Credit: Department of Biology,TMDU
Researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) in Japan show that melatonin and its metabolites promote the formation of long-term memories in mice and protect against cognitive decline.
Chiba, Japan — Walk down the supplement aisle in your local drugstore and you’ll find fish oil, ginkgo, vitamin E, and ginseng, all touted as memory boosters that can help you avoid cognitive decline. You’ll also find melatonin, which is sold primarily in the United States as a sleep supplement. It now looks like melatonin marketers might have to do a rethink. In a new study, researchers led by Atsuhiko Hattori at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) in Japan have shown that melatonin and two of its metabolites help memories stick around in the brain and can shield mice, and potentially people, from cognitive decline.
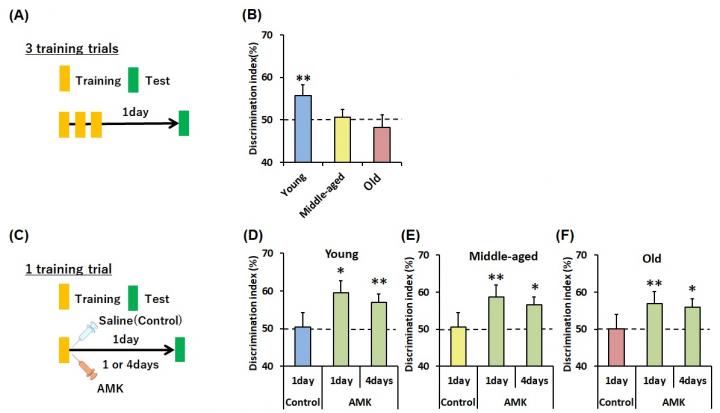
One of the easiest ways to test memory in mice is to rely on their natural tendency to examine unfamiliar objects. Given a choice, they’ll spend more time checking out unfamiliar objects than familiar ones. The trick is that for something to be familiar, it has to be remembered. Like in people, cognitive decline in mice manifests as poor memory, and when tested on this novel object recognition task, they behave as if both objects are new.
The group of researchers at TMDU were curious about melatonin’s metabolites, the molecules that melatonin is broken down into after entering the body. “We know that melatonin is converted into N1-acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AFMK) and N1-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine (AMK) in the brain,” explains Hattori, “and we suspected that they might promote cognition.” To test their hypothesis, the researchers familiarized mice to objects and gave them doses of melatonin and the two metabolites 1 hour later. Then, they tested their memory the next day. They found that memory improved after treatment, and that AMK was the most effective. All three accumulated in the hippocampal region of the brain, a region important for turning experiences into memories.
For young mice, exposure to an object three times in a day is enough for it to be remembered the next day on the novel object recognition task. In contrast, older mice behave as if both objects are new and unfamiliar, a sign of cognitive decline. However, one dose of AMK 15 min after a single exposure to an object, and older mice were able to remember the objects up to 4 days later.
Lastly, the researchers found that long-term memory formation could not be enhanced after blocking melatonin from being converted into AMK in the brain. “We have shown that melatonin’s metabolite AMK can facilitate memory formation in all ages of mice,” says Hattori. “Its effect on older mice is particularly encouraging and we are hopeful that future studies will show similar effects in older people. If this happens, AMK therapy could eventually be used to reduce the severity of Mild Cognitive Impairment and its potential conversion to Alzheimer’s disease.”
###
The article, “The melatonin metabolite N1-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine facilitates long-term object memory in young and aging mice,” was published in Journal of Pineal Research at DOI: https:/
Media Contact
Atsuhiko HATTORI
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.
https://scienmag.com/melatonin-finally-a-supplement-that-actually-boosts-memory/




