Many therapeutic cancer vaccines that are currently being developed are designed to direct the immune system against altered cancer-cell proteins. However, these vaccines can only be effective if the tumor cells present the altered protein to the immune system in a perfectly matching shape. Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and Heidelberg University Hospital have now described a test to predict whether this prerequisite for effective tumor vaccination is fulfilled.
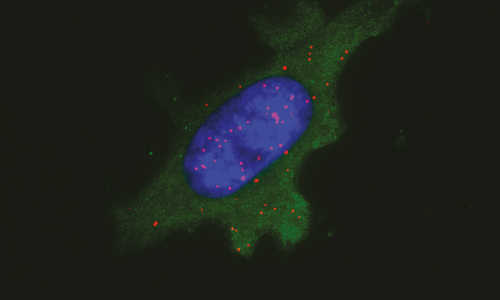
A cancer cell displaying tumor antigens at its surface. The red dots indicate where MCH molecules and tumor antigen co-locate. Photo Credit: M. Platten/DKFZ
Cancer vaccines are designed to turn the body’s own immune system specifically against tumor cells. Particularly promising are vaccines that are directed against so-called neoantigens: These are proteins that have undergone a genetic mutation in tumor cells and, therefore, differ from their counterparts in healthy cells. The tiny alteration – sometimes only a single protein building block has been changed – gives the protein on the tumor cell surface novel immunological characteristics that can be recognized as “foreign” by the immune system’s T cells. Therapeutic vaccines using a short protein fragment, or peptide, specifically containing the mutated site can then direct immune cells specifically to the tumor.
“However, a basic prerequisite for the effectiveness of a vaccine of this type is that the vaccine peptide is presented to the immune cells on the surface of the tumor, and it must be tailored to a shape that matches exactly. Our new test can detect whether this is the case,” says Professor Michael Platten, who heads a department at the German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ) and also works as a senior consultant in the Department of Neurology at Heidelberg University Hospital.
The vaccine peptide must exactly match specific presentation molecules, called MHC molecules, on the surface of the tumor cells. This will only be possible if the cell has the appropriate molecular make-up. Immune cells will only respond if the antigen is displayed on the matching MHC molecules. If this is not the case, the body will fail to mount an immune response.
Even if cancer-specific neoantigens are present in tumor cells, this does not necessarily mean that they can be presented by the MHC molecules. Michael Platten, who is himself working on a tumor vaccine, has therefore been searching for a method to test, in tumor biopsies, whether or not MHC molecules display the neoantigen on the tumor cell surface.
Platten and his colleagues have now described a clever solution to this problem: The PLA test* is based on the use of two antibodies, one that recognizes the neoantigen, and another that recognizes the MHC molecule. Only if the target structures of both antibodies are located in immediate proximity to each other will specific molecular-biological reactions produce a light signal.
The investigators have now demonstrated the effectiveness of the new test by using a tumor neoantigen found in brain cancer as an example. More than 70 percent of the time, specific brain tumors known as low-grade gliomas exhibit an identical “typo” in their DNA. As a result, a single, specific protein building block in an enzyme called isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH-1) is exchanged at the 132nd position in the protein’s sequence.
The researchers used their PLA test in tissue samples from glioma cells and were able to show that the IDH-1-mutated peptide is actually found on the surface of the cancer cells together with MHC molecules.
The test worked equally well for another tumor antigen called NY-ESO-1. This antigen is not a mutation-induced neoantigen, but rather a protein in the body that normally only plays a role in certain developmental steps. In many types of cancer, however, it is produced “out of line” by cancer cells. The PLA test enabled the researchers to detect NY-ESO-1 in conjunction with MHC molecules in melanoma cells.
Numerous clinical trials are currently being conducted across the globe with the goal of testing promising vaccines and targeted immunotherapies, e.g. to treat malignant melanoma, renal cell cancer and lung cancer. “Our test could help identify those patients beforehand who might actually benefit from such a vaccination,” says Lukas Bunse, one of the first authors of the study. He adds: “However, the prerequisite is that a specific antibody against the tumor antigen be available.”
Michael Platten and his colleagues recently demonstrated that the mutated IDH-1 peptide induces specific immune responses against brain tumors. Now they plan to launch a clinical Phase I trial with the goal of evaluating the safety of the peptide vaccine against IDH-1-mutated glioma.
*PLA = Proximity Ligation Assay
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by German Cancer Research Center (Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum, DKFZ).