Credit: Texas A&M Engineering
Baby diapers, contact lenses and gelatin dessert. While seemingly unrelated, these items have one thing in common — they’re made of highly absorbent substances called hydrogels that have versatile applications. Recently, a type of biodegradable hydrogel, dubbed microporous annealed particle (MAP) hydrogel, has gained much attention for its potential to deliver stem cells for body tissue repair. But it is currently unclear how these jelly-like materials affect the growth of their precious cellular cargo, thereby limiting its use in regenerative medicine.
In a new study published in the November issue of Acta Biomaterialia, researchers at Texas A&M University have shown that MAP hydrogels, programmed to biodegrade at an optimum pace, create a fertile environment for bone stem cells to thrive and proliferate vigorously. They found the space created by the withering of MAP hydrogels creates room for the stem cells to grow, spread and form intricate cellular networks.
“Our research now shows that stem cells flourish on degrading MAP hydrogels; they also remodel their local environment to better suit their needs,” said Dr. Daniel Alge, assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering. “These results have important implications for developing MAP hydrogel-based delivery systems, particularly for regenerative medicine where we want to deliver cells that will replace damaged tissues with new and healthy ones.”
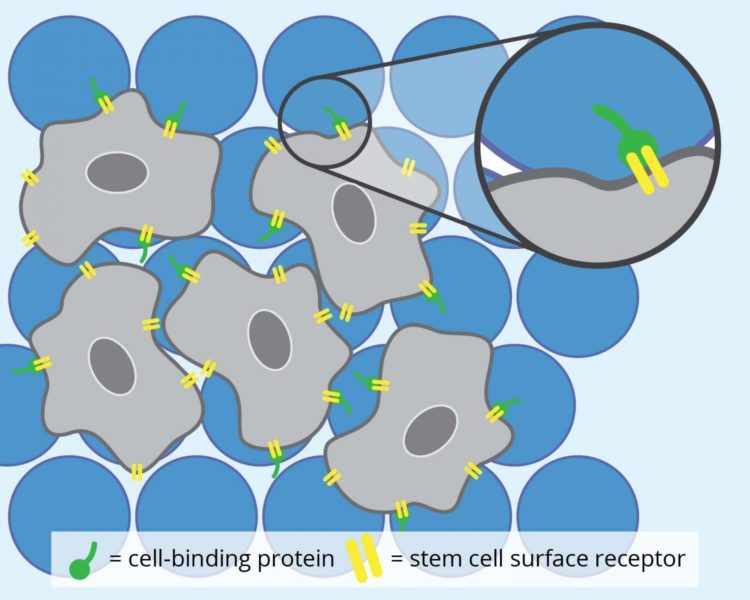
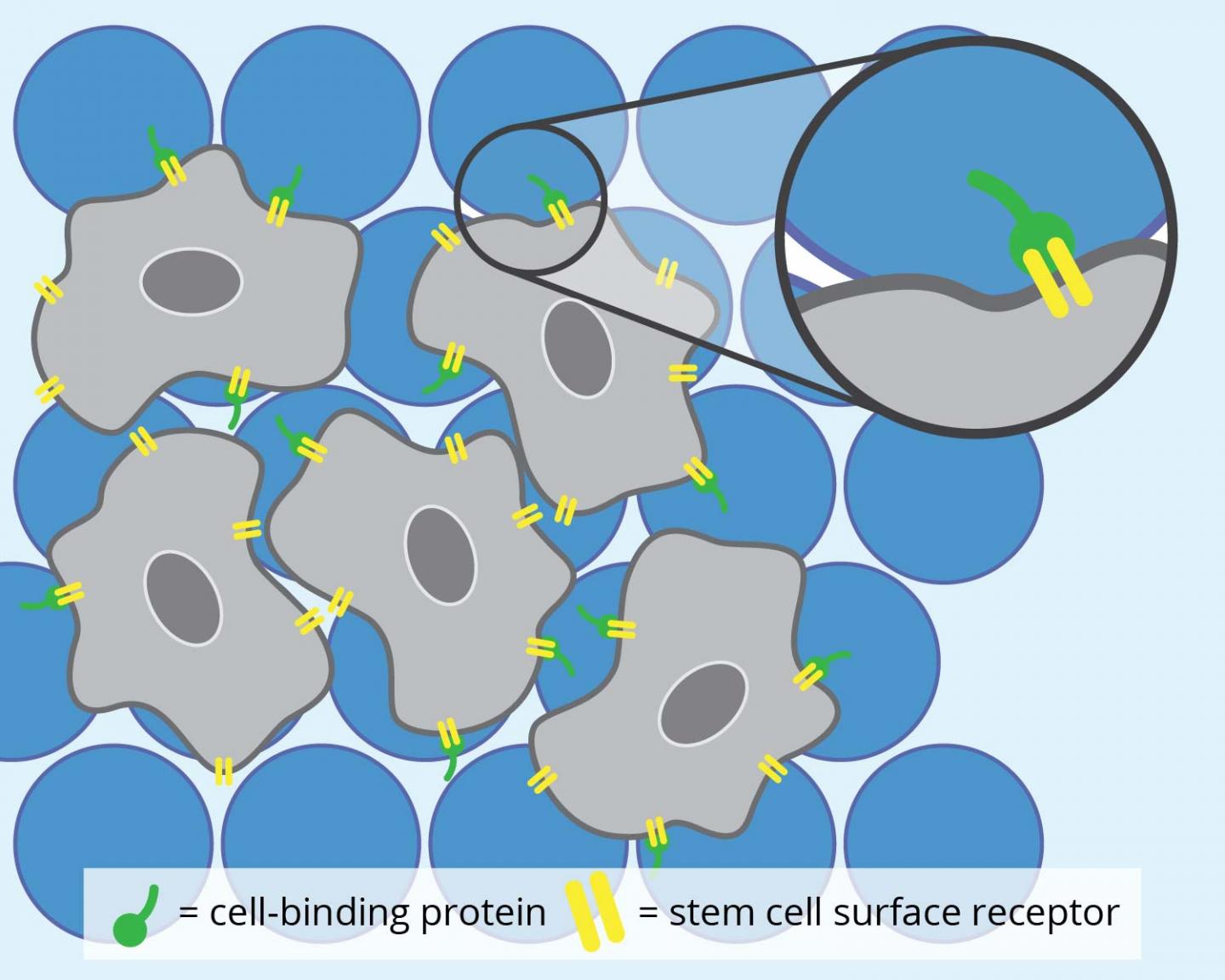
MAP hydrogels are a newer breed of injectable hydrogels. These soft materials are interconnected chains of extremely small beads made of polyethylene glycol, a synthetic polymer. Although the microbeads cannot themselves cling to cells, they can be engineered to present cell-binding proteins that can then attach to receptor molecules on the stem cells’ surface.
Once fastened onto the microbeads, the stem cells use the space between the spheres to grow and transform into specialized cells, like bone or skin cells. And so, when there is an injury, MAP hydrogels can be used to deliver these new cells to help tissues regenerate.
However, the health and behavior of stem cells within the MAP hydrogel environment has never been fully studied.
“MAP hydrogels have superior mechanical and biocompatible properties, so in principle, they are a great platform to grow and maintain stem cells,” said Alge. “But people in the field really don’t have a good understanding of how stem cells behave in these materials.”
