Metasurfaces are highly versatile for manipulating the amplitude, phase, or polarization of light. During the last decade, metasurfaces have been proposed for a vast range of applications — from imaging and holography to the generation of complex light field patterns. Yet, most optical metasurfaces developed to date are isolated optical elements that work only with external light sources.
Credit: Jia, Gao, et al., doi 10.1117/1.AP.5.2.026002
Metasurfaces are highly versatile for manipulating the amplitude, phase, or polarization of light. During the last decade, metasurfaces have been proposed for a vast range of applications — from imaging and holography to the generation of complex light field patterns. Yet, most optical metasurfaces developed to date are isolated optical elements that work only with external light sources.
Despite their versatility for manipulating a light field spatially, most metasurfaces have only a fixed, time-invariant response and a limited ability to control the temporal shape of a light field. To overcome such limitations, researchers are looking into ways to use nonlinear metasurfaces for spatiotemporal light field modulation. However, most materials for constructing metasurfaces have a relatively limited nonlinear optical response on their own.
One solution to the limited nonlinearity of metasurface materials is near-field coupling to a medium with extremely large optical nonlinearity. Epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) materials, an emerging class of materials with vanishing permittivity, have drawn much attention in recent years. For instance, indium tin oxide (ITO), a conductive metal oxide widely used as transparent electrodes in solar cells and consumer electronics, typically has permittivity beyond zero in the near-infrared regime. An ENZ material, with its linear refractive index approaching zero, is endowed with an extremely large nonlinear refractive index and nonlinear absorption coefficient.
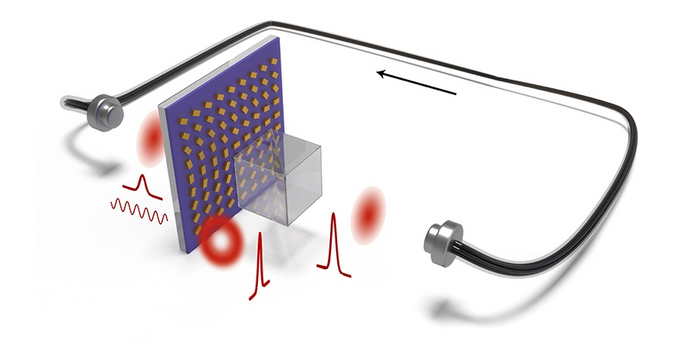
As reported in Advanced Photonics, researchers from Tsinghua University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences recently generated laser pulses with tailored spatiotemporal profiles by directly incorporating an ENZ material coupled to a metasurface in a fiber laser cavity.
The researchers used the geometric phase of a metasurface made of spatially inhomogeneous anisotropic metallic nano-antennas to tailor the transverse mode of the output laser beam. The giant nonlinear saturable absorption of the ENZ-coupled system allows pulsed laser generation via a Q-switching process. To provide a prototype, the researchers realized a microsecond pulsed vortex laser with varying topological charges.
This work provides a new route to construct a laser with a tailored spatiotemporal mode profile in a compact form. For further system miniaturization, the metasurface may be integrated on the fiber-end face. According to corresponding author Yuanmu Yang, professor at the Tsinghua University State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments, “We hope that our work may further exploration of metasurface versatility for spatial light field manipulation, with its giant and tailorable nonlinearity for generating laser beams with arbitrary spatial and temporal profiles.” Yang notes that this innovative method may pave the way for the next generation of miniaturized pulsed laser sources, which could be used in various applications, such as light trapping, high-density optical storage, superresolution imaging, and 3D laser lithography.
Read the Gold Open Access article by W. Jia, C. Gao, et al., “Intracavity spatiotemporal metasurfaces,” Adv. Photon. 5(2) 026002 (2023), doi 10.1117/1.AP.5.2.026002.
Journal
Advanced Photonics
DOI
10.1117/1.AP.5.2.026002
Article Title
Intracavity spatiotemporal metasurfaces
Article Publication Date
22-Feb-2023




