An image of the HDAC enzyme is available here: https://www.dropbox.com/sh/tafbpgai7ufo1hk/AAA3a1vCIEApA3srynHXnKfta?dl=0
New knowledge about the mechanism of specific protein complexes in the body could help in the development of better drugs for the treatment of diseases such as cancer and Alzheimer's, according to research led by the University of Leicester.
The team, working under Professor John Schwabe from the University of Leicester's Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, focuses on understanding the structure and function of large protein complexes in the body that are involved in the regulation of gene expression called co-repressor complexes.
These complexes contain histone deacetylase (HDAC) enzymes, which alter how DNA is packaged within cells.
HDACs are implicated in many different diseases from cancer to Alzheimer's — and several drugs are in clinical use for the treatment of different types of lymphoma and myeloma.
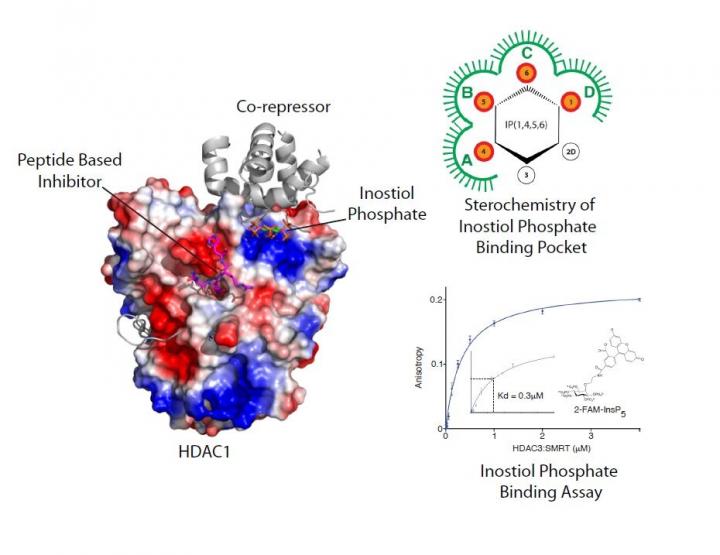
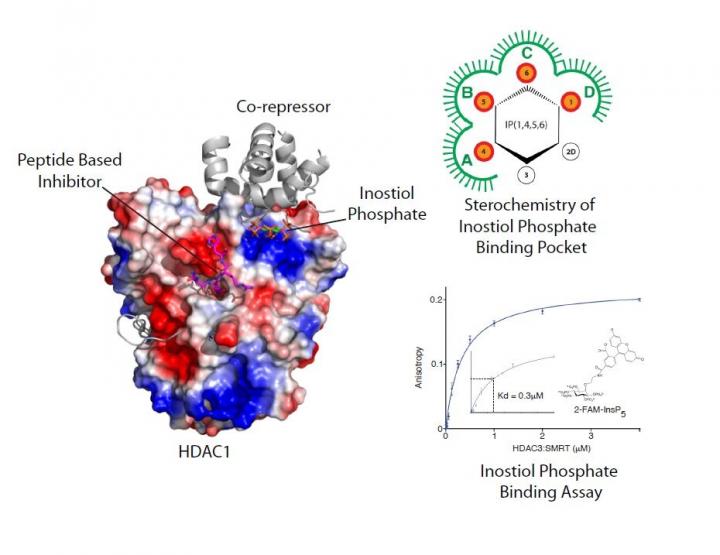
In a new paper published in the journal Nature Communications, the interdisciplinary team led by Professor Schwabe has developed a novel peptide-based inhibitor and gained insights into how the enzymes are activated by the small molecule inositol phosphate.
Professor Schwabe explained: "Previously our team had discovered that the activity of the enzymes in co-repressor complexes is regulated by a small molecule called inositol phosphate.
"We wished to further understand the mechanism of enzyme activation by inositol phosphates and how substrate is recognised.
"This work provides fundamental basic insights into the HDAC enzymes and may provide the basis for the development of drugs that are more specific and efficient. Ultimately, a greater understanding of how these enzymes work and how substrate interacts may lead to the development of better drugs."
Working with collaborators from the University of Leicester's Department of Chemistry (Dr Andrew Jamieson's research group) and researchers at the University of Bath (Professor Barry Potter's research group), the team synthesised a number of unique tool compounds which allowed them to investigate how inositol phosphates and substrate bind to co-repressor complexes.
They were then able to work out the specific features of inositol phosphates and how they bind to activate the HDAC enzyme. They then solved the crystal structure of a novel peptide inhibitor, which is based upon the enzymes' substrate, in complex with HDAC1: co-repressor. This not only gave insights into how substrate interacts with the enzyme but could also help to improve drug treatments for a variety of health issues. Taken together these results have shed light on the mechanism of activation by inositol phosphates.
Professor Schwabe added: "We are very proud of this publication, which has been a collaboration between various groups both within the University of Leicester and from outside. It has been a fabulous journey using these chemical tools to fully unravel the mechanism as to how inositol phosphates regulate HDAC activity."
###
The study, 'Insights into the activation mechanism of class I HDAC complexes by inositol phosphates' is published in the journal Nature Communications and is supported by the Wellcome Trust and the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research (BBSRC).
Media Contact
Professor John Schwabe
[email protected]
01-162-297-030
@UoLNewsCentre
http://www.leicester.ac.uk
The post New understanding of enzymes could help to develop new drugs to treat diseases appeared first on Scienmag.