Credit: Alexandre Kitching
Virtual reality software which allows researchers to ‘walk’ inside and analyse individual cells could be used to understand fundamental problems in biology and develop new treatments for disease.
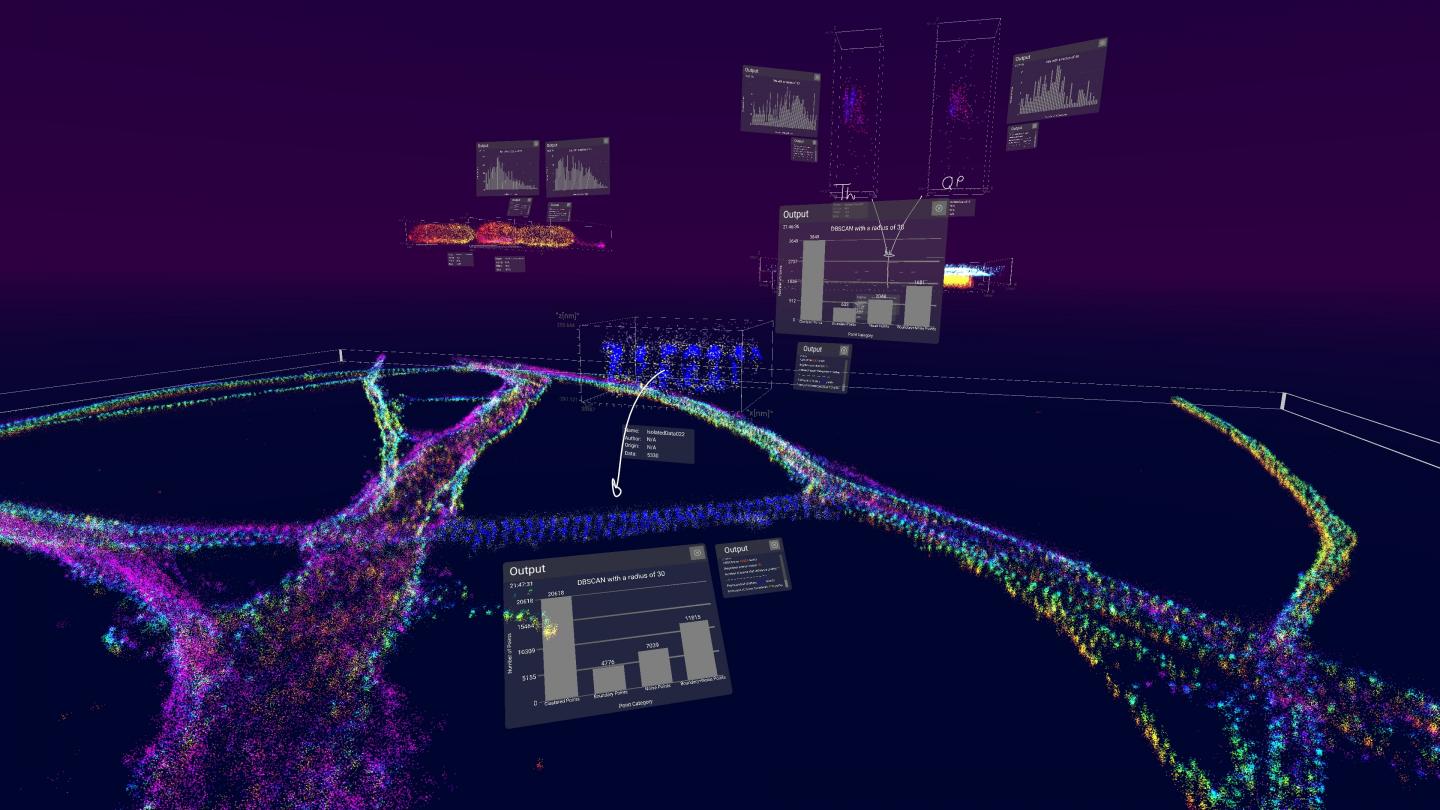
The software, called vLUME, was created by scientists at the University of Cambridge and 3D image analysis software company Lume VR Ltd. It allows super-resolution microscopy data to be visualised and analysed in virtual reality, and can be used to study everything from individual proteins to entire cells. Details are published in the journal Nature Methods.
Super-resolution microscopy, which was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 2014, makes it possible to obtain images at the nanoscale by using clever tricks of physics to get around the limits imposed by light diffraction. This has allowed researchers to observe molecular processes as they happen. However, a problem has been the lack of ways to visualise and analyse this data in three dimensions.
“Biology occurs in 3D, but up until now it has been difficult to interact with the data on a 2D computer screen in an intuitive and immersive way,” said Dr Steven F. Lee from Cambridge’s Department of Chemistry, who led the research. “It wasn’t until we started seeing our data in virtual reality that everything clicked into place.”
The vLUME project started when Lee and his group met with the Lume VR founders at a public engagement event at the Science Museum in London. While Lee’s group had expertise in super-resolution microscopy, the team from Lume specialised in spatial computing and data analysis, and together they were able to develop vLUME into a powerful new tool for exploring complex datasets in virtual reality.
“vLUME is revolutionary imaging software that brings humans into the nanoscale,” said Alexandre Kitching, CEO of Lume. “It allows scientists to visualise, question and interact with 3D biological data, in real time all within a virtual reality environment, to find answers to biological questions faster. It’s a new tool for new discoveries.”
Viewing data in this way can stimulate new initiatives and ideas. For example, Anoushka Handa – a PhD student from Lee’s group – used the software to image an immune cell taken from her own blood, and then stood inside her own cell in virtual reality. “It’s incredible – it gives you an entirely different perspective on your work,” she said.
The software allows multiple datasets with millions of data points to be loaded in and finds patterns in the complex data using in-built clustering algorithms. These findings can then be shared with collaborators worldwide using image and video features in the software.
“Data generated from super-resolution microscopy is extremely complex,” said Kitching. “For scientists, running analysis on this data can be very time consuming. With vLUME, we have managed to vastly reduce that wait time allowing for more rapid testing and analysis.”
The team are mostly using vLUME with biological datasets, such as neurons, immune cells or cancer cells. For example, Lee’s group has been studying how antigen cells trigger an immune response in the body. “Through segmenting and viewing the data in vLUME, we’ve quickly been able to rule out certain hypotheses and propose new ones,” said Lee. This software allows researchers to explore, analyse, segment and share their data in new ways. All you need is a VR headset.”
###
Media Contact
Sarah Collins
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.





