Credit: Dr. Yuichiro Arima
Ketone bodies are generally an alternative energy source during starvation, but in newborns, ketogenesis is active regardless of nutritional status. In a recent study from Kumamoto University (Japan), researchers analyzed the effects of ketogenesis in mice and found that it has a protective effect on cells by maintaining the function of mitochondria. They expect that this effect can be used in future therapies for protecting mitochondria and organs.
Ketones, along with glucose and fatty acids, are metabolites used as energy sources. In particular, ketones are known to be an alternative energy source during periods of fasting or starvation. However, ketogenesis is known to be active in the neonatal period regardless of the number of calories consumed during nursing, and role it plays in newborns is not well understood.
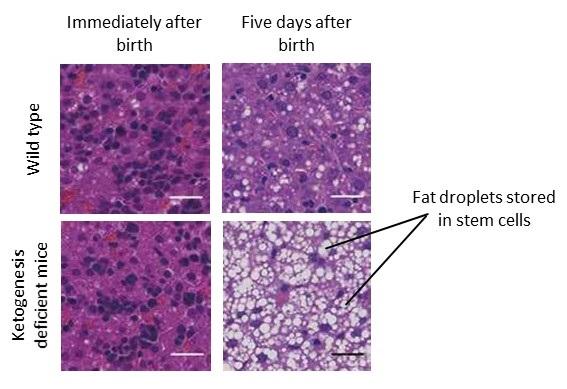
To search for answers, researchers generated ketogenesis-deficient mice that lacked the gene for HMG-CoA Synthase 2 (HMGCS2), an important enzyme ketogenesis. Their analysis showed that, in the absence of ketone bodies, the mice developed a severely fatty liver during the neonatal period.
Focusing on the mitochondria, they showed that enzymatic reactions in the mitochondria, mainly the Krebs cycle, were impaired. Nutrients are converted to acetyl CoA during the Krebs cycle, which is then converted to citric acid and seven other acids to produce energy. In the search for the cause of the dysfunction, researchers confirmed that the accumulation of the substrate acetyl CoA (due to insufficient ketogenesis) impairs the functions of proteins in the mitochondria by adding excessive acetylation.
“During a rapid increase in fatty acid intake with postnatal nursing, active ketogenesis under normal conditions has a protective effect by preventing excessive acetylation of mitochondrial proteins and maintaining mitochondrial function,” said study leader Dr. Yuichiro Arima. “We believe that this result will be used in therapeutic applications for mitochondrial and organ protection in the future.”
###
This research was posted online in Nature Metabolism on 18 February 2021.
Source:
Arima, Y., Nakagawa, Y., Takeo, T., Ishida, T., Yamada, T., Hino, S., … Tsujita, K. (2021). Murine neonatal ketogenesis preserves mitochondrial energetics by preventing protein hyperacetylation. Nature Metabolism. doi:10.1038/s42255-021-00342-6
Media Contact
J. Sanderson & N. Fukuda
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




