Credit: UNIST
Chronic liver disease is known as the silent killer, as it shows no obvious symptoms until the disease has progressed to an advanced stage. Therefore, making a proper diagnosis in the early stage of disease progression can be a clinical challenge.
An international team of researchers, affiliated with UNIST, has identified a novel route that regulates the signaling pathways induced by extracellular matrix (ECM). This may serve as a new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target in the fight against chronic liver diseases.
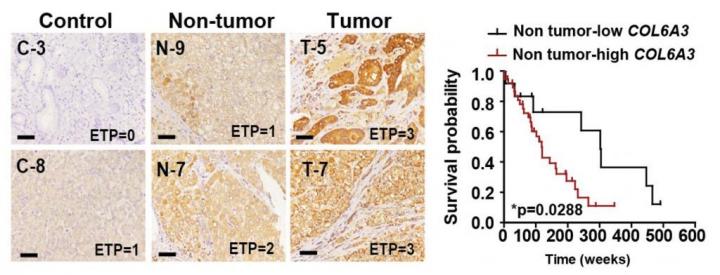
Led by Professor Jiyoung Park in the School of Life Sciences at UNIST, the research team has discovered that endotrophin (ETP) plays a crucial role in producing a pathological microenvironment in liver tissues of chronic liver disease. ETP is a marker of collagen type VI (COL6) formation, known as the link between obesity and cancer.
“ETP levels in adipose tissues are elevated in obesity or diabetes and are associated with adipose tissue fibrosis, inflammation, and angiogenesis, leading to metabolic dysfunction in adipose tissues and systemic insulin resistance,” says Professor Park who first discovered ETP in 2012. “Through the identification of the correlation between ETP and chronic liver disease, this study opened new doors in the fight against liver diseases.”
The study reveals ETP plays an important role in the interaction between ‘hepatocytes’ and ‘non-parenchymal cells’ in the progression of liver disease, as follows: ? the signaling pathways from ETP kills the hepatocytes, ? the substances from the dead hepatocytes interact with the hepatocytes, ? cause inflammation and make the liver hard. Finally, if the vicious cycle that leads to ‘apoptosis – fibrosis – inflammation’ continues, and ? chronic liver disease and liver cancer also occur.
In this work, Professor Park and her research team examined the liver tissues from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients and found that the presence of ETP in tumor-neighboring regions are strongly associated with poor prognosis in HCC patients. Moreover, to assess the direct function of ETP in liver tissues, the research team generated an inducible, liver-specific ETP transgenic mouse (Alb-ETP) and discovered that ETP overexpression is a trigger of liver cancer.
“Therapeutic antibodies that inhibit the activity of ETP can be used to break the vicious circle that occurs between liver tissue cells,” says Professor Park. “This suggests that ETP may be developed as a target substance for a specific therapeutic agent for treating patients with chronic liver disease.”
“ETP is an extracellular substance that can be easily detected in blood,” says Professor Park. “ETP, which appears in the early stage of chronic liver disease, may also serve as an early diagnostic marker.”
###
This research has been supported by the Research-driven Hospitals Project through the Ministry of Health & Welfare, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation. The study was published in Journal of Pathology, one of the leading scientific journals in the field of pathology.
Media Contact
JooHyeon Heo
[email protected]
82-522-815-502
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




