New tools and methods have been described by WEHI researchers to study an unusual protein modification and gain fresh insights into its roles in human health and disease.
Credit: WEHI
New tools and methods have been described by WEHI researchers to study an unusual protein modification and gain fresh insights into its roles in human health and disease.
The study – about how certain sugars modify proteins – was published today in Nature Chemical Biology. Led by WEHI researcher Associate Professor Ethan Goddard-Borger, this work lays a foundation for better understanding diseases like muscular dystrophy and cancer.
At a glance
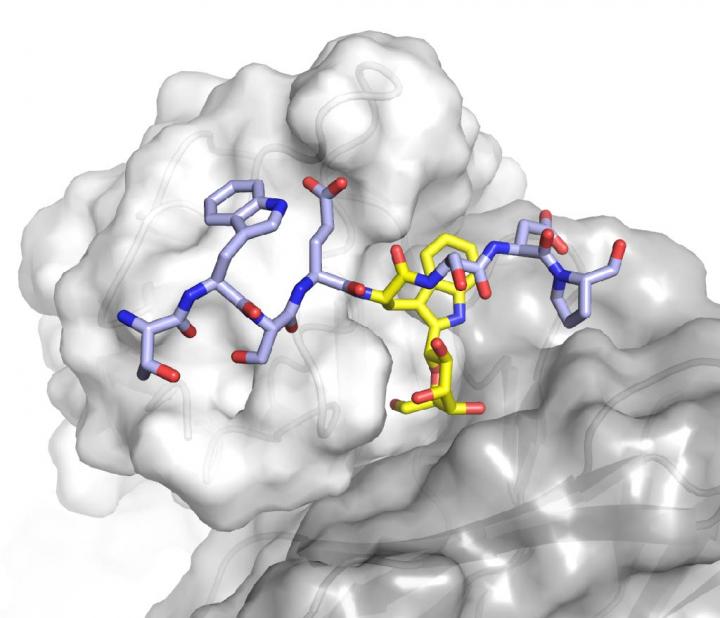
The ‘dark matter’ of biology
Glycosylation is the process by which proteins are modified with sugars. About 90 per cent of proteins on the surface of human cells – and half of the cells’ total proteins – are modified with sugars. These modifications can range from the addition of a single sugar, to long complex polymer chains. They’ve been described as the ‘dark matter’ of biology because their distribution, variability and biological functions are, for the most part, not well understood.
Associate Professor Goddard-Borger said his team, and the glycobiology field more generally, are making concerted efforts to build a better understanding of the roles that glycosylation plays in health and disease.
“There are a whole range of diseases that feature aberrant cellular glycosylation – a change in ‘normal’ glycosylation patterns,” he said.
“These changes may yield new therapeutic strategies, however a better understanding of what constitutes ‘normal’ glycosylation is required before we can further develop drugs targeting protein glycosylation.”
“It’s a scenario that is akin to the ‘dark matter’ of the universe: we know that all of this protein glycosylation exists in the body, but we don’t fully appreciate its composition and function.”
Shedding light on a sweet process
Glycosylation usually occurs on the nitrogen or oxygen atoms of a protein. However, it can also occur on carbon atoms through the process of ‘tryptophan C-mannosylation’. This latter protein modification is particularly poorly understood and so the WEHI team set out to develop tools and methods to shed light on this aspect of the biological ‘dark matter’.
“We’ve developed methods that will enable researchers to easily install this unusual modification on nearly any protein they want, allowing them to investigate its effect on protein stability and function,” Associate Professor Goddard-Borger said.
“In this work, we’ve shown that a common feature of tryptophan C-mannosylation is that it stabilises proteins. Diverse, unrelated proteins all appear to be more stable once modified. However, we’ve also demonstrated for the first time that some proteins’ functions can be modulated by tryptophan C-mannosylation’. There is clearly much left to learn about this process and now we have the means to perform these studies.”
Mapping the prevalence of tryptophan C-mannosylation
Associate Professor Goddard-Borger said the tools developed by his team also enable the abundance of this poorly understood protein modification to be determined in healthy and diseased tissues, which will fortify efforts by scientists around the world to map and understand protein glycosylation in health and disease.
“The methods we describe combine state-of-the-art mass spectrometry techniques with recombinant antibody tools generated at WEHI,” he said.
“We’ve reported some really unexpected results regarding the prevalence of this modification in healthy brain tissue. At present, we are extending this to map the modification across most tissues in the body to better understand the biology of this weird and wonderful form of protein glycosylation, as well as its role in cancer and muscular dystrophies.”
###
This research was funded by the Brian M Davis Charitable Foundation, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council and the Victorian Government.
Media Contact
Samantha Robin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




