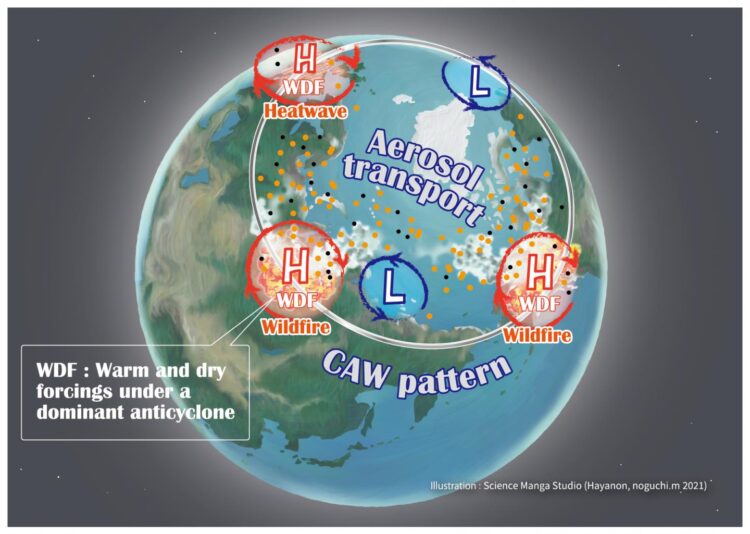
Scientists have uncovered a summertime climate pattern in and around the Arctic that could drive co-occurrences of European heatwaves and large-scale wildfires with air pollution over Siberia and subpolar North America.
In recent years in summer, there have often been extremely high temperatures over Europe, including heatwaves and active wildfires in and around the Arctic such as Siberia and subpolar North America (Alaska and Canada), which have caused widespread air pollution. For instance, in July 2019, significant Alaskan wildfires were detected by satellites. The recent unusual climate phenomena are of immense concern to many people living in these regions.
A team of scientists from Japan, South Korea, and the USA, including Hokkaido University’s Assistant Professor Teppei J. Yasunari, have revealed relationships among wildfires, aerosols (air pollution), and climate patterns in and around the Arctic. They have published their discoveries in the journal Environmental Research Letters. Involved in this study were Professor Hisashi Nakamura, The University of Tokyo, Japan; Dr. Nakbin Choi and Professor Myong-In Lee, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, Republic of Korea; and Professor Yoshihiro Tachibana, Mie University, Japan, and two scientists from the Goddard Space Flight Center, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), USA.
“Wildfires lead to extensive air pollution, primarily in the form of inhalable particulate matter with diameters of 2.5 micrometers or smaller (PM2.5). Arctic hazes during winter and spring are typical phenomena due to aerosols existing in the Arctic. In our scientific field, it is also known that deposition of light-absorbing aerosols onto snow surfaces can induce the so-called snow darkening effect, contributing to accelerated snow melting. For these reasons, long-term assessments of PM2.5 and aerosols in the Arctic and surrounding regions are required,” said Yasunari.
For their investigations, the scientists used the MERRA-2 (Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications, version 2) dataset and fire data by satellite, both produced by NASA, focusing on the recent period from 2003 to 2017. They assessed comprehensive air pollution (i.e., PM2.5) in the Arctic for as long as the past 15 years, seeking to clarify the relationships between variations in PM2.5 and aerosols, wildfires, and the relevant climate patterns.
“We found 13 out of the 20 months with highest PM2.5 in the Arctic during the 15 year period were in summer. The elevated PM2.5 levels were highly correlated with relatively higher organic carbon aerosol concentrations, implying active wildfires. We concluded that the summertime wildfires contributed to those months with exceptionally high PM2.5 in the Arctic. In those months, the wildfires likely occurred under extremely warm and dry conditions. Those were due to concomitantly persistent or developed high-pressure systems over Europe, Siberia, and subpolar North America, namely, Alaska and Canada,” explained Yasunari.
The scientists named this climate (atmospheric circulation) pattern, the circum-Arctic wave (CAW) pattern, as a driver for enhancing the co-occurrence of heatwaves in Europe and wildfires in Siberia and subpolar North America. In fact, the CAW-like pattern was also seen in the early summer of 2019, which was outside the period of the MERRA-2 analyses.
###
Joint release by Hokkaido University, Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Tokyo, Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology, and Mie University.
Media Contact
Sohail Keegan Pinto
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.