Credit: Credits: NASA/MAVEN/Goddard Space Flight Center/CU/LASP
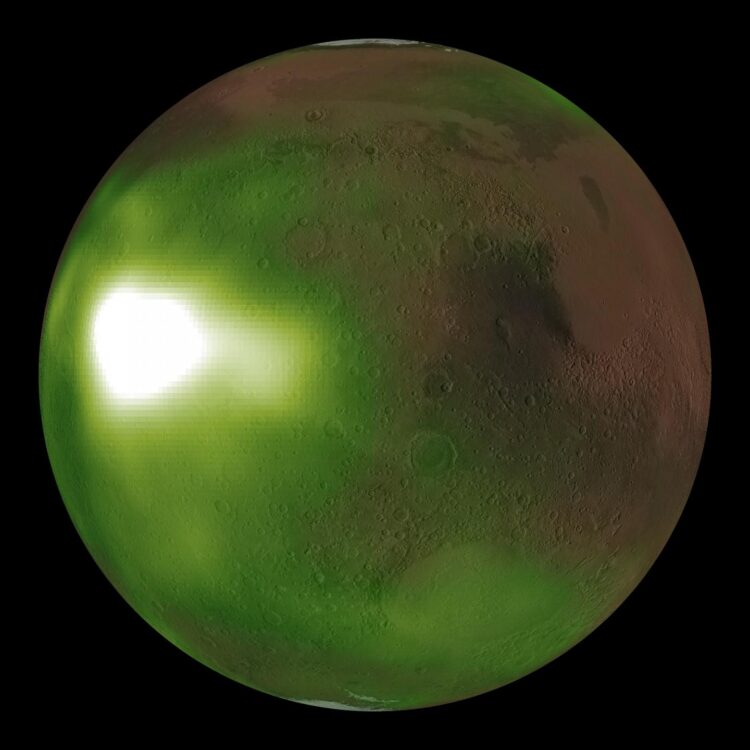
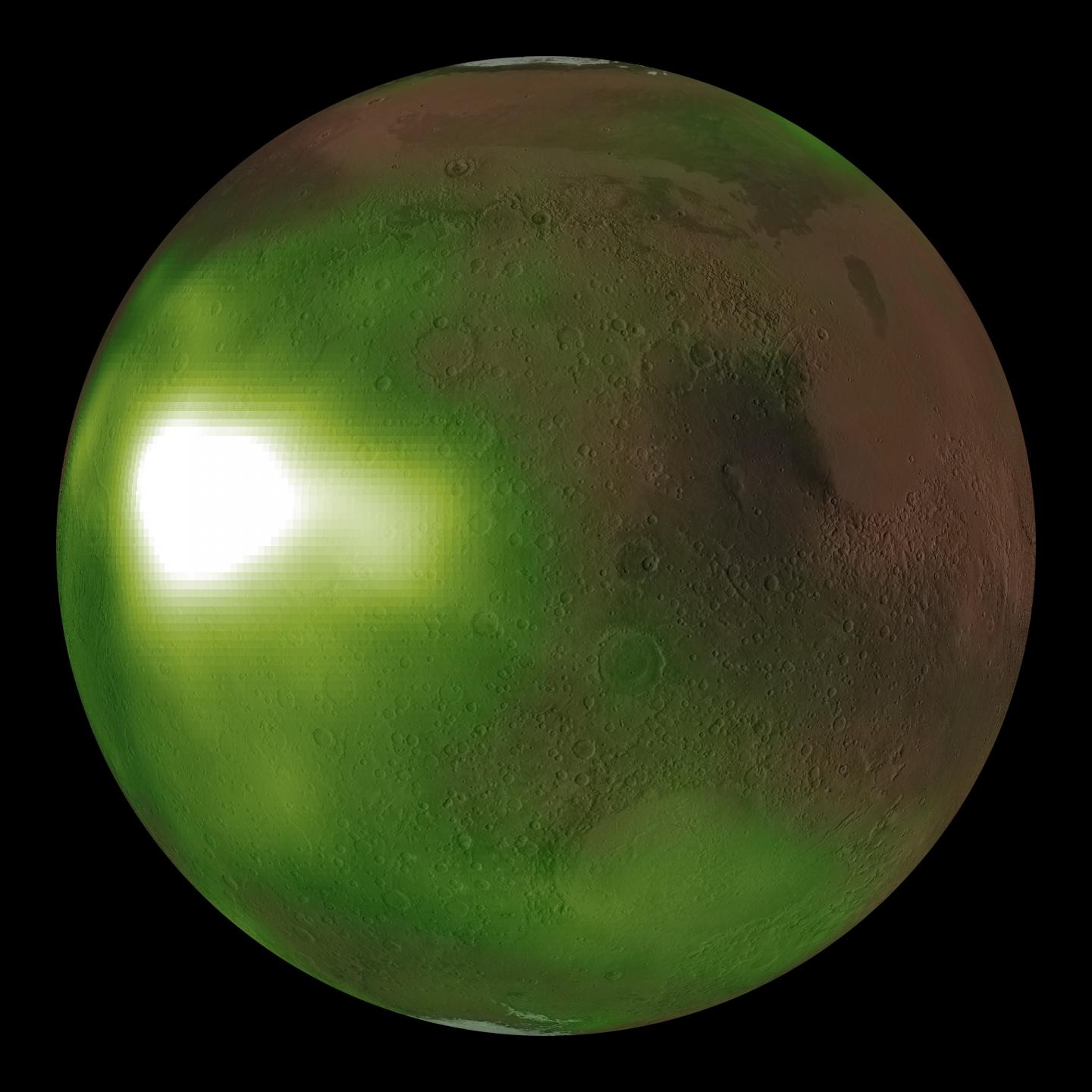
Vast areas of the Martian night sky pulse in ultraviolet light, according to images from NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft. The results are being used to illuminate complex circulation patterns in the Martian atmosphere.
The MAVEN team was surprised to find that the atmosphere pulsed exactly three times per night, and only during Mars’ spring and fall. The new data also revealed unexpected waves and spirals over the winter poles, while also confirming the Mars Express spacecraft results that this nightglow was brightest over the winter polar regions.
“MAVEN’s images offer our first global insights into atmospheric motions in Mars’ middle atmosphere, a critical region where air currents carry gases between the lowest and highest layers,” said Nick Schneider of the University of Colorado’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics (LASP), Boulder, Colorado. The brightenings occur where vertical winds carry gases down to regions of higher density, speeding up the chemical reactions that create nitric oxide and power the ultraviolet glow. Schneider is instrument lead for the MAVEN Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph (IUVS) instrument that made these observations, and lead author of a paper on this research appearing August 6 in the Journal of Geophysical Research, Space Physics. Ultraviolet light is invisible to the human eye but detectable by specialized instruments.
“The ultraviolet glow comes mostly from an altitude of about 70 kilometers (approximately 40 miles), with the brightest spot about a thousand kilometers (approximately 600 miles) across, and is as bright in the ultraviolet as Earth’s northern lights,” said Zac Milby, also of LASP. “Unfortunately, the composition of Mars’ atmosphere means that these bright spots emit no light at visible wavelengths that would allow them to be seen by future Mars astronauts. Too bad: the bright patches would intensify overhead every night after sunset, and drift across the sky at 300 kilometers per hour (about 180 miles per hour).”
