Credit: Olaia Naveiras (EPFL)
The bone marrow is the soft tissue inside our bones. Its main role is to produce stem cells that will go on to become various cells of the blood, including white blood cells that fight infections, red blood cells that carry oxygen throughout the body, and platelets that control bleeding.
But the bone marrow also contains fat cells, the adipocytes, which were for a long time thought of as “passive fillers” of the marrow cavity. In recent years, however, bone marrow adipocytes have been shown to carry out a far more important role within the microenvironment of the bone marrow than initially thought.
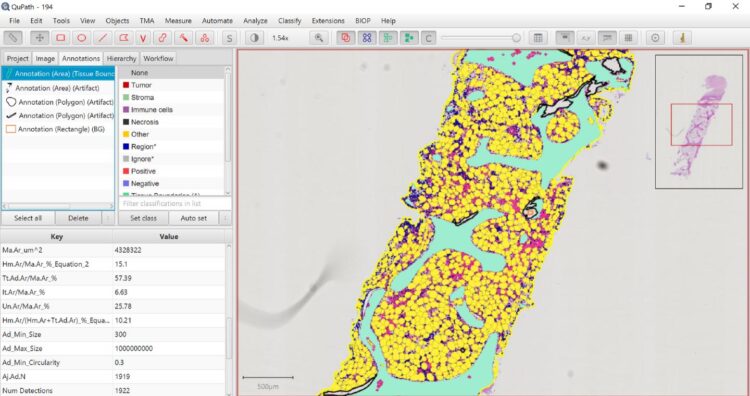
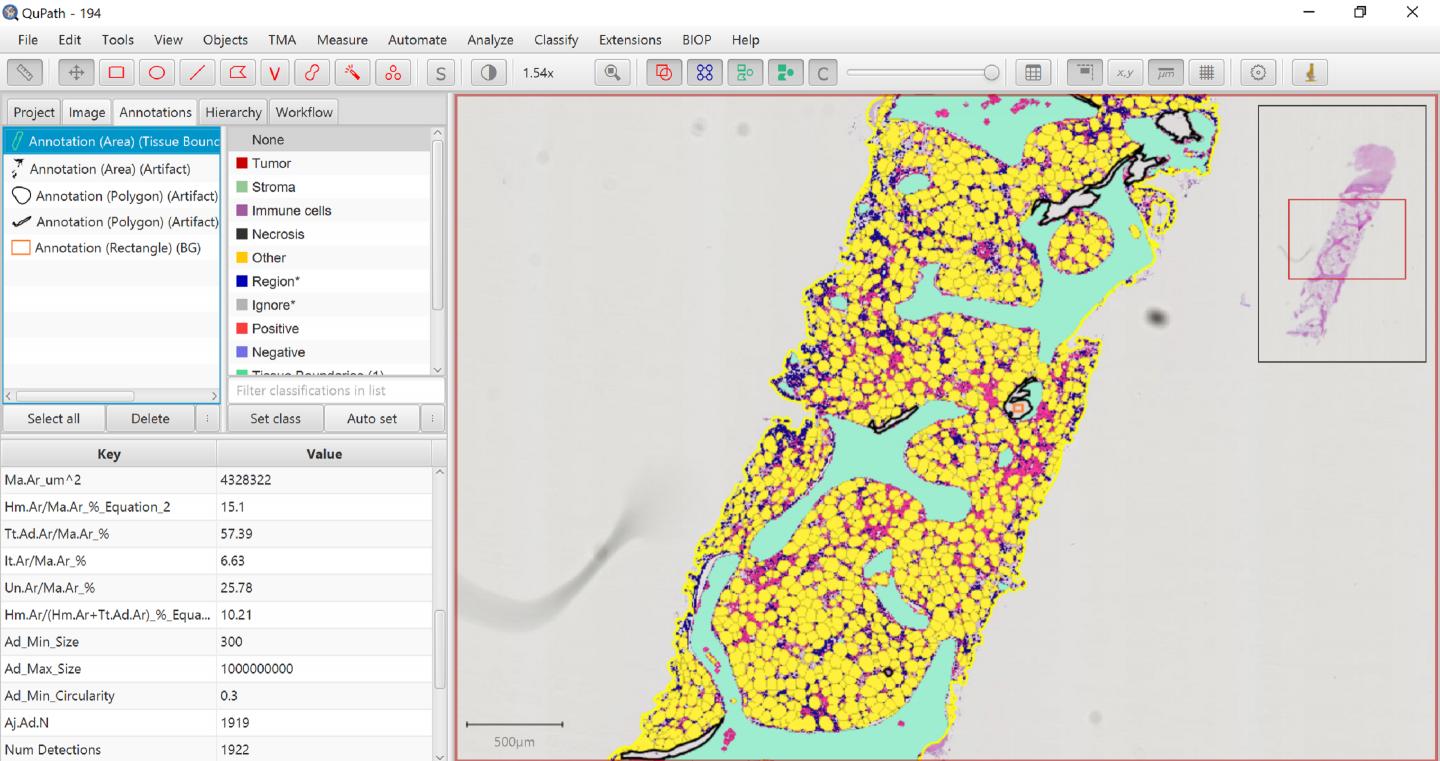
The ratio between blood-forming cells (red color) and adipocytes (yellow color) is not constant. It changes with age, between different parts of the skeleton, and in various disease conditions or cancer treatments like chemo- and radio-therapy, which cause a condition called “bone marrow aplasia”. Changes in the cells’ ratio produce so-called “yellow-to-red” and “red-to-yellow” shifts in the color of the bone marrow, which is used for monitoring its condition.
This monitoring however is not entirely standardized, but relies on assessments by pathologists of histological images. In research, the relative health of bone marrow samples is also assessed qualitatively, through histological images. This subjectivity, although greatly compensated for, can still cause diagnostic and research limitations.
Publishing in Frontiers Endocrinology, scientists led by Olaia Naveiras at EPFL, introduce MarrowQuant, a new digital pathology software that can “read” histological images of bone marrow and “describe” them quantitatively, building maps based on values to complement the images. The potential applications of this approach can revolutionize digital histology.
Its code already uploaded on GitHub, MarrowQuant is described as “a user-friendly algorithm for the quantification of H&E bone marrow tissue biopsies in whole slide images.”
