First clinical trial of an automated blood drawing and testing device
Credit: Unnati Chauhan
In the future, robots could take blood samples, benefiting patients and healthcare workers alike.
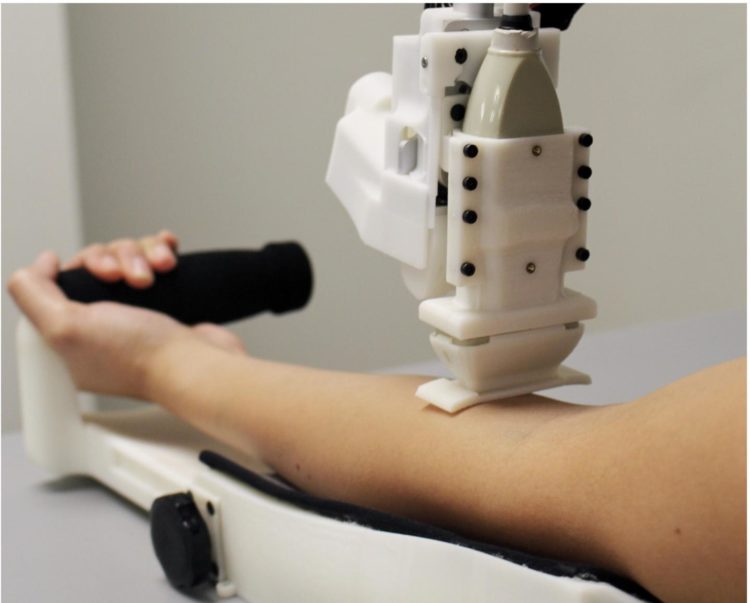
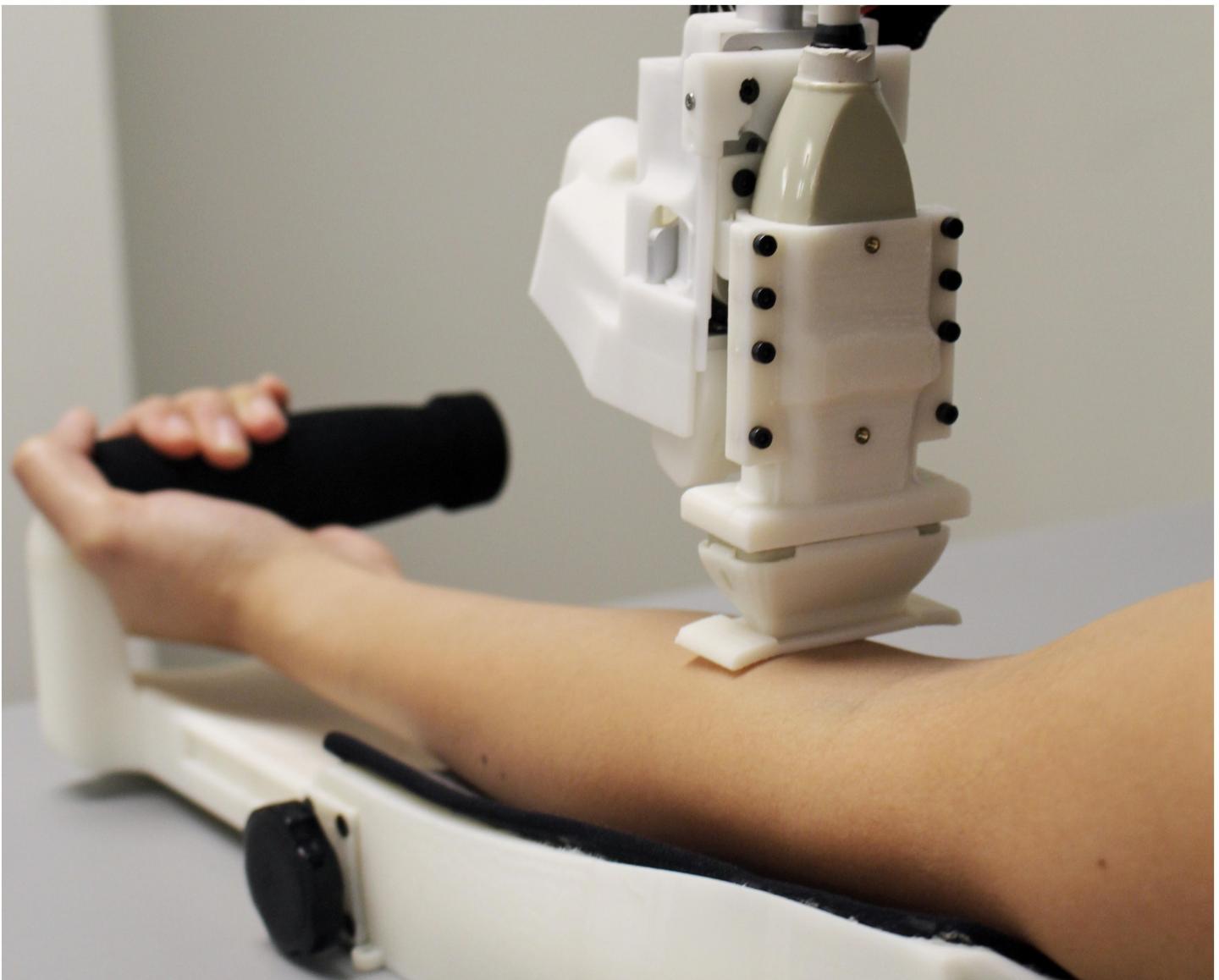
A Rutgers-led team has created a blood-sampling robot that performed as well or better than people, according to the first human clinical trial of an automated blood drawing and testing device.
The device provides quick results and would allow healthcare professionals to spend more time treating patients in hospitals and other settings.
The results, published in the journal Technology, were comparable to or exceeded clinical standards, with an overall success rate of 87% for the 31 participants whose blood was drawn. For the 25 people whose veins were easy to access, the success rate was 97%.
The device includes an ultrasound image-guided robot that draws blood from veins. A fully integrated device, which includes a module that handles samples and a centrifuge-based blood analyzer, could be used at bedsides and in ambulances, emergency rooms, clinics, doctors’ offices and hospitals.
Venipuncture, which involves inserting a needle into a vein to get a blood sample or perform IV therapy, is the world’s most common clinical procedure, with more than 1.4 billion performed daily in the United States. But clinicians fail in 27% of patients without visible veins, 40% of patients without palpable veins and 60% of emaciated patients, according to previous studies.
