Credit: Kanazawa University
Sigma receptors are proteins found on mainly the surface of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in certain cells. Sigma-1 and sigma-2 are the two main classes of these receptors. The sigma-1 receptor is involved neurological disorders and certain types of cancer. To understand better how the receptor is involved in disease and whether drugs developed to target it are working, it is important to be able to accurately trace the sigma-1 receptor. Researchers at Kanazawa University have developed a probe, which can identify and latch onto the sigma-1 receptor.
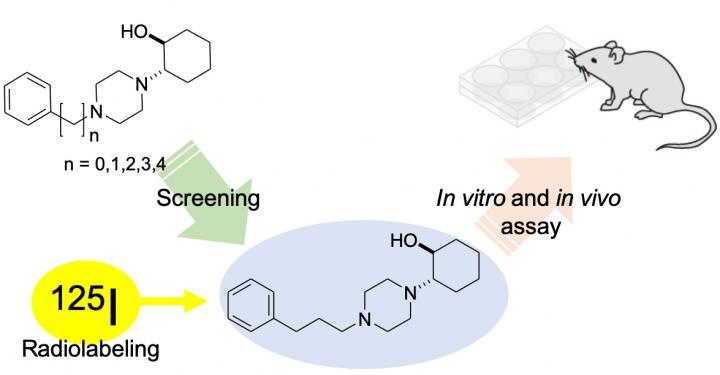
The research team led by Kazuma Ogawa had previously developed molecules with such binding potential. However, upon detailed analysis of the sigma-1 receptor structure, they realized that extending the length of these molecules would increase their binding affinity further. The team therefore created molecules with varying lengths and found one probe that bound to the receptor exceptionally well. For measuring and mapping the sigma receptors by nuclear imaging, radiolabeled iodine was introduced into the probe. The structure created subsequently bound to both sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptors.
Since sigma-1 and sigma-2 receptors are involved in prostate cancer, the team then tested the effects of their newly created molecular probe on prostate cancer cells. These cells have sigma receptors and thus any probe with a high affinity will attach to them and enter the cell. As expected, the probe signal from within the cell was high. When haloperidol–a drug specific to the sigma-1 receptor–was added to the mix this signal dropped, suggesting a competition between the two.
To finally assess the affinity of the probe for different tissues within the body, mice with prostatic tumors were used. While the probe easily entered and stayed within the tumors, its presence in the muscles and blood was less. The probe was thus highly specific for tissues with the presence of sigma receptors.
This study reports a sophisticated probe that binds to sigma-1 receptors better than previous probes developed. This coupled with its ability to escape non-specific tissues is a promising step forward in studying changes induced in the sigma-1 receptor in various disorders. The probe can also be used when developing drugs against the sigma-1 receptor to compare the binding affinities of such drugs. “These results provide useful information for developing sigma-1 receptor imaging probes”, conclude the researchers.
###
Media Contact
Tomoya Sato
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




