A new, improved diagnostic classification technique enables stratification of pediatric patients with irritable bowel syndrome with greater precision so they can receive optimal treatment, reports The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics
Credit: Journal of Molecular Diagnostics
Philadelphia, April 17, 2019 – To improve the treatment of children with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), investigators have developed a sophisticated way to analyze the microbial and metabolic contents of the gut. A report in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, published by Elsevier, describes how a new battery of tests enables researchers to distinguish patients with IBS from healthy children and identifies correlations between certain microbes and metabolites with abdominal pain. With this information, doctors envision tailoring nutritional and targeted therapies that address a child’s specific gastrointestinal problems.
“This research highlights the importance of the microbiome-gut-brain axis and our understanding of chronic abdominal pain. Development of new disease classifiers based on microbiome data enables precision diagnostics to be developed for IBS and similar disorders. Although other studies have found differences in the gut microbiomes of patients with IBS, this study is the first to combine deep microbiome analysis with development of new diagnostic strategies,” explained James Versalovic, MD, PhD, of the Department of Pathology & Immunology at Baylor College of Medicine and the Department of Pathology at Texas Children’s Hospital, Houston, TX, USA. The term microbiome refers to the genetic material of all the microbes–bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and viruses–that live on and inside the human body.
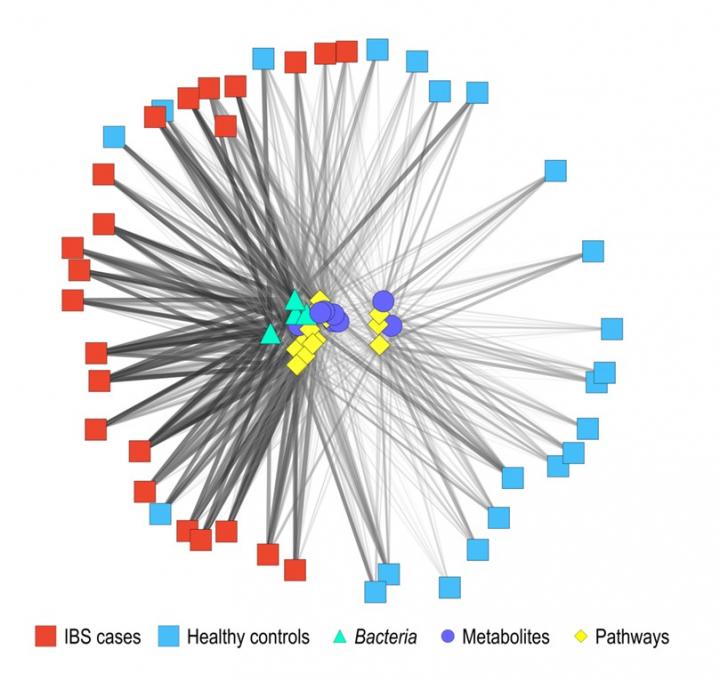
Samples for this study were obtained from 23 preadolescent children with IBS (age 7 to 12 years) and 22 healthy controls. Participants were asked to maintain daily pain and stool diaries for two weeks and to provide stool (fecal) samples.
Investigators found that there are differences in bacterial composition, bacterial genes, and fecal metabolites in children with IBS compared to healthy controls. In addition to identifying correlations of these factors with abdominal pain, they generated a highly accurate classifier using metagenomic and metabolic markers that distinguishes children with IBS from healthy controls with 80 percent or greater accuracy. This classifier assesses specific metabolites, types of bacteria, functional pathways, and other factors. “This disease classifier represents a significant advance in the diagnosis of IBS and could be clinically impactful,” commented Dr. Versalovic.
This microbiome-based classifier can potentially help identify subpopulations of children with IBS that are more likely to benefit from microbiome-related therapies including diet modification, while guiding others to alternative appropriate treatment plans. The investigators also provide insights into how specific microbiome-related findings may be related to abdominal pain, thus opening up potential novel treatment approaches.
A chronic disease that is evaluated clinically can be stratified in the future based on differences in the composition and function of the intestinal microbiome. Dr. Versalovic envisions that these findings will begin to usher in an era of metagenomics-based, data-driven precision diagnostics for IBS and other functional gastrointestinal disorders. “Microbiome-based diagnosis and disease stratification of patients with IBS means that we create hope for tailored nutrition and targeted therapies in the future, leading to better outcomes for patients with chronic disease,” noted Dr. Versalovic.
IBS is a disruptive gastrointestinal condition characterized by bloating, changes in bowel habits, and pain that affects up to 20 percent of the world’s population (children and adults). Increasing evidence indicates that the onset and symptoms of IBS are related to the gut microbiome. Deficiencies or excesses of specific gut microbes or metabolites may contribute to the disease process of IBS.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