Repeated failures to start an IV line boost the likelihood of phlebitis, thrombosis and infections, and may require targeting large veins in the body or arteries – at much greater cost and risk. As a result, venipuncture is among the leading causes of injury to patients and clinicians. Moreover, a hard time accessing veins can increase procedure time by up to an hour, requires more staff and costs more than $4 billion a year in the United States, according to estimates.
“A device like ours could help clinicians get blood samples quickly, safely and reliably, preventing unnecessary complications and pain in patients from multiple needle insertion attempts,” said lead author Josh Leipheimer, a biomedical engineering doctoral student in the Yarmush lab in the biomedical engineering department in the School of Engineering at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
In the future, the device could be used in such procedures as IV catheterization, central venous access, dialysis and placing arterial lines. Next steps include refining the device to improve success rates in patients with difficult veins to access. Data from this study will be used to enhance artificial intelligence in the robot to improve its performance.
Rutgers co-authors include Max L. Balter and Alvin I. Chen, who both graduated with doctorates; Enrique J. Pantin at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School; Professor Kristen S. Labazzo; and principal investigator Martin L. Yarmush, the Paul and Mary Monroe Endowed Chair and Distinguished Professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering. A researcher at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital also contributed to the study.
Media Contact
Todd Bates
[email protected]
848-932-0550
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.