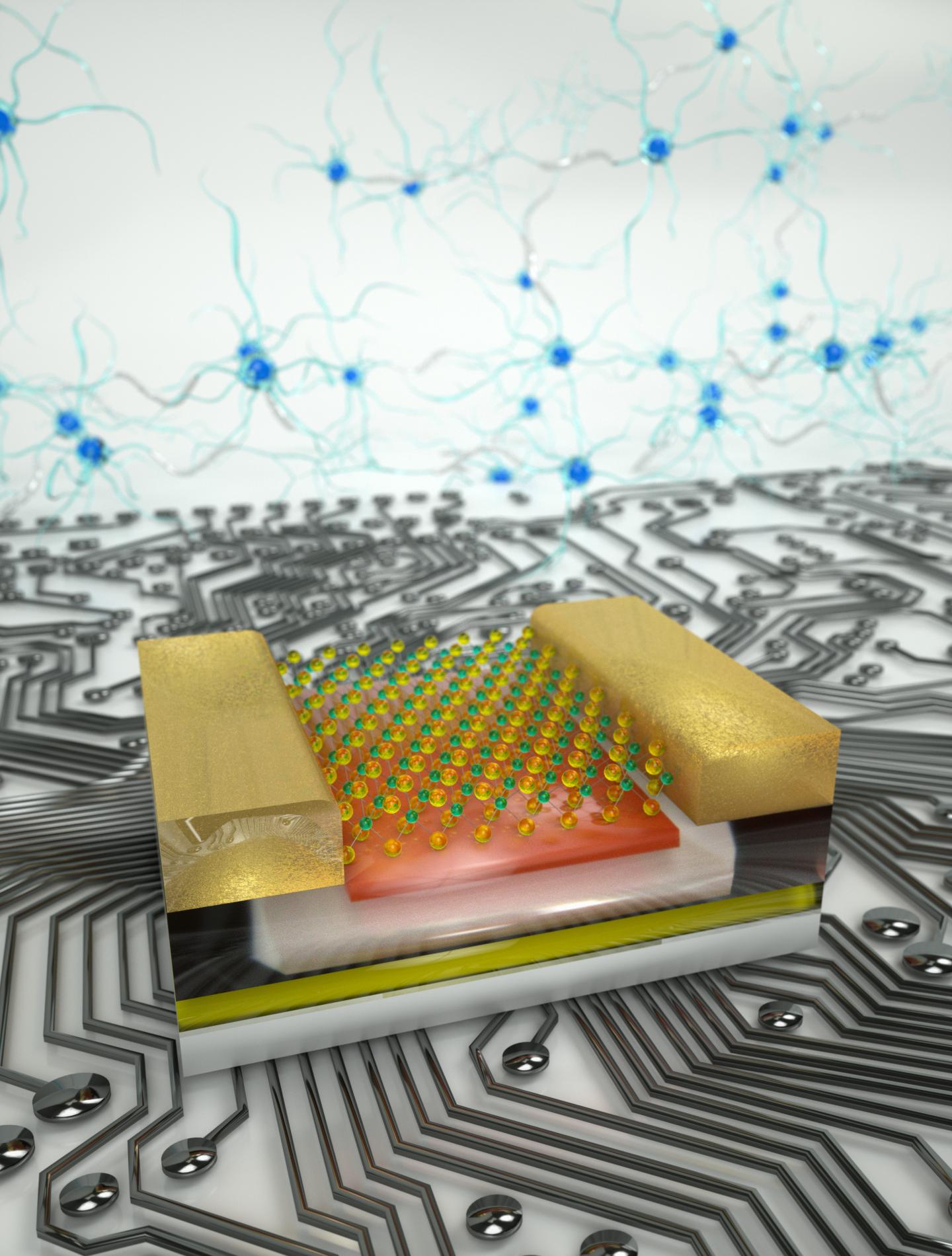
Credit: EPFL /LANES 2020
It’s a major breakthrough in the field of electronics. Engineers at EPFL’s Laboratory of Nanoscale Electronics and Structures (LANES) have developed a next-generation circuit that allows for smaller, faster and more energy-efficient devices – which would have major benefits for artificial-intelligence systems. Their revolutionary technology is the first to use a 2D material for what’s called a logic-in-memory architecture, or a single architecture that combines logic operations with a memory function. The research team’s findings appear today in Nature.
Until now, the energy efficiency of computer chips has been limited by the von Neumann architecture they currently use, where data processing and data storage take place in two separate units. That means data must constantly be transferred between the two units, using up a considerable amount of time and energy.
By combining the two units into a single structure, engineers can reduce these losses. That’s the idea behind the new chip developed at EPFL, although it goes one step beyond existing logic-in-memory devices. The EPFL chip is made from MoS2, which is a 2D material consisting of a single layer that’s only three atoms thick. It’s also an excellent semi-conductor. LANES engineers had already studied the specific properties of MoS2 a few years ago, finding that it is particularly well-suited to electronics applications. Now the team has taken that initial research further to create their next-generation technology.
The EPFL chip is based on floating-gate field-effect transistors (FGFETs). The advantage of these transistors is that they can hold electric charges for long periods; they are typically used in flash memory systems for cameras, smartphones and computers. The unique electrical proprieties of MoS2 make it particularly sensitive to charges stored in FGFETs, which is what enabled the LANES engineers to develop circuits that work as both memory storage units and programmable transistors. By using MoS2, they were able to incorporate numerous processing functions into a single circuit and then change them as desired.
In-depth expertise
“This ability for circuits to perform two functions is similar to how the human brain works, where neurons are involved in both storing memories and conducting mental calculations,” says Andras Kis, the head of LANES. “Our circuit design has several advantages. It can reduce the energy loss associated with transferring data between memory units and processors, cut the amount of time needed for computing operations and shrink the amount of space required. That opens the door to devices that are smaller, more powerful and more energy efficient.”
The LANES research team has also acquired in-depth expertise in fabricating circuits out of 2D materials. “We made our first chip ten years ago by hand,” says Kis. “But we have since developed an advanced fabrication process that lets us make 80 or more chips in a single run, with well-controlled properties.”
###
Media Contact
Andras Kis
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.