Astrogliosis, an inflammation that occurs in the brain tissue, is common to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases
Credit: Pablo Trindade
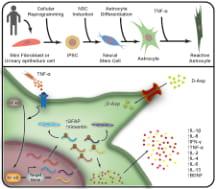
Astrocytes are neural cells with many important functions in the nervous system. The inflammation of these cells occurs in brain infections and neurodegenerative disorders, a process called astrogliosis. Aware of this fundamental process for the prevention of diseases and improvement of current treatments, a team led by researchers at the D’Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) and other five Brazilian Federal Universities published one of the first studies to categorically observe this inflammatory reaction in human astrocytes created in the laboratory.
The term astrogliosis may sound unfamiliar to the general public, but this inflammatory process is common to several diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, multiple sclerosis and congenital malformations caused by the Zika virus. Although astrogliosis is well studied in the neuroscience field, most of the knowledge came from animal models, an experimental strategy that contributes to scientific advancement, but it does not reproduce human brain complexity. “Animal testing has its indubitable relevance in science, but the reality is that it doesn’t fully reproduce some human aspects, especially when related to responses of the immune system. This is the case of human glial cells, including astrocytes, which are responsible for the metabolic maintenance of neurons and their nerve impulses”, says Pablo Trindade, the study’s first author.
To understand the inflammatory process of astrogliosis, the research coordinator and scientist at Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ) and IDOR, Stevens Rehen, adopted a cell culture procedure that is already his signature in several other studies on the human brain – among them, the development of brain organoids that helped to correlate Zika virus infection to the onset of microcephaly. The method used by Rehen’s team is the reprogramming of human cells found in the urine of voluntary donors, turning them into pluripotent stem cells. These stem cells are then stimulated to become healthy astrocytes or any other human cell necessary for the research at the time. In this case, from the creation of astrocytes, the scientists have put these cells to react with an inflammatory protein, known as TNF, obtaining a map of the human astrogliosis in the laboratory. The observed results indicate that the inflammation process already occurs within the first hour, and it gradually impairs astrocytes function over time.
In addition to morphological changes of these cells, which start to show smaller nuclei and stretched shapes, the inflammation also interfered with the primary function of astrocytes: the regulation of neurotransmitters, that are substances secreted by neurons responsible for information transmission across synapses. The study identified that human astrocytes under astrogliosis showed impairment in the glutamate uptake. Of note, glutamate is the most important stimulatory neurotransmitter involved in many brain functions including learning and memory.
The publication is a highlight in studies about astrogliosis, since the approach allowed scientists to analyze the phenomenon in a non-invasive way using human cells. The researchers point out that the evidence and methods from this study can serve as a basis for other investigations, including those aimed at discovering new treatments, which can improve the quality of life of people suffering from brain inflammation triggered by infections or neurodegenerative diseases.
###
Media Contact
Maria Eduarda Ledo de Abreu
[email protected]
55-021-992-213-040
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




