Credit: Carlos Hernández-Monteagudo (IAC).
Scientists estimate that dark matter and dark energy together are some 95% of the gravitational material in the universe while the remaining 5% is baryonic matter, which is the “normal” matter composing stars, planets, and living beings. However for decades almost one half of this matter has not been found either. Now, using a new technique, a team in which the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) has participated, has shown that this “missing” baryonic matter is found filling the space between the galaxies as hot, low density gas. The same technique also gives a new tool that shows that the gravitational attraction experienced by galaxies is compatible with the theory of General Relativity. This research is published today in three articles in the journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (MNRAS).
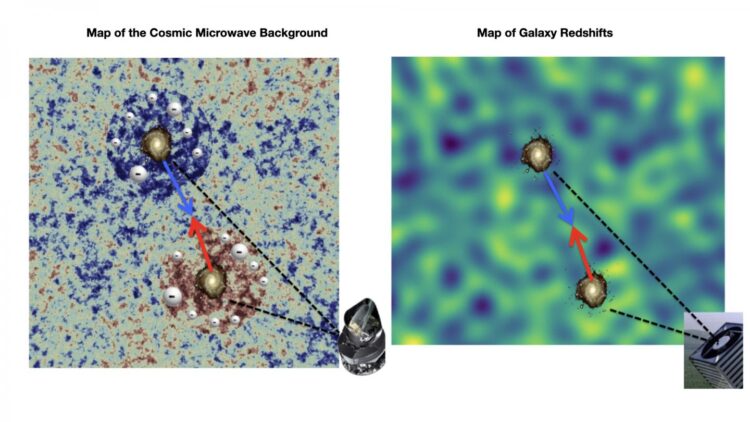
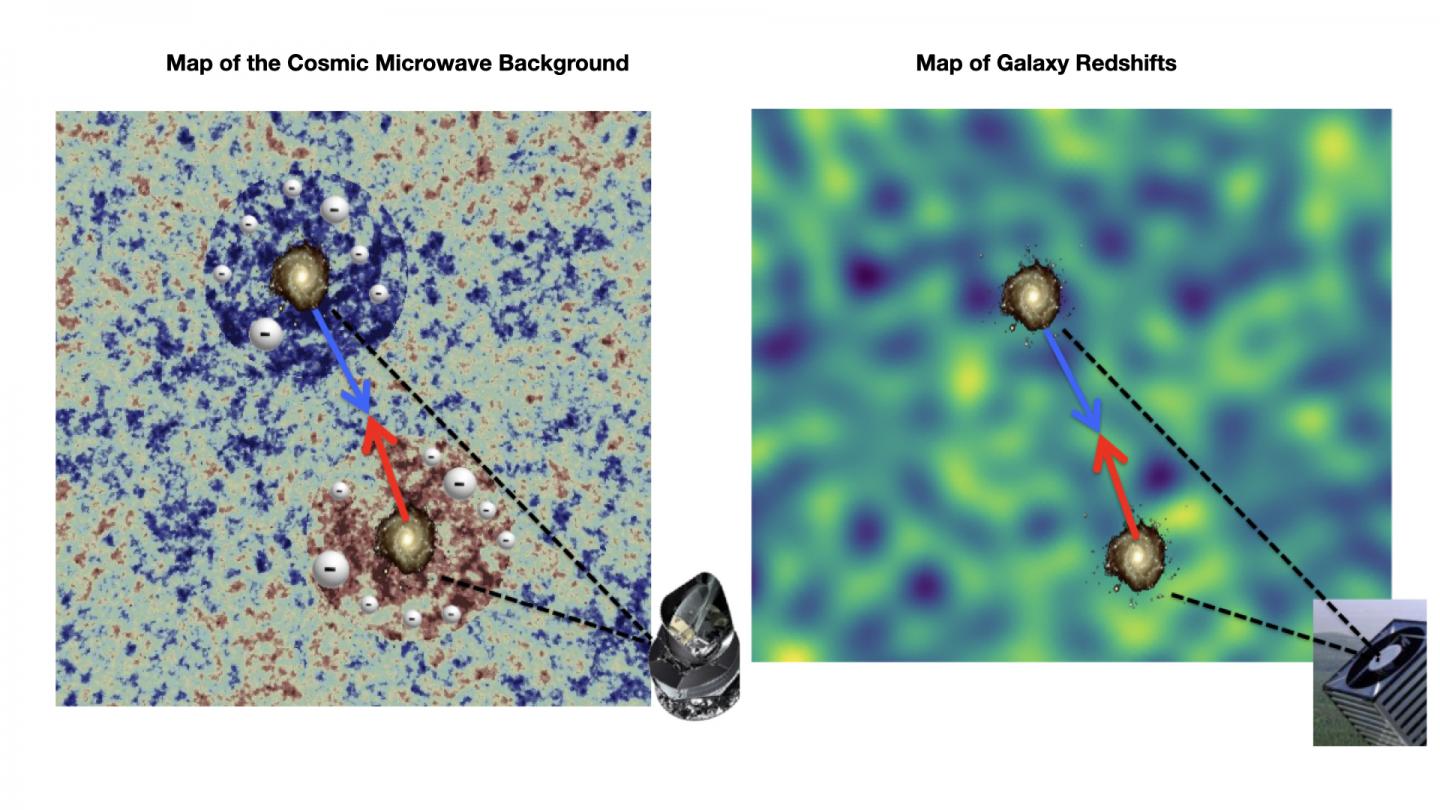
In designing this new technique they have analyzed the changes in the electromagnetic spectrum, its shift to the red, caused by the reddening of the light from the galaxies as they speed away from us. In the Universe, the sources which move away show a redder spectrum, and those which approach us show a bluer spectrum. This effect has given essential data for the development of modern cosmology. Almost a century ago, Edwin Hubble discovered that the redshifts of galaxies are bigger the further away from us they are, and this was the initial evidence which eventually led to the Big Bang model of the universe. Since then these redshifts have been used to find the distances to the galaxies and to build three dimensional maps of their distribution in the Universe.
In the work we are reporting here a new method has been developed, which studies the statistics of the redshifts of galaxies, without converting them to distances. In their first article, the team shows that these maps are sensitive to the gravitational attraction between galaxies on cosmological scales. In a second article, the same team compare the maps with observations of the cosmic microwave background,, and they permit, for the first time, a complete census of the baryonic matter during 90% of the life of the Universe.
