New study explores children’s perception of their own wellbeing using art
Credit: Anglia Ruskin University
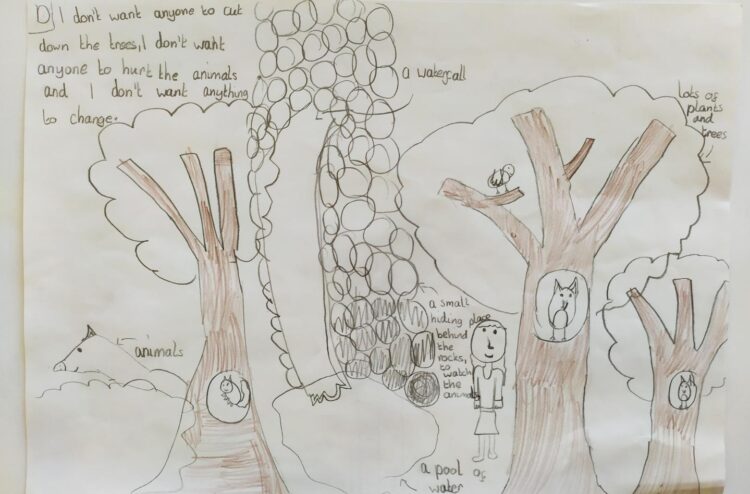
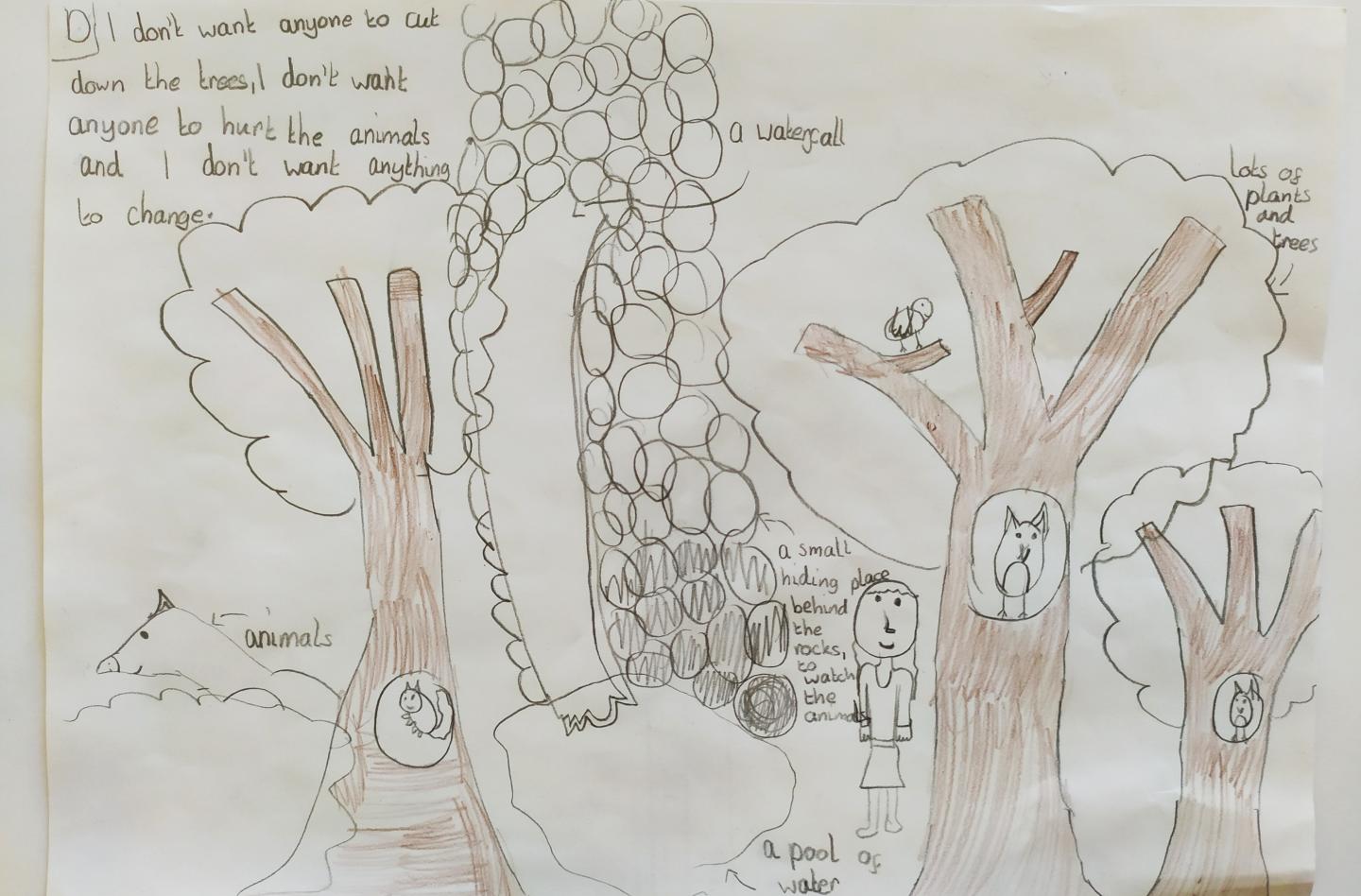
Young children in deprived areas see nature and outdoor spaces as being associated with “happy places”, according to a new study published in the journal Child Indicators Research.
Researchers Dr Nicola Walshe and Dr Zoe Moula from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) asked 91 children aged seven and eight from two primary schools in areas of relatively high deprivation in the East of England to draw their happy place, before engaging them in group discussions about how they perceive their own wellbeing.
More than half of the children created drawings that included aspects of nature and outdoor spaces, such as trees, grass, parks, gardens, lakes, rivers, outdoor playgrounds, rainbows or sunlight. Trees, in particular, were drawn by a third of the children.
However, the study found the elements of nature mainly existed in the background of the drawings. Other aspects of wellbeing, such as a sense of safety, positive relationships with family and friends, and the need for love and happiness, were more explicit in the pictures.
The fieldwork for the study took place a week before the UK’s first COVID-19 lockdown, in March 2020, and when asked which elements they would want to keep away from their happy place, 14 of the children specifically mentioned coronavirus.
Co-author Dr Walshe, Head of the School of Education and Social Care at ARU, said: “We wanted this study to explore children’s own perceptions of wellbeing, as most previous research has focused on adults. This is despite a consensus that children’s perspectives differ significantly from adults.
“We identified indicators of wellbeing that were made explicit in children’s drawings, such as the need for safety, happiness and positive relationships. Interestingly, the representations of nature mainly exist in the background and were rarely the main focus of the drawings..
“The drawings depicted nature and outdoor spaces as being interconnected with all aspects of wellbeing. For example, being able to play outside boosts physical wellbeing, while being able to stay calm and appreciate the beauty of nature can be linked to emotional or mental health.
“Previous research has shown that wealth affects access to nature, with children living in deprived areas significantly less likely to have access to green spaces and outdoor places to play. Our research suggests that nature and open spaces underpin these children’s consideration of wellbeing.
“As such, making nature explicit, and restoring the interconnectedness between the arts and nature should be a key priority for research to help improve children’s wellbeing.”
###
For further information about this project, please visit eco-capabilities.co.uk
Media Contact
Jamie Forsyth
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.