New study: Nano-scientists develop a molecular tool to change the structure of a metal surface
Credit: Saeed Amirjalayer
The surface of metals plays a key role in many technologically relevant areas, such as catalysis, sensor technology and battery research. For example, the large-scale production of many chemical compounds takes place on metal surfaces, whose atomic structure determines if and how molecules react with one another. At the same time, the surface structure of a metal influences its electronic properties. This is particularly important for the efficiency of electronic components in batteries. Researchers worldwide are therefore working intensively on developing new kinds of methods to tailor the structure of metal surfaces at the atomic level.
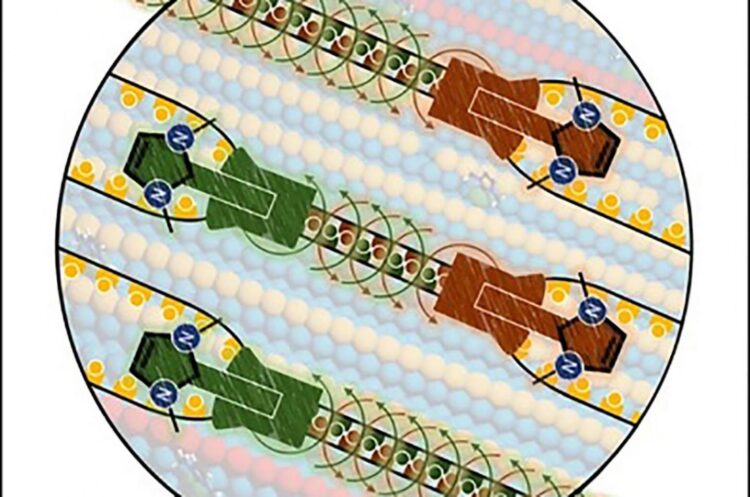
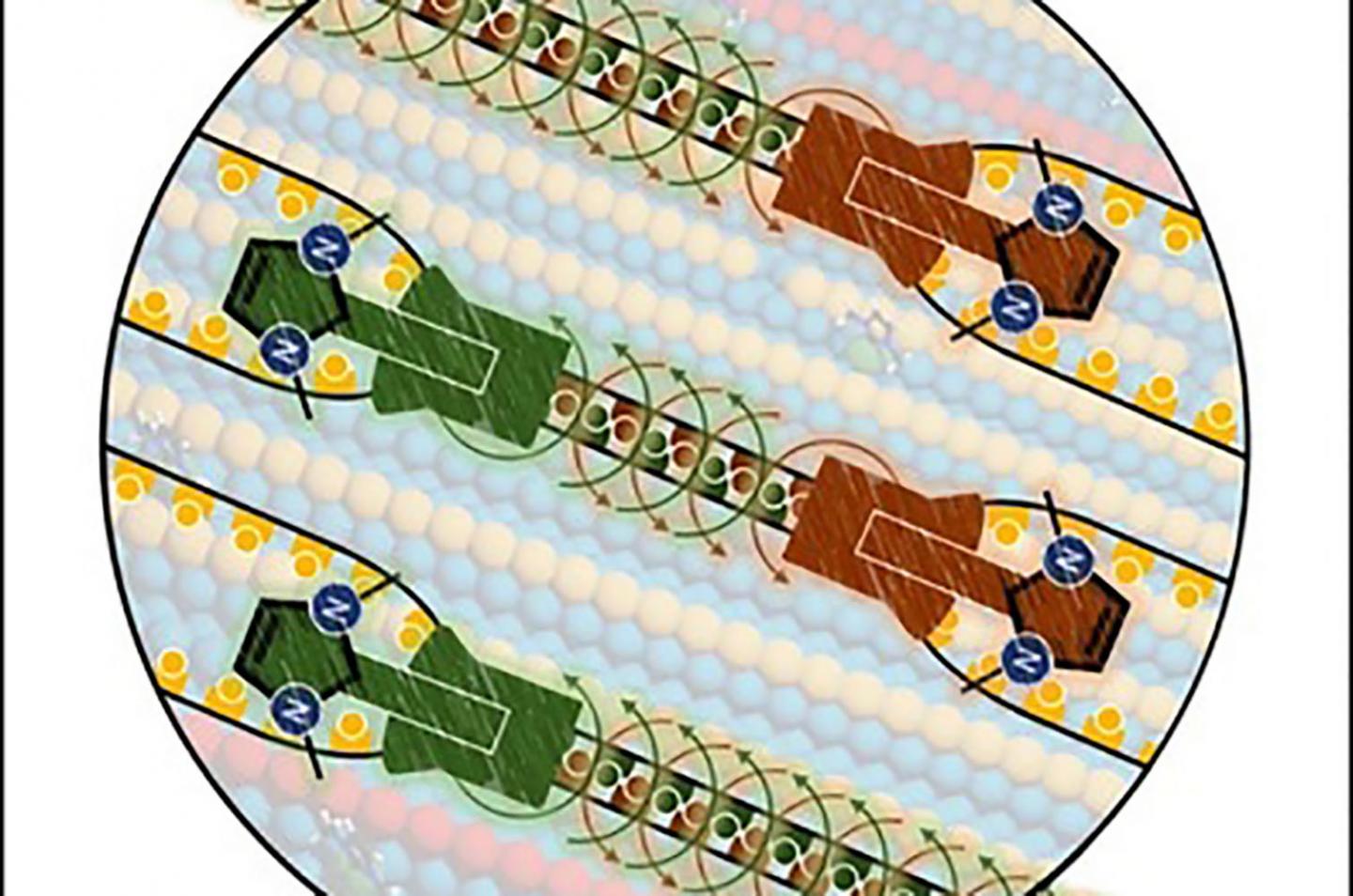
A team of researchers at the University of Münster, consisting of physicists and chemists and led by Dr. Saeed Amirjalayer, has now developed a molecular tool which makes it possible, at the atomic level, to change the structure of a metal surface. Using computer simulations, it was possible to predict that the restructuring of the surface by individual molecules – so-called N-heterocyclic carbenes – takes place similar to a zipper. During the process, at least two carbene molecules cooperate to rearrange the structure of the surface atom by atom. The researchers could experimentally confirm, as part of the study, this “zipper-type” mechanism in which the carbene molecules work together on the gold surface to join two rows of gold atoms into one row. The results of the work have been published in the journal “Angewandte Chemie International Edition”.
In earlier studies the researchers from Münster had shown the high stability and mobility of carbene molecules at the gold surface. However, no specific change of the surface structure induced by the molecules could previously be demonstrated. In their latest study, the researchers proved for the first time that the structure of a gold surface is modified very precisely as a result of cooperation between the carbene molecules. “The carbene molecules behave like a molecular swarm – in other words, they work together as a group to change the long-range structure of the surface,” Saeed Amirjalayer explains. “Based on the ‘zipper’ principle, the surface atoms are systematically rearranged, and, after this process, the molecules can be removed from the surface.”
The new method makes it possible to develop new materials with specific chemical and physical properties – entirely without macroscopic tools. “In industrial applications often macroscopic tools, such presses or rollers, are used,” Amirjalayer continues. “In biology, these tasks are undertaken by certain molecules. Our work shows a promising class of synthesized molecules which uses a similar approach to modify the surface.” The team of researchers hopes that their method will be used in future to develop for examples new types of electrode or to optimize chemical reactions on surfaces.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Saeed Amirjalayer
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.