The pulsations reveal the importance of planet-encircling waves in the Mars atmosphere. The number of waves and their speed indicates that Mars’ middle atmosphere is influenced by the daily pattern of solar heating and disturbances from the topography of Mars’ huge volcanic mountains. These pulsating spots are the clearest evidence that the middle atmosphere waves match those known to dominate the layers above and below.
“MAVEN’s main discoveries of atmosphere loss and climate change show the importance of these vast circulation patterns that transport atmospheric gases around the globe and from the surface to the edge of space.” said Sonal Jain, also of LASP.
Next, the team plans to look at nightglow “sideways”, instead of down from above, using data taken by IUVS looking just above the edge of the planet. This new perspective will be used to understand the vertical winds and seasonal changes even more accurately.
The Martian nightglow was first observed by the SPICAM instrument on the European Space Agency’s Mars Express spacecraft. However, IUVS is a next-generation instrument better able to repeatedly map out the nightside glow, finding patterns and periodic behaviors. Many planets including Earth have nightglow, but MAVEN is the first mission to collect so many images of another planet’s nightglow.
###
The research was funded by the MAVEN mission. MAVEN’s principal investigator is based at the University of Colorado’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, Boulder, and NASA Goddard manages the MAVEN project. NASA is exploring our Solar System and beyond, uncovering worlds, stars, and cosmic mysteries near and far with our powerful fleet of space and ground-based missions.
For video, visit:
https:/
Media Contact
Bill Steigerwald
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.