In the paper, the researchers use MarrowQuant to build the first-ever quantitative map of the heterogeneity of bone marrow throughout the skeleton of mice suffering from age-induced and radiation-induced aplasia.
“The work was a massive effort only possible thanks to the long and fruitful collaboration with EPFL’s BioImaging and Optics Platform [BIOP],” says Naveiras who is also the President of the International Bone Marrow Adiposity Society (BMAS).
MarrowQuant, uses the open-source software QuPath, and can systematically quantify multiple bone components in histological images without bias. It does this by discerning and quantifying the areas occupied by various parts of the bone marrow – including the vasculature and the bone itself.
One of the potential uses of MarrowQuant will be to re-examine historical sample collections of bone samples and even data from old clinical trials.
“MarrowQuant has already been extremely well received by the digital pathology community,” says Naveiras. “Moreover, the very selective Image Database Resource (IDR) has selected the associated dataset for publication, which includes over 300 annotated images.”
Professor Olaia Naveiras’ lab is part of EPFL’s Swiss Institute for Experimental Cancer Research (ISREC), situated in the School of Life Sciences.
###
Other contributors
EPFL Center for Biomedical Imaging,
Washington University
Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV)
University of Lausanne (UNIL)
University Hospital de Octubre
Harvard Medical School
Reference
Tratwal J, ID Bekri, C Boussema, N Kunz, R Sarkis, T Koliqi, S Rojas-Sutterlin, F Schyrr, DN Tavakol, V Campos, Scheller EL, R Sarro, C Bárcena, B Bisig, V Nardi, L de Leval, O Burri, O Naveiras. MarrowQuant in Aging and Aplasia: A Digital Pathology Workflow for Quantification of Bone Marrow Compartments in Histological Sections. Front Endocrinol. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00480
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.