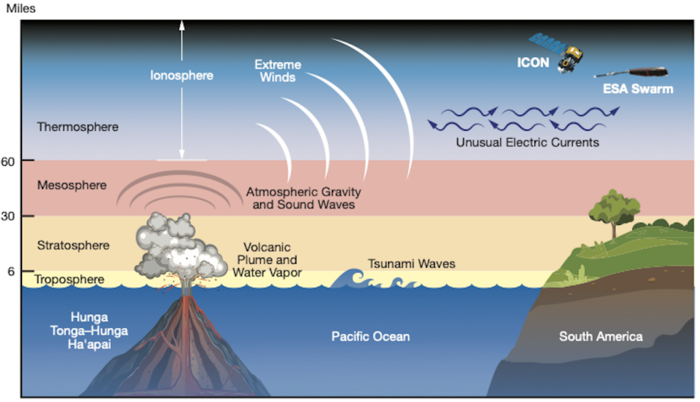
When the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha‘apai volcano erupted on Jan. 15, 2022, it sent atmospheric shock waves, sonic booms, and tsunami waves around the world. Now, scientists are finding the volcano’s effects also reached space.
Credit: Credits: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Mary Pat Hrybyk-Keith
When the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha‘apai volcano erupted on Jan. 15, 2022, it sent atmospheric shock waves, sonic booms, and tsunami waves around the world. Now, scientists are finding the volcano’s effects also reached space.
Analyzing data from NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer, or ICON, mission and ESA’s (the European Space Agency) Swarm satellites, scientists found that in the hours after the eruption, hurricane-speed winds and unusual electric currents formed in the ionosphere – Earth’s electrified upper atmospheric layer at the edge of space.
“The volcano created one of the largest disturbances in space we’ve seen in the modern era,” said Brian Harding, a physicist at University of California, Berkeley, and lead author on a new paper discussing the findings. “It is allowing us to test the poorly understood connection between the lower atmosphere and space.”
ICON launched in 2019 to identify how Earth’s weather interacts with weather from space – a relatively new idea supplanting previous assumptions that only forces from the Sun and space could create weather at the edge of the ionosphere. In January 2022, as the spacecraft passed over South America, it observed one such earthly disturbance in the ionosphere triggered by the South Pacific volcano.
“These results are an exciting look at how events on Earth can affect weather in space, in addition to space weather affecting Earth,” said Jim Spann, space weather lead for NASA’s Heliophysics Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C. “Understanding space weather holistically will ultimately help us mitigate its effects on society.”
When the volcano erupted, it pushed a giant plume of gases, water vapor, and dust into the sky. The explosion also created large pressure disturbances in the atmosphere, leading to strong winds. As the winds expanded upwards into thinner atmospheric layers, they began moving faster. Upon reaching the ionosphere and the edge of space, ICON clocked the windspeeds at up to 450 mph – making them the strongest winds below 120 miles altitude measured by the mission since its launch.
In the ionosphere, the extreme winds also affected electric currents. Particles in the ionosphere regularly form an east-flowing electric current – called the equatorial electrojet – powered by winds in the lower atmosphere. After the eruption, the equatorial electrojet surged to five times its normal peak power and dramatically flipped direction, flowing westward for a short period.
“It’s very surprising to see the electrojet be greatly reversed by something that happened on Earth’s surface,” said Joanne Wu, a physicist at University of California, Berkeley, and co-author on the new study. “This is something we’ve only previously seen with strong geomagnetic storms, which are a form of weather in space caused by particles and radiation from the Sun.”
The new research, published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, is adding to scientists’ understanding of how the ionosphere is affected by events on the ground as well as from space. A strong equatorial electrojet is associated with redistribution of material in the ionosphere, which can disrupt GPS and radio signals that are transmitted through the region.
Understanding how this complex area of our atmosphere reacts in the face of strong forces from below and above is a key part of NASA research. NASA’s upcoming Geospace Dynamics Constellation, or GDC, mission will use a fleet of small satellites, much like weather sensors on the ground, to track the electrical currents and atmospheric winds coursing through the area. By better understanding what affects electrical currents in the ionosphere, scientists can be more prepared to predict severe problems caused by such disturbances.
Journal
Geophysical Research Letters
DOI
10.1029/2022GL098577
Article Title
Impacts of the January 2022 Tonga Volcanic Eruption on the Ionospheric Dynamo: ICON-MIGHTI and Swarm Observations of Extreme Neutral Winds and Currents
Article Publication Date
10-May-2022




