An international researcher team of Louisiana Tech University, Gubkin University and Kazan Federal University reported the fabrication of nanoscale insecticidal hair coating for prolonged anti-lice protection. The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation.
Credit: Kazan Federal University, Louisiana Tech University, Gubkin University
An international researcher team of Louisiana Tech University, Gubkin University and Kazan Federal University reported the fabrication of nanoscale insecticidal hair coating for prolonged anti-lice protection. The study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation.
“Treating agricultural and domestic animals infected with ectoparasites (such as lice, fleas, chewing lice, etc.) is among the primary challenges of veterinary medicine and agriculture. In case of mass infestation, regular measures, such as isolation of infected animals or repeated reapplication of insecticides, are not always effective. These methods are time-limited and provide a short-term therapeutic effect,” explains co-author Rawil Fakhrullin, Head of Kazan University’s Bionanotechnology Lab. “Using an inorganic nanoscale carrier as a component of a therapeutic formulation for topical application of insecticides might be the optimal way to address this challenge.”
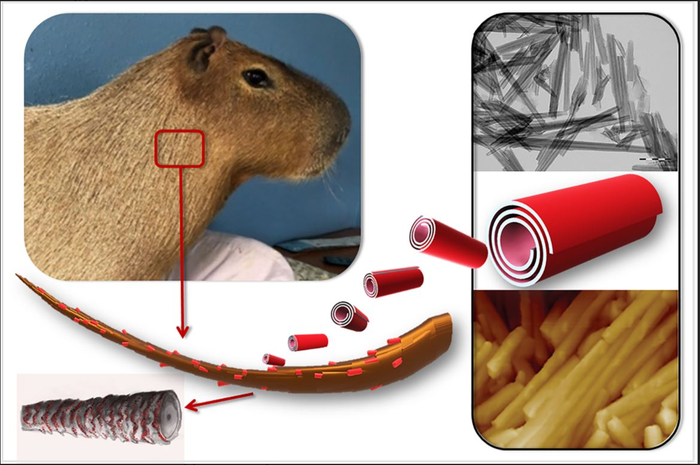
Halloysite, a natural nanosized tubular mineral, was used as a drug carrier capable of forming a durable and uniform coating on the surface of animal hair.
“Loading an insecticidal drug, permethrin, into halloysite nanotubes reduces the release rate, leading to fewer re-treatments and fewer side effects,” continues Dr. Fakhrullin.
The paper shows that after goat hair samples were treated with halloysite-based nanocontainers, a stable 2-3 micron waterproof coating was formed on the surface of the hair, suitable for long-term antiparasitic protection.
“Long-term insecticidal activity is the result of the gradual release of the drug from the nanotubes. A formulation based on halloysite retains its protective antiparasitic properties after washing the animal’s hair with water. This stable and water-resistant composite coating provides a drug dose effective for long-term protection of animals,” says the interviewee.
The authors also examined the hair structure of the capybara, world’s largest rodent native to South America. They found that the wax-like layer present on the hair surface of this semi-aquatic animal facilitates the formation of a denser and more durable coating of halloysite than in terrestrial animals (guinea pigs and goats). The wax helps retaining nanoclay particles on the surface of the animal’s hair.
Dr. Fakhrullin comments about the test subjects, “We studied the suppressive effects of nanocontainers on goat ectoparasites Damalinia caprae from the Trichodectidae family. At the same time, our technique can be effective towards other types of lice, since these parasites live in hair and maintain close contact with hair cuticles, regardless of the animal’s dietary preferences. We believe that this approach can be used for long-term and sustainable antiparasitic protection of farm animals, especially if other insecticidal preparations are encapsulated in addition to permethrin. In addition, similar drugs can be used for the prevention or treatment of head lice in humans.”
Furthermore, the described material can also be helpful in treating fur in zoological collections.
Journal
Pharmaceutics
DOI
10.3390/pharmaceutics13091477
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Clay Nanotube Immobilization on Animal Hair for Sustained Anti-Lice Protection
Article Publication Date
15-Sep-2021
COI Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.