“Most of this ‘ordinary’ matter is invisible to us because it is not sufficiently hot to emit energy. However, by using maps of the redshifts of the galaxies we find that all of this matter fills the space between them”, explains Jonás Chaves-Montero, a researcher at the Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) and first author of this article.
Finally, as found in a third article, the researchers have also used the redshift maps of the galaxies to study the nature of gravity. “In contrast to previous approaches, our new method is not based on any conversion of redshift to distance, and it is shown to be robust agains noise and data impurities. Thanks to that it allow us to conclude with high accuracy, that the observations are compatible with Einstein’s theory of gravity”, notes Carlos Hernández-Monteagudo, an IAC researcher who is the first author on this third article.
These studies have been performed by researchers Carlos Hernández-Monteagudo, Jonás Chaves-Montero, Raúl Angulo and Giovanni Aricò, who designed the research during their time at the Centre for Studies of Cosmic Physics of Aragón (CEFCA), even though now they are working at other Spanish research centres, such as the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, and the Donostia International Physics Center. In one of the articles there was participation also by J. D. Emberson, a Canadian researcher at the Argonne National Laboratory, Illinois, USA.
###
Articles:
Hernandez-Monteagudo, Carlos; Chaves-Montero, Jonas; Angulo, Raul E. “Angular Redshift Fluctuations: a New Cosmological Observable”. MNRAS: https:/
Chaves-Montero, Jonas; Hernandez-Monteagudo, Carlos; Angulo, Raul E.; Emberson, J. D. “Measuring the evolution of intergalactic gas from z=0 to 5 using the kinematic Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect”. MNRAS: https:/
Hernández-Monteagudo, Carlos; Chaves-Montero, Jonás; Angulo, Raúl E.; Ariccò, Giovanni. “Tomographic Constraints on Gravity from Angular Redshift Fluctuations in the Late Universe”, MNRAS: https:/
Media Contact
Prensa IAC
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/