Towards application of materials informatics to development of thermal functional materials
Credit: The University of Tokyo
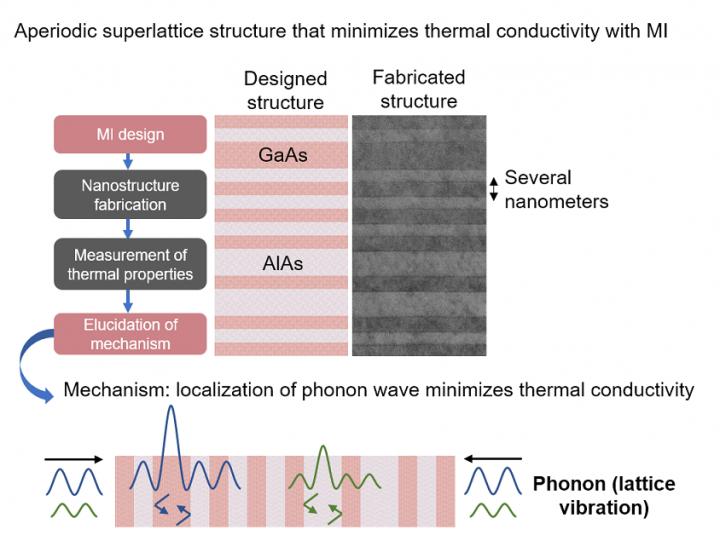
Professor Junichiro Shiomi et al. from The University of Tokyo aimed to reduce the thermal conductivity of semiconductor materials by reducing the internal nanostructure, and successfully minimized thermal conductivity by designing, fabricating, and evaluating the optimal nanostructure-multilayer materials through materials informatics (MI), which combines machine learning and molecular simulation. In 2017, this research group developed a method to design an optimal structure that minimizes or maximizes thermal conductivity via MI based on computational science. However, it has not been experimentally demonstrated, and preparation of nano-scale structures and realization of an optimal structure based on property measurements were desired.
Thus, the research group utilized a film deposition method able to regulate, at a molecular level, a superlattice structure wherein two materials were alternately layered at several nm thick, and a measurement method that could assess thermal conductivity of a film at nano-scale, and realized the optimal aperiodic superlattice structure that minimizes thermal conductivity. With the optimal structure, wave interference of the lattice vibration (phonon) that conducts heat was maximized, and thermal conductivity was strongly regulated.
In the present study, using the semiconductor lattice structure as the model, the research group verified the utility of the MI method in design, fabrication, assessment, and mechanism elucidation toward regulation of thermal conductivity. In the future, application of the MI method to various material systems is anticipated. It was also shown that optimization of the aperiodic structure can regulate thermal conductivity by fully controlling the wave property of a phonon at near room temperature. This is expected to contribute to developments in phonon engineering for instance in thermoelectric conversion devices, optical sensors, and gas sensors, where low thermal conductivity is needed while maintaining electric conductivity and mechanical properties.
###
The research was conducted as part of the JST Strategic Basic Research Programs (CREST): the research theme of “Development of multifunctional and purpose thermoelectric device by mechano-thermal functionalization” under the research area of “Scientific Innovation for Energy Harvesting Technology.”
Media Contact
Junichiro Shiomi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