To address this question, the researchers studied the growth, spread and function of bone stem cells in MAP hydrogels. Alge and his team used three samples of MAP hydrogels that differed only in the speed at which they degraded, that is, either slow, fast or not at all.
First, for the stem cells to attach onto the MAP hydrogels, the researchers decorated the MAP hydrogels with a type of cell-binding protein. They then tracked the stem cells as they grew using a high-resolution, fluorescent microscope. The researchers also repeated the same experiment using another cell-binding protein to investigate if cell-binding proteins also affected stem cell development within the hydrogels.
To their surprise, Alge’s team found that for both types of cell-binding proteins, the MAP hydrogels that degraded the fastest had the largest population of stem cells. Furthermore, the cells were changing the shape of the MAP hydrogel as they spread and claimed more territory.
“In the intact MAP hydrogel, we could still see the spherical microbeads and the material was quite undamaged,” said Alge. “By contrast, the cells were making ridges and grooves in the degrading MAP hydrogels, dynamically remodeling their environment.”
The researchers also found that as the stem cells grew, the quantity of bone proteins produced by the growing stem cells depended on which cell-binding protein was initially used in the MAP hydrogel.
Alge noted that the insight gained through their study will greatly inform further research and development in MAP hydrogels for stem-cell therapies.
“Although MAP hydrogel degradability profoundly affects the growth of the stem cells, we found that the interplay between the cell-binding proteins and the degradation is also important,” he said. “As we, as a field, make strides toward developing new MAP hydrogels for tissue engineering, we must look at the effects of both degradability and cell-binding proteins to best utilize these materials for regenerative medicine.”
###
Other contributors to the research include Dr. Shangjing Xin from the Department of Biomedical Engineering at Texas A&M and Dr. Carl A. Gregory from the Institute for Regenerative Medicine at the Texas A&M Health Science Center.
This research was supported by funds from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health.
Media Contact
Amy Halbert
[email protected]
979-458-4243
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.