Credit: ©Science China Press
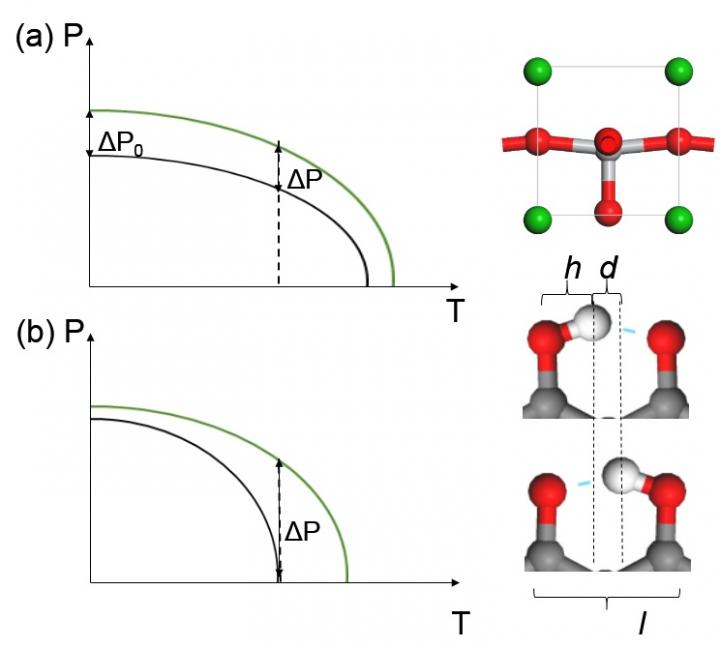
Prevalent piezoelectric materials like barium titanate (BaTiO3) and lead zirconate titanate (PZT) possess high piezoelectric coefficients 20-800 pC/N, which are also ferroelectric. The Curie temperature of those ferroelectrics are mostly far above room temperature, so the change of polarization ΔP upon a strain at room temperature is approximately the same as ΔP0 at 0K.
Recently, scientists at Huazhong University of Science and Technology and at the Nanjing University in China proposed a new possibility of inducing ultra-high piezoelectric coefficient, which will be theoretically infinitely large if the Curie temperature is right at the working temperature and sensitive to strain. Well-known ferroelectric perovskites like BaTiO3 or PZT are not such candidates due to their high Curie temperature that is insensitive to strain. However, many hydrogen-bonded ferroelectrics with Curie temperature ranging from 200 to 400K can be ideal candidates, which are also soft, flexible and lead-free. For examples, the measured Curie temperature of organic PhMDA and [H-55DMBP][Hia] were respectively 363 and 268K. For hydrogen bonds like O-H…O, each proton will be covalently bonded to only one side of O atom due to the saturation of covalent bond. The O-H bond is on the verge of breaking at the hopping transition state where the proton locates at the midpoint. Due to the brittle nature of covalent bond, if the O-H…O bonds are prolonged upon a tensile strain, the hopping barrier as well as Curie temperature may be greatly enhanced with a much larger transfer distance. Meanwhile their hydrogen-bonded network can be easily compressed or stretched due to low bulk modulus.
The authors have shown first-principles evidence combined with Monte Carlo simulation, that the proton-transfer barriers as well as the Curie temperature of some hydrogen-bonded ferroelectrics can be approximately doubled upon a tensile strain of as low as 2 %. Their Curie temperature can be tuned exactly to room-temperature by applying a fixed strain in one direction, and the systems will exhibit ultra-high piezoelectricity in another direction. The unprecedented piezoelectric coefficient of 2058 pC/N obtained in PhMDA is more than 3 times higher than PZT, and an order of magnitude higher than the highest value obtained in current lead-free piezoelectrics. This value is even underestimated and can be greatly enhanced upon smaller strain. Since this proposed principle for such piezoelectricity can be applied to most hydrogen-bonded ferroelectrics, the large number of organic or inorganic candidates should facilitate its experimental realizations and optimizations in future, which will be a breakthrough for the long-sought lead-free high-coefficient piezoelectrics. This mechanism may also clarify the previously reported drastic rise in piezoelectric coefficient for SbSI when approaching its Curie temperature.
###
See the article:
Yangyang Ren, Menghao Wu, Jun-Ming Liu
Ultra-High Piezoelectric Coefficients and Strain-Sensitive Curie Temperature in Hydrogen-Bonded Systems
Natl Sci Rev (2020)
https:/
Media Contact
Menghao Wu
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




