Materials could boost battery performance in consumer electronics, electric vehicles, and more
Credit: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
TROY, N.Y. — Creating a lithium-ion battery that can charge in a matter of minutes but still operate at a high capacity is possible, according to research from Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute just published in Nature Communications. This development has the potential to improve battery performance for consumer electronics, solar grid storage, and electric vehicles.
A lithium-ion battery charges and discharges as lithium ions move between two electrodes, called an anode and a cathode. In a traditional lithium-ion battery, the anode is made of graphite, while the cathode is composed of lithium cobalt oxide.
These materials perform well together, which is why lithium-ion batteries have become increasingly popular, but researchers at Rensselaer believe the function can be enhanced further.
“The way to make batteries better is to improve the materials used for the electrodes,” said Nikhil Koratkar, professor of mechanical, aerospace, and nuclear engineering at Rensselaer, and corresponding author of the paper. “What we are trying to do is make lithium-ion technology even better in performance.”
Koratkar’s extensive research into nanotechnology and energy storage has placed him among the most highly cited researchers in the world. In this most recent work, Koratkar and his team improved performance by substituting cobalt oxide with vanadium disulfide (VS2).
“It gives you higher energy density, because it’s light. And it gives you faster charging capability, because it’s highly conductive. From those points of view, we were attracted to this material,” said Koratkar, who is also a professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
Excitement surrounding the potential of VS2 has been growing in recent years, but until now, Koratkar said, researchers had been challenged by its instability–a characteristic that would lead to short battery life. The Rensselaer researchers not only established why that instability was happening, but also developed a way to combat it.
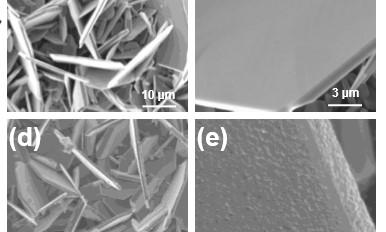
The team, which also included Vincent Meunier, head of the Department of Physics, Applied Physics, and Astronomy, and others, determined that lithium insertion caused an asymmetry in the spacing between vanadium atoms, known as Peierls distortion, which was responsible for the breakup of the VS2 flakes. They discovered that covering the flakes with a nanolayered coating of titanium disulfide (TiS2)–a material that does not Peierls distort–would stabilize the VS2 flakes and improve their performance within the battery.
“This was new. People hadn’t realized this was the underlying cause,” Koratkar said. “The TiS2 coating acts as a buffer layer. It holds the VS2 material together, providing mechanical support.”
Once that problem was solved, the team found that the VS2-TiS2 electrodes could operate at a high specific capacity, or store a lot of charge per unit mass. Koratkar said that vanadium and sulfur’s small size and weight allow them to deliver a high capacity and energy density. Their small size would also contribute to a compact battery.
When charging was done more quickly, Koratkar said, the capacity didn’t dip as significantly as it often does with other electrodes. The electrodes were able to maintain a reasonable capacity because, unlike cobalt oxide, the VS2-TiS2 material is electrically conductive.
Koratkar sees multiple applications for this discovery in improving car batteries, power for portable electronics, and solar energy storage where high capacity is important, but increased charging speed would also be attractive.
###
About Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute:
Founded in 1824, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute is America’s first technological research university. Rensselaer encompasses five schools, 32 research centers, more than 145 academic programs, and a dynamic community made up of more than 7,900 students and over 100,000 living alumni. Rensselaer faculty and alumni include more than 145 National Academy members, six members of the National Inventors Hall of Fame, six National Medal of Technology winners, five National Medal of Science winners, and a Nobel Prize winner in Physics. With nearly 200 years of experience advancing scientific and technological knowledge, Rensselaer remains focused on addressing global challenges with a spirit of ingenuity and collaboration. To learn more, please visit http://www.
Media Contact
Reeve Hamilton
[email protected]




