Prostate cancer stands as a prevalent threat to men’s health, ranking second in cancer-related deaths in the United States. Each year, approximately 250,000 men in the U.S. receive a prostate cancer diagnosis. While most cases have low morbidity and mortality rates, a subset of cases demands aggressive treatment. Urologists assess the need for such treatment primarily through the Gleason score, which evaluates prostate gland appearance on histology slides. However, there’s considerable variability in interpretation, leading to both undertreatment and overtreatment.
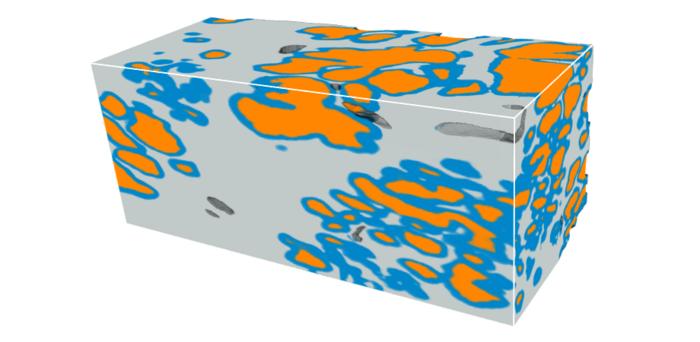
Credit: Rui Wang, University of Washington.
Prostate cancer stands as a prevalent threat to men’s health, ranking second in cancer-related deaths in the United States. Each year, approximately 250,000 men in the U.S. receive a prostate cancer diagnosis. While most cases have low morbidity and mortality rates, a subset of cases demands aggressive treatment. Urologists assess the need for such treatment primarily through the Gleason score, which evaluates prostate gland appearance on histology slides. However, there’s considerable variability in interpretation, leading to both undertreatment and overtreatment.
The current method, based on histology slides, has limitations. Only a small fraction of the biopsy is viewed in 2D, risking missed crucial details, and interpretations of complex 3D glandular structures can be ambiguous when viewed on 2D tissue sections. Moreover, conventional histology destroys tissue, limiting downstream analyses. To address these shortcomings, researchers have developed nondestructive 3D pathology methods, offering complete imaging of biopsy specimens while preserving tissue integrity.
Recent advancements include techniques for obtaining 3D pathology datasets, enabling improved risk assessment for prostate cancer. Research published in Journal of Biomedical Optics (JBO) harnesses the full power of 3D pathology by developing a deep-learning model to improve the 3D segmentation of glandular tissue structures that are critical for prostate cancer risk assessment.
The research team, led by Professor Jonathan T. C. Liu from the University of Washington in Seattle, trained a deep-learning model, nnU-Net, directly on 3D prostate gland segmentation data obtained from previous complex pipelines. Their model efficiently generates accurate 3D semantic segmentation of the glands within their 3D datasets of prostate biopsies, which were acquired with open-top light-sheet (OTLS) microscopes developed within their group. The 3D gland segmentations provide valuable insights into the tissue composition, which is crucial for prognostic analyses.
Liu remarks, “Our results indicate nnU-Net’s remarkable accuracy for 3D segmentation of prostate glands even with limited training data, offering a simpler and faster alternative to our previous 3D gland-segmentation methods. Notably, it maintains good performance with lower-resolution inputs, potentially reducing resource requirements.”
The new deep-learning-based 3D segmentation model represents a significant step forward in computational pathology for prostate cancer. By facilitating accurate characterization of glandular structures, it holds promise for guiding critical treatment decisions to ultimately improve patient outcomes. This advancement underscores the potential of computational approaches in enhancing medical diagnostics. Moving forward, it holds promise for personalized medicine, paving the way for more effective and targeted interventions.
Transcending the limitations of conventional histology, computational 3D pathology offers the ability to unlock valuable insights into disease progression and to tailor interventions to individual patient needs. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of medical innovation, the quest to conquer prostate cancer enters a new era of precision and possibility.
For details on the recent advance, see the Gold Open Access article by Rui Wang et al., “Direct three-dimensional segmentation of prostate glands with nnU-Net,” J. Biomed. Opt. 29(3) 036001 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.JBO.29.3.036001.
Journal
Journal of Biomedical Optics
DOI
10.1117/1.JBO.29.3.036001
Article Title
Direct three-dimensional segmentation of prostate glands with nnU-Net
Article Publication Date
1-Mar-2